5.1: Definition and Measurement of Pressure: Atmospheric Pressure, Barometer, and Manometer
Gas pressure is caused by force exerted by gas molecules colliding with the surfaces of objects. Although the force of each collision is very small, any surface of an appreciable area experiences a large number of collisions in a short time, which can result in high pressure.
In general, pressure is defined as the force exerted on a given area:
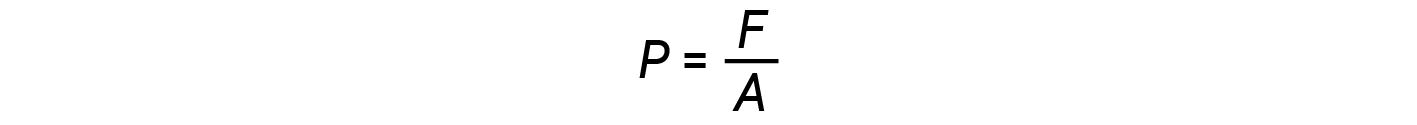
Pressure is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to area. Thus, pressure can be increased either by increasing the amount of force or by decreasing the area over which it is applied; pressure can be decreased by decreasing the force or increasing the area.
The SI unit of pressure is the pascal (Pa), with 1 Pa = 1 N/m2, where N is the newton, a unit of force defined as 1 kg·m/s2. One pascal is a small pressure; in many cases, it is more convenient to use units of kilopascal (1 kPa = 1000 Pa) or bar (1 bar = 100,000 Pa). Pressure can also be measured using the unit atmosphere (atm).
Measuring Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, the force exerted by the atmosphere on the earth’s surface, is measured with a barometer. A barometer is a glass tube that is closed at one end, filled with a nonvolatile liquid, such as mercury, and then inverted and immersed in a container of that liquid. The atmosphere exerts pressure on the liquid outside the tube, the column of liquid exerts pressure inside the tube, and the pressure at the liquid surface is the same inside and outside the tube. The height of the liquid in the tube is, therefore, proportional to the pressure exerted by the atmosphere.
In the barometer, mercury is the preferred choice over water, since it is 13.5 times denser than water. The atmospheric pressure can support a column of mercury that is only about 0.760 m tall, whereas a column of water would need to be 10.3 m tall. This makes a column of mercury a convenient way to measure pressure.
Standard atmospheric pressure of 1 atm at sea level (101,325 Pa) corresponds to a column of mercury that is about 760 mm (29.92 in.) high. The pressure exerted by a fluid due to gravity is known as hydrostatic pressure, p:
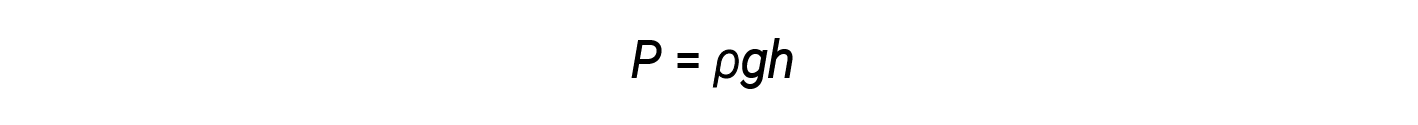
where h is the height of the fluid, ρ is the density of the fluid, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
A manometer is a device used to measure the pressure of a gas trapped in a container. A closed-end manometer is a U-shaped tube with one closed arm, one arm that connects to the gas to be measured, and mercury in between. The distance between the liquid levels in the two arms of the tube, h, is proportional to the pressure of the gas in the container. In an open-end manometer, one arm of the tube is open to the atmosphere. In this case, the distance between the liquid levels corresponds to the difference in pressure between the gas in the container and the atmosphere.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 9.1: Gas Pressure.


