Abstract
וידאו זה מדגים בפירוט פרוטוקול במבחנה חד-סיבי אלקטרו הקלטה באמצעות הכנת colorectum עצבים עכבר. הגישה מאפשרת זיהוי משוחד ואפיון פונקציונלי של afferents מעי גס בודדת. הקלטות תאית של פוטנציאלים מופצים פעולה (APS) שמקורם אחד או כמה מביא (כלומר, חד-סיבים) שדות פתוחים (RFS) בcolorectum עשויים מסיבי עצב fascicles הקניט. Colorectum מוסר גם עם האגן (PN) או עצב splanchnic המותני (LSN) מצורף ופתח longitudinally. הרקמה ממוקמת בחדר הקלטה, הצמיד את שטוח וperfused עם פתרון קרבס מחומצן. גירוי חשמלי מוקד משמש כדי לאתר את קצוות מביא המעי הגס, אשר נבדקו על ידי שלושה נוספות גירויים מכאניים שונים (להקהות חיטוט, ליטוף הרירי ומתיחה היקפית) לסווג תפקודי afferents לחמש mechanosensiשיעורים מופרזים. סופים מגיבים לאף אחד מגירויים מכאניים אלה מסווגים כafferents מכאנית שאינו רגישה ל( נעדרים). שני mechanosensitive והנעדרים ניתן להעריך ולרגישות (כלומר תגובה משופרת סף,, מופחת, ו / או רכישה של mechanosensitivity) על ידי חשיפה מקומית של RFS לכימיקלים (למשל, מרק דלקתי (IS), קפסאיצין, אדנוזין טריפוספט (ATP)). אנו מתארים את הציוד והכנת הקלטת colorectum עצבים, קציר של colorectum עם PN המצורף או LSN, זיהוי של RFS בcolorectum, ההקלטה חד-סיבים מfascicles העצב, ויישום מקומי של כימיקלים לRF. בנוסף, אתגרים של ההכנה והיישום של גירוי מכאני סטנדרטי גם דנו.
Introduction
כאב ורגישות יתר הם התלונות העיקריות של חולים הסובלות מהפרעות תפקודיות במערכת העיכול, כוללים תסמונת מעי רגיז (IBS), אשר קיימים בהעדר הסיבה הנראית לעין pathobiological או נזק לרקמות. לדוגמא, חולי IBS להפגין רגישות יתר, כולל תגובות מוגברות להתנפחות בלון רקטלית ורגישות מוגברת במהלך פעולת מעיים רגילה, כמו גם רגישות יתר של הפניה גופנית (כלומר, רגישות למישוש באזור הבטן) 1. בגלל מיקוד afferents מעי גס הוכיח להיות יעיל בהקלת כאב ורגישות יתר בחולי IBS (למשל, החדרה תוך-רקטלי בהרדמה מקומית 2,3; בליעה דרך הפה של linaclotide guanylate cyclase-C אגוניסט 4-6) הבנה, שיפור של עצבוב מביא של colorectum חשוב.
afferents הקרביים, כולל afferents מעי גס, הם מסוגלים להגיב לשיטות כימיות / nutrient- ותרמית (למשל, 7-9). עם זאת, afferents הקרביים להגיב לגירויים מכאניים (כלומר, afferents mechanosensitive) הייתה נחקר ביותר ביסודיות כי גירויים מכאניים (למשל, התנפחות luminal, מתיחה) הם אלה שבדרך כלל להצמיח תחושות מודעים, כוללים אי נוחות וכאב 10-16. בנוסף, את הקרביים גם innervated ידי afferents מכאנית רגישה (נעדרים), בדרך כלל מכונים nociceptors שקט או שינה 17. בתנאים פיסיולוגיים נורמלים, נעדרים אינם מגיבים לגירוי מכאני או שיש לי גבוהה מאוד תגובת ספי 18, אבל יכולים להיות פעיל ולרכוש mechanosensitivity בתנאי pathophysiological ולתרום לרגישות יתר.
שימוש בהכנה במבחנה והפרוטוקול המתוארת כאן, שפיתחנו ומועסקים אסטרטגית גירוי חשמלית לים rch לסופים פתוחים, המאפשרים זיהוי משוחד של שני קצות mechanosensitive וMIA בcolorectum 19. עצבוב המעי הגס נובע מsplanchnic המותני (LSN) ומסלולי עצבים אגן (PN), וכולל afferents מעי גס שיכול להיות מסווגת לחמש כיתות mechanosensitive (serosal, ריריים, שרירים, שרירי-רירית, mesenteric) ואחד בכיתה MIA 20. שימוש בתכשיר זה במבחנה, מצאנו כי mechanosensitivity רכש נעדרי מעי גס (רגישות) בעקבות חשיפה קצרה של השדות פתוחים שלהם למרק דלקתי (IS), אשר רגיש 71% מנעדרים במסלול PN ו -23% מנעדרים במסלול LSN 19. אנחנו גם תיעדנו רגישות לטווח ארוך (עד 28 יום) של נעדרים בהקשר של רגישות יתר לטווח ארוך התנהגות קרביים (כלומר, בעכברים שקבלו טיפולי intracolonic עם zymosan 21 או חומצת 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic (TNBS) 22) .
jove_content "> בין afferents mechanosensitive, afferents שרירים ושרירים-הרירית הם השיעורים היחידים שtonically לקודד מתיחה היקפית של colorectum (כלומר, הם מתיחה רגישה) וsubserve הקידוד של התנפחות מעי גס רעיל 23,24. שימוש במחשב שבשליטה כוח מפעיל, אנחנו מוחלים סטנדרטיים ואחידים, ולמתוח ramped לשחזור בכיוון ההיקפי של רקמת המעי הגס השטוחה ומסווגים נוסף afferents למתוח רגיש כנמוך סף וגבוה סף 23. בנוסף, במהלך הרגישות של הזמן למתוח afferents -sensitive לאחר zymosan intracolonic 21 או 22 TNBS טיפול מתאים לתחילה, ההתמדה, ו / או ההתאוששות של רגישות יתר קרביים התנהגות, המצביעה על תפקידו של מעי גס afferents למתוח רגיש בכאב ורגישות יתר קרביים.Subscription Required. Please recommend JoVE to your librarian.
Protocol
הערה: פרוטוקול זה נבדק ואושר על ידי אוניברסיטת פיטסבורג מוסדית טיפול בבעלי חיים ושימוש הוועדה.
1. הכנת פתרון קרבס השתנה ובדיקת הסמים Aliquots
- הפוך 6 L של פתרון קרבס שונה המכיל (מ"מ): 117.9 NaCl, 4.7 KCl, 25 3 NaHCO, 1.3 Nah 2 PO 4, 1.2 MgSO 4, 2.5 CaCl 2, 11.1 D-גלוקוז, וטיראט 2 נתרן, אצטט נתרן 20 , 0.004 nifedipine (לחסום התכווצויות שרירים ספונטניות), ו0.003 indomethacin (לחסום סינתזה של פרוסטגלנדינים אנדוגני). השתמש בפתרוני קרבס קרים כקרח וחמים לנתיחה רקמה והקלטה חד-סיבים, בהתאמה.
- להכין תמיסות כימיות כלשהו (למשל, IS, קפסאיצין, ATP) בaliquots בריכוזים רצויים.
2. Dissection של רקמות Colorectum העצבים
- הרדימי ולהרדים עכברי זכרים (6 - 20, 8 שבועות - 30 גרם) בתא CO 2 בקצב זרימה שמחליף 10-30% מתא הנפח לדקה עד עכברים להפסיק לנשום לחלוטין כפי שעולה מהיעדר התנועה בחזה.
- מייד לאחר המתת חסד, exsanguinate על ידי חיתוך פתוח קאמרי בית החזה, ניקוב העלייה הימנית, וטבילת פגר העכבר בנפח מספיק (~ 500 מיליליטר) של קרבס קר כקרח (4 ° C) פתרון מבעבע עם carbogen (95% O 2 , 5% CO 2).
- מוציא בזהירות את כל הקרביים אבל איברי מעי גס ואגן. Transect העכבר במחצית פני מגזר השדרה T12 מעט מעל הסרעפת ולהעביר את מחצית הזנב לחדר נתיחה המכיל קר כקרח, מבעבע פתרון קרבס.
- תחת סטראו, להסיר את שלפוחית השתן ואברי רבייה על ידי transecting בצמתים שלהם לשופכה, ולהסיר יורד / אב העורקים בבטן עד שמתפצל לעורקי הכסל משותפים. לשחרר את PN או LSN מsurroundinרקמות g ידי נתיחה בוטה ובצע את העצבים מחוץ לפסגת הכסל עד נקודת כניסת גחונה לL6 והעמודה S1 חוליות (לPN) או T13 ועמוד השדרה L1 (לLSN).
- חותך את תִצמוֹדֶת הערווה ותקינה ומפרקי מרחשתי עזבו, ולהסיר את עצם הכסל. חופשי בזהירות או PN או LSN מהשרירים ורקמות חיבור המצורפים מקרובים לcolorectum עד היכן העצב נכנס לעמוד השדרה.
- לכרות בזהירות את עצם הכסל לחשוף colorectum דיסטלי. לנתח את colorectum הדיסטלי עם PN המצורף או LSN ברצף.
- העבר את colorectum עם העצב המחובר לתא האמבטיה של חדר הרקמה. הסר רקמת חיבור מופרזת על ידי נתיחה נוספת, ולפתוח את colorectum longitudinally לאורך הגבול נגד mesenteric.
- עם צד הרירי פונה כלפי מעלה, להצמיד את קצה mesenteric של colorectum הסמוך לתא ההקלטה לתוך בסיס סיליקון של chamber ולצרף את אורך antimesenteric של colorectum למגרפה של קרסים מחוברים למפעיל כוח (באיור 1 וצילם באיור 2 א).
- להאריך את PN או LSN לתוך תא ההקלטה, אשר מחובר לתא האמבטיה על ידי חור עכבר ושער. בעדינות להניח את תא מטען העצב על מראה זכוכית קטן בתא ההקלטה, אשר מספק משטח הידרופילי לעצב לדבוק. Superfuse תא האמבטיה עם חמה (30-32 מעלות צלזיוס), מחומצן פתרון קרבס ולמלא את תא ההקלטה עם שמן מינרלים.
הקלטת 3. Single-סיבים ולוקליזציה של שדה פתוח
- לקלף בזהירות בחזרה epineurium (נדן עצב) מPN או LSN תחת סטראו בהגדלה גבוהה (50 - 60x). באמצעות מלקחיים עדינים, להקניט את תא מטען העצב לתוך 5-8 צרורות עצבים של ~ עובי 100 מיקרומטר.
- הנח את התייחסות הפלטינה-אירידיוםהאלקטרודה במגע עם פתרון קרבס בתא הרקמה. רצף למקם את צרורות עצבים בודדות על האלקטרודה ההקלטה שנעשתה מאותו החומר.
- השתמש במברשת צבע רכה לעורר נקודתי גישה מafferents המעי הגס על ידי בעדינות ליטף למעלה ולמטה על פני השטח המעי הגס. אתר את צרור העצבים (ים) שמעצבב את המעי הגס דרך AP זיהוי (פוטנציאל פעולה) הקלטות.
הערה: PN וLSN גם מעצבבים את שלפוחית השתן ואברי אגן אחרים. - השתמש זוג 30 טיפים מחט G לפצל עוד יותר את צרור עצבים לחוטי צרור נאה של ~ 10 מיקרומטר עובי ולמקם את נימה אישית על גבי האלקטרודה ההקלטה.
- מניחים את האלקטרודה קונצנטריים הטה העגולה בניצב למשטח הרירי לרגש חשמלי סופים מביא בעוצמת גירוי suprathreshold (10 גודל mA, 0.5 משך msec @ 0.3 הרץ), אשר מייצרת רדיוס ~ 2 מ"מ של התפשטות נוכחית. הזז את האלקטרודה באופן שיטתי (~ 1.5 מ"מ צעדים) לאורכו ורוחבו של colorectum השטוח למקם סופים פתוחים.
- כאשר סוף מביא מתרגש, להתאים את המיקום האלקטרודה כדי לאתר את האתר של ההפעלה (שדה פתוח, RF) שדורש עוצמת מינימום גירוי (סף גירוי). בטל סופים עם סף גירוי> 3 mA 19.
- לחשב את מהירות ההולכה (CV) מ1) המרחק בין האלקטרודה מגרה בשדה פתוח (RF) ואתר ההקלטה ו -2) עיכוב ההולכה (למשל, איור 2) בין חפץ הגירוי ותחילתו של פוטנציאל הפעולה .
קורות חיים (m / sec) = מרחק (מ"מ) / עיכוב הולכה (אלפיות שני).
4. סיווג פונקציונלי של afferents המעי הגס Mechanosensitive
- לאחר איתור RF על ידי גירוי חשמלי, חלים שלושה הגירויים מכאניים הבאים כדי RF:
- לנהל את גירוי החיטוט על ידי לחיצה על קצה calibramonofilament כמו-פריי טד פון ניילון (0.4 ו 1 כוח g) בניצב לכיוון RF על colorectum השטוח.
- לנהל את הגירוי מלטף בעדינות על ידי מלטף את רירית המעי הגס עם גדיל קנס חוט ניילון (10 כוח מ"ג) כדי ליצור לחץ גזירת משטח קטן בRF.
- לנהל את המתיחה היקפית באמצעות מפעיל כוח מבוקר מחשב, אשר מספק כוח מתיחת ramped (0-170 MN ב 5 MN / sec) בכיוון היקפי לאורך הקצה אנטי-mesenteric של colorectum באמצעות המגרפה של קרסים מתוארים בשלב 2.8 .
- לסווג afferents כserosal (להגיב רק כדי להקהות חיטוט), רירית (להגיב לרירית מלטפת ולהקהות חיטוט), שרירי (מגיב למתיחה היקפית ולהקהות חיטוט) שרירי / רירית (מגיב למתיחה היקפית, ליטוף הרירי ולהקהות חיטוט), או MIA (לא מגיב לכל אחת משלושת הגירויים מכאניים).
- לafferents mesenteric (רק בעצבוב LSN) שקשה להפעיל באופן סלקטיבי על ידי גירוי חשמלי, איתור קצוות פתוחים שלהם על ידי ליטוף מכאני / חיטוט של לפדר.
- לafferents למתוח רגיש (-רירית שרירי שרירים ו), לקבוע את סף התגובה, אשר מוגדר ככוח המעורר את AP הראשון במתיחת ramped.
- לafferents serosal, להקליט את התגובות שלהם לעולים רמות של punctate חיטוט של השדה פתוח מונע על ידי מפעיל הכוח מבוקר מחשב.
5. כימי יישום / אפנון של Endings פתוח
- רשום את התגובה בסיסית לגירוי מכאני (כלומר, תגובה למתיחת ramped, punctate חיטוט, או ליטוף הרירי).
- מעיל הקצה התחתון של פיסת צינור (פליז או נירוסטה, 10 מ"מ גבוה ו -4 x 4 מ"מ מרובע או 2 4-5 מ"מ קוטר) עם וזלין ולמקם אותו על פני השדה פתוח בcolorectum.
- הסרפתרון קרבס בתוך צינורות, ולחשוף את הסוף פתוח במשך 3 - 5 דקות ל -170 μl של התמיסה המכילה את הכימיקל (ים) להיבדק.
- לפקח על התגובה של הביא במהלך יישום כימי (כמה afferents היא chemosensitive).
- הסר את הפתרון הכימי וצינורות כדי לסיים את הפעולה של החומר הכימי. תוך 4 - 6 דקות, לבדוק את התגובה מביא לאותו גירוי מכאני כמו בתגובת תחילת המחקר.
- החל מחדש את הגירוי המכני שוב לאחר תקופה מספיקה של שטיפה-out (> 15 דקות).
6. קוצים ההקלטה והאפליה AP
- ספרת האותות החשמליים שנרשמו מהאקסונים ב 20 קילוהרץ ולשמור את הנתונים למחשב. לפקח על האות על-ידי קו צג אודיו.
- נתח את הקוצים AP off-line ולהפלות יחידות בודדות המבוססות על ניתוח מרכיבים עיקרי של צורות גל עלייה חדה פרט 25.
הערה: שיא אחת צריך להכיל לא יותר השתי יחידות פעילים בקלות discriminable.
Subscription Required. Please recommend JoVE to your librarian.
Representative Results
ההתקנה מתוארת באיור 1. הוא כולל תא רקמת מחוייט כי בתי colorectum בתא מרחץ מצופה סיליקון והעצב המצורף בתא מלא שמן מינרלים רציפים. התא דו-התא היה במכונה מגוש מוצק של פלסטיק אקרילי על ידי מכונת CNC; החלק התחתון של שני התאים היה מצופה לאחר מכן עם סיליקון המוצק כדי לאפשר סיכה קלה כלפי מטה של רקמת המעי הגס. נקודתי גישה תאית מfascicles העצב הקניט נרשמות באמצעות רעש נמוך, מגבר ההפרש המופעל באמצעות סוללות עם יחס גבוה נפוץ במצב דחייה (CMRR ~ 60 dB). הרווח של המגבר מוגדר x10,000 ומגוון מסנן הלהקה ב0.3-10 kHz. גירוי חשמלי של colorectum מועבר על ידי ממריץ בשילוב אופטי במצב נוכחי קבוע באמצעות אלקטרודה קונצנטריים במגע עם רירית המעי הגס. גירוי מכאני (מתיחת מעי גס וpunctate חיטוט) מועבר על ידי acomputer בשליטת כוח הינע. ממיר AD ותוכנה מתאימה לפקח על שני תהליכי הגירוי והקלטה על ידי שליחת יציאות פיקוד המתח ליזום גירויים מכאניים וחשמליים, כמו גם הקלטה והפיכת קובץ לדיגיטלי אותות AP תאיים ממגבר ההפרש. כדי לבודד ממקורות רעש מכאניים וחשמליים, תא רקמה, מיקרוסקופ ומגבר ההפרש ממוקמים בתוך כלוב פאראדיי רכוב על שולחן אוויר פנאומטי.
כפי שניתן לראות באיור 2 א, colorectum עם העצב המצורף גזור החוצה מעכבר, לחתוך פתוח לאורך הקצה אנטי-mesenteric, והצמיד את שטוח בתא הרקמה מצופה סיליקון; העצב מושם על מראה זכוכית בחדר ההקלטה הסמוך. מוצג באיור 2 הוא שיא נציג של פוטנציאל פעולה (AP) בתגובה לגירוי חשמלי של RF על סף. AP ברשומה זו מפגר אחרי אמנות הגירויעובדבר (•) על ידי 49 אלפיות שניים בשל עיכוב ההולכה מRF לאלקטרודה ההקלטה, וכתוצאה מכך מהירות הולכה מחושבת של 0.43 מ '/ שנייה, גם בטווח של C-סיבי unmyelinated. מוצגות באיור 2C הם תגובות אופייניות למביא לגירויים נמסרו ביד (חיטוט של RF עם monofilaments פון כמו-פריי, g 1, וליטוף עדין ברירית של RF, 10 מ"ג). שיא זה מכיל שתי afferents קלות discriminable; רק מביא משרעת הגדולה מגיב לליטוף. כפי שניתן לראות באיור 2 ד, תגובות מביא לחיטוט היו גם הוערכו על ידי מפעיל כוח מבוקר מחשב, המספק לאותו אתר על colorectum סדרה של כוחות מכאניים בדיוק בעיתוי ושחזור (5, 10, 20, 40 ו -80 MN, 5 משך שניות). באופן דומה, מתיחה היקפית של colorectum (0-170 MN ב 5 MN / sec) מועברת על ידי אותו המפעיל עם תגובת נציג מוצגת באיור 2E
כפי שניתן לראות באיור 3, afferents מעי גס יכולה להיות מסווגת מבחינה תפקודית לשש כיתות המבוססות על פרופילי תגובתם לשלושה גירויים מכאניים שונים (ראה שלב 4.2 לעיל). כל קצוות מביא למעט afferents mesenteric אותרו על ידי גירוי חשמלי (e-Stim; השמאלי ביותר הטור, חיצים מצביעים על חפץ גירוי). מכאני afferents רגישה (נעדרים) אינה מגיבה לכל אחת משלושת הגירויים מכאניים. בניגוד לכך, כל הסופים mechanosensitive להגיב לחיטוט (0.4-1.4 ז). ביניהם, סופים שרירים ושרירים-ריריים גם מופעלים על ידי היקפית מתיחה (0-170 MN), ובכך מכונים afferents למתוח רגיש; הסופים שרירים-ריריים גם מופעלים על ידי ליטוף (10 מ"ג). סופים ריריים גם מופעלים על ידי ליטוף (10 מ"ג), אבל לא למתוח וסופי serosal אינם מופעלים על ידי שתי מתיחה או ליטוף. הסופים mesenteric מזוהים על ידי מכאני בממהר לפדר.
מוצג באיור 4 א הן תגובות נציג ממביא למתוח רגיש שמעורר שלוש מתיחות היקפיות רצופות מופרדות על ידי 5 דקות. מספרי ספייק הם זרקו לפח באופן שווה לשלושה פחים ומוצגים כפונקציות גירוי-תגובה באיור 4, חושפים שחזור גבוה בשני ממדי התגובה (מספר ספייק) וסף תגובה.
הכנת colorectum עצבים במבחנה זו גם מאפשרת יישום מקומי של כימיקלים למביאים סופים פתוחים. החשיפה לכימיקלים מוגבלת לאזורים סביב RF מביא על ידי הצבת פליז או צינורות נירוסטה על גבי רירית המעי הגס לבודד פיזי RF משאר colorectum. תוצאות אופייניות הבאות יישום כימי כוללות: הפעלה ישירה של afferents על יישום של פתרון hypertonic חומצה (AHS 26; איור 5 א '), לא הפעלה, אבל רכישה של mechanosensitivity ידי MIA לאחר היישום של מרק דלקתי (IS 19; איור 5), תגובה מוגברת (כלומר, רגישות) למתיחה מכאנית לאחר היישום של IS (איור 5 ג), ותגובה מופחתת למתיחה מכאנית לאחר יישום של cGMP (איור 5D).

איור 1. ייצוג סכמטי של הגדרת הניסוי. Colorectum העצבים ממוקם בתא רקמה דו-תא ומבודד יחד עם שלב ראש מגבר ההפרש מציוד אלקטרוני אחר על ידי כלוב פאראדיי. כל RF מביא מזוהה על ידי גירוי חשמלי (e-סטים) של colorectum ונבדק על ידי שלושה גירויים מכאניים: monofilament ניילון חיטוט, ליטוף הרירי, ולמתוח היקפיים. דף ttps: //www.jove.com/files/ftp_upload/52310/52310fig1highres.jpg "target =" _ blank "> לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
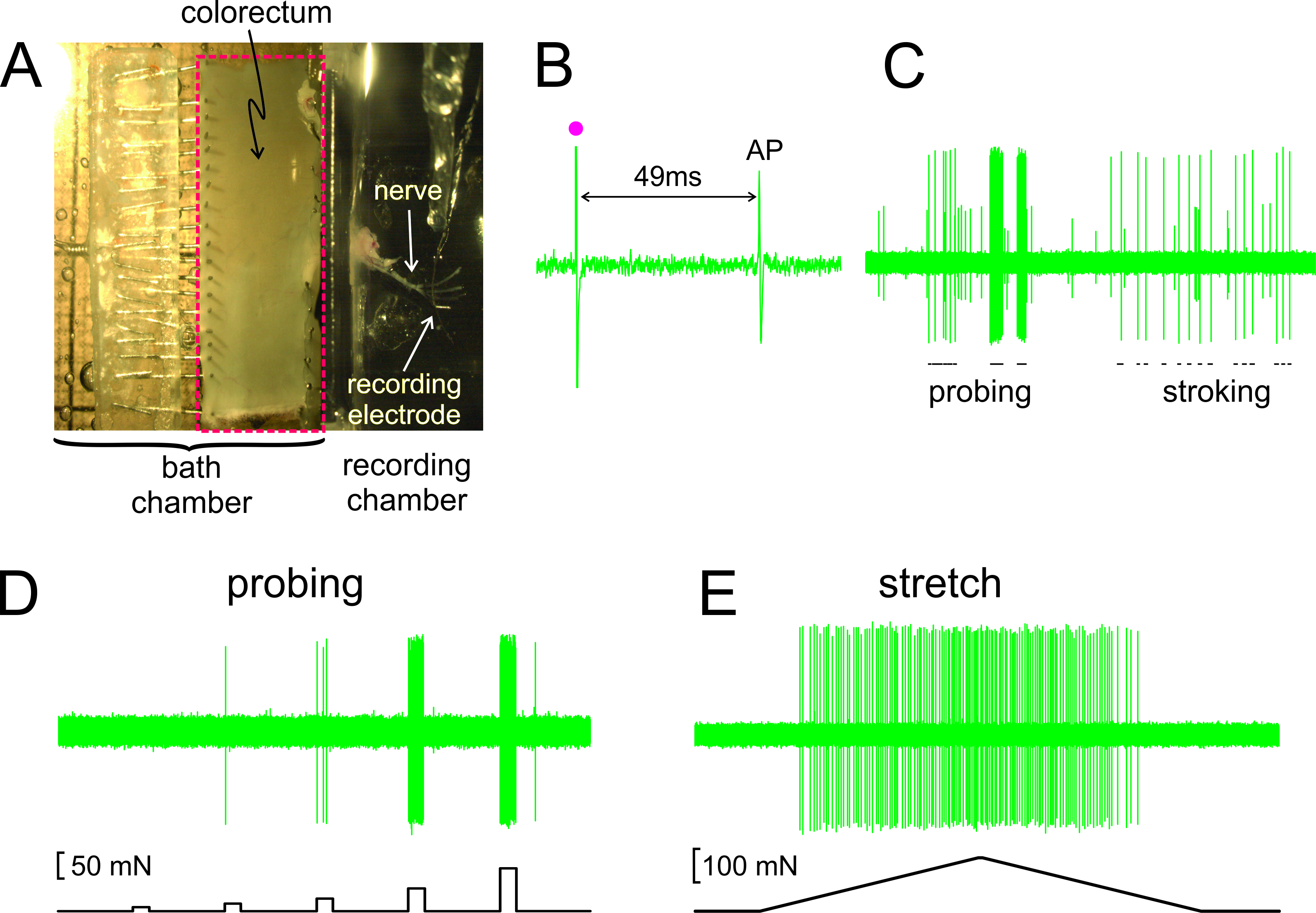
איור 2. תמונה דרך סטראו של colorectum גזור עם עצב מצורף אגן () B -. E להראות רשומות נציג. פוטנציאל פעולה (B) (AP) עורר על ידי גירוי חשמלי (חפץ גירוי, •). תגובות אופייניות (C) לכף יד monofilament חיטוט וליטוף ברירית. (D, E) תגובות לחיטוט ולמתיחה היקפית מועברת על ידי מפעיל הכוח מבוקר מחשב, בהתאמה. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.

איור 3. אפיון פונקציונלי של כיתות מביא מעי גס. Afferents נמצאות על ידי גירוי חשמלי (e-סטים, ↑) של colorectum ומסווג לחמש כיתות mechanosensitive ומביאה אחד מכאנית שאינו רגישים לכיתה (MIA) המבוססת על פרופילי התגובה שלהם לשלושה גירויים מכאניים:. חיטוט, ללטף, ולמתוח אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.

איור 4. תגובות מביא לגירוי מכאני לשחזור, מבוקרת מחשב. (א) תגובות של שרירים-ריריתfferent לשלוש רצופים ramped מותח (0-170 MN ב 5 MN / sec; מרווח בין גירוי 5 דקות). תגובות (B) (קוצים פוטנציאל פעולה) היו זרקו לפח באופן שווה לשלושה פחים (0 - 57, 57-113, ו113-170 MN) ומוצגות כפונקציות גירוי-תגובה; סף תגובה מוצג בהבלעה. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.

איור 5. תגובות מביא ליישום כימי מקומי לסופים פתוחים. (א) דוגמא של chemosensitivity של הביא serosal ליישום של תמיסה חומצית hypertonic (AHS). (ב) דוגמא של רכישת mechanosensitivity (רגישות) על ידי MIA שהסתיים. זה MIA לא הגיב ישירותלמרק דלקתי (IS), אבל הגיב ל- 1.4 monofilament g חיטוט לאחר מכן. (C) רגישות (גידול בהיקף תגובה וירידה בסף תגובה) למתוח של הביא שרירים לאחר החשיפה שלה שהסתיים להוא. הנחתה (ד ') בתגובה ללמתוח על ידי מביא שרירים-ריריים לאחר החשיפה של סיומה monophosphate guanosine המחזורית (cGMP). אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
Subscription Required. Please recommend JoVE to your librarian.
Discussion
בהכנת colorectum העצבים מבחנה המתוארת כאן הוכיחה להיות גישה רבת עוצמה כדי לחקור פונקציות קידוד עצביות של מעי גס afferents בודדת, אשר יפה משלימה גישות אחרות שאינם פונקציונליות (למשל מחקרים, סלולריים, מולקולריים, והיסטולוגית) על עצב סנסורי קרביים ( ראה סקירה 27 לפרטים נוספים). מנגנונים עצביים תורמים לnociception ורגישות יתר מעי גס לטווח ארוך נחשפו ומניפולציות תרופתיות בוצעו כי יש מטרות גילו כי יכול להקל על כאב בטן. נקודות המפתח הבאות הקשורים ליישום מוצלח של הכנה זו נדונות להלן: הפחתת 1) של רעש חשמלי, 2) העלייה בזיהוי אות, ו 3) בחירה של גירוי סטנדרטי כדי להעריך את השינויים של קידוד מביא. בנוסף, מספר מגבלות של טכניקה זו נדונות.
פוטנציאל פעולה propagati (APS)ng intracellularly לאורך עצב, בדרך כלל, יש לי האקסונים פוטנציאל הטרנסממברני של 100-130 mV. עם זאת, בשל הקיבול הספציפי הקטן של קרום האקסון, שלילת קוטביות גדולה יחסית זה תוצאות רק בתזוזה קטנה מטען חשמלי על פני קרום התא, שיכול בקלות להפיג לתוך הרקמה תאית / נוזל ביניים שמסביב (שבו יש עכבה חשמלית נמוכה באופן משמעותי מהקרום השומני). להקלטה תאית מסיבי עצב / האקסונים, האות החשמלי הוא בדרך כלל בטווח של מייקרו-וולטים, קרובים לגודל של הרעש התרמי / לבן קשור להגדרת הקלטת bioelectrical טיפוסית, עיבוד הפחתת רעש בעדיפות הראשונה להקלטה מוצלחת. כדי לבודד בצורה היעילה ביותר מרעש חשמלי הסביבה, זה יכול להיות מועיל כדי למקם את האלקטרודות תא רקמה, הקלטה והארקה, מגבר ההפרש (DC סוללה המופעלת) וסטראו בכלוב פאראדיי. אם חפץ תנועהs להתרחש, הצבת כלוב פאראדיי על שולחן אוויר פנאומטי ללצנן את הרטט מכאני שימושי. באופן אידיאלי, אלקטרודות ההקלטה והתייחסות שנכנסות ו" + "" - "היציאות של מגבר ההפרש, בהתאמה, צריכים להשוות עכבה יחסית לקרקע המשותפת שלהם ולהיות ממוקמות קרוב אחד לשני. לפיכך, כל רעש חיצוני יירשם על מידה שווה על ידי שני אלקטרודות ונתונים לדחיית מצב נפוץ המחמירה על ידי מגבר ההפרש.
בהגדרה שלנו (איור 2 א), את האלקטרודה ההתייחסות הוא טבל פתרון זלוף קרבס בתא הרקמה ואילו האלקטרודה ההקלטה היא במגע עם נימה עצב קנס של עכבה ניכרת. תצורה חד-אלקטרודה זו עם חוסר התאמת עכבה לא טריוויאלי היא בדרך כלל לא אידיאלית להפחתת רעש. עם זאת, בתצורה זו מציעה את הנוחות של הצבת נימה עצב הקנס על רק חשמל אחדשיר הלל, שהוא מושך במיוחד בעת הקלטה מחוטי עצב מעי גס עכבר באורך מוגבל (10 - 15 מ"מ). בהתבסס על הניסיון שלנו, בתצורה חד-אלקטרודה מקובלת כאשר רעש רקע שיא-לשיא הוא מתחת ל -20 μV בשיא. אחרת, הפחתת רעש נוסף תדרוש תצורת הקלטה דו-אלקטרודה שבי נימה העצב בסדר יש להיות בקשר עם שתי אלקטרודות ההקלטה והתייחסות המונחות במקביל זה לזה. כל חלקי המתכת הגדולים בתוך כלוב פאראדיי צריכים להיות מעוגנים באופן כמו כוכבים לקרקע משותפת אחד, גוש נחושת בהגדרה שלנו. טיפול יש לנקוט כדי למנוע היווצרות של לולאות קרקע.
כדי להבטיח איתור תאי של נקודתי גישה, הצעד הראשון הוא נתיחה מוצלחת של רקמת colorectum העצבים. צביטה או משיכת יש להימנע העצב במהלך נתיחה, אשר באופן בלתי הפיך עלולים לגרום נזק לעצבים ומשפיעים על ההולכה AP. הגזע העצבי גזור גם צריך to להיות נקי מכל רקמת שריר מחוברת, שדולפת אשלגן כאשר ניזוק ויכול לחסום הולכה עצבית על ידי שלילת קוטביות. מיומנות נתיחה זו נרכשה בדרך כלל באמצעות תרגול שקדן מעל שבועות עד חודשים ודורשת רמה גבוהה של תיאום עין-יד ומיומנות בטיפול ובשימוש במכשירי ניתוח. בנוסף, כדי למנוע נזק לרקמת המעי הגס, אסטרטגיית החיפוש החשמלית מנצלת אלקטרודה קונצנטריים שיש לו בוטה, קצה מעוגל וקוטר גדול יחסית (מ"מ Φ0.55 חיצוני, מ"מ Φ0.125 פנימי) והוא מחובר לmicromanipulator על ידי גשר תואם, וכתוצאה מכך כוח מכאני צנוע מוחל על פני השטח הרירי (~ 100 מ"ג). על מנת לרכוש אות גדולה יותר בזכר ההקלטה, הנוכחי הטרנסממברני המושרית AP צריך להיות מתועל ו" לכודים "על האלקטרודה על ידי יצירת גשר עכבה קטנה בין האקסון העצב (ים) ופני האלקטרודה. לפיכך, epineurium וperineurium שלבודדהעצב צריך להיות גזור ללא תשלום במהלך התהליך של פיצול העצבים לחוטים דקים של ~ 10 מיקרומטר עבה. כיוון הזרם המושרה הטרנסממברני-AP מתפוגג במידה ניכרת במרחק קצר מן הקרום האקסון, נימה עצב דקה יותר גורמת בדרך כלל ליחס אות לרעש טוב יותר בשל הקרבה קרובה יותר "אקסונים אל פני השטח האלקטרודה. בתא שמן מינרלים, המראה שהעצב הוא דגש על לעתים קרובות מושך שכבה דקה של פתרון קרבס (משטח הזכוכית הוא הידרופילי). זהו אפוא צורך שאלקטרודה ההקלטה ונימת עצב אינן באות במגע עם משטח המראה בזמן ההקלטה. כל טיפות שייר של פתרון קרבס, המספקות גשר נמוך עכבה בין האלקטרודה ומשטח המראה (כלומר, הסטה) תצמצם משמעותית את משרעת האות בשיא.
הכנת colorectum עצבים זו מאפשרת הלימוד של שינויים תפקודיים של afferents לאחר חשיפתRFS למגוון רחב של מתווכים ועלבונות במבחנה כימיים, כמו גם בהקשר של תנאי pathophysiological לטווח ארוך (לדוגמא, colorectums נלקח מעכברים שטופלו בעבר). מדד אובייקטיבי של שינויים תפקודיים של afferents תלוי הבא: 1) הגירוי סטנדרטי עם דיוק גבוה ושחזור ו -2) תגובות מביא כי הם חזקים ושחזור. משלושה הגירויים מכאניים להחיל colorectum, חיטוט ומלטפים את גירויים של RF לעתים קרובות מועברים על ידי monofilaments כמו-פריי פון כף יד. לחיטוט, monofilament בדרך כלל מכויל כדי לספק כוח בניצב לשחזור בעת כיפוף. monofilaments כמו-Frey עם זאת, פון (0.4 וg 1) יש לי קטרים קטנים ושונים חתך (0.2 ו -0.3 מ"מ, בהתאמה), וכתוצאה מכך מתח נומינלי גבוה כאשר מיושמים בניצב לפני שטח המעי הגס (124.8 kPa ל0.4 גרם ו 138.7 kPa לז 1), גירוי עז, punctate מכאנית beyonד הטווח הפיזיולוגי הנורמלי. בנוסף, הקצה החד של חוט הלהט סביר גורם לחלוקה לא שווה של לחצים עם לחץ שיא מוקד גבוה משמעותי מהמתח הנומינלי (ריכוז לחץ). בהתחשב בכך שהגודל האופייני RF (1 מ"מ 2) הוא גדול יותר באופן משמעותי מהחתך של חוט, וחוסר היכולת לעורר reproducibly האתר הזהה עם monofilament כף יד, זה נפוץ להתבונן תגובות לגירויים חוזרים ונשנים שונים באופן משמעותי בתדירות ומשך AP. כדוגמא, את התגובות לחיטוט שמוצג באיור 2C על ידי אותו monofilament כף היד (ז 1) השתנה באופן ניכר שסביר להניח שתרמו לעל ידי חוסר יכולת לחקור reproducibly האתר הזהה ומשך זמן משתנה ומרווח בין גירויים ברציפות. הרירית מלטפת מועברת על ידי חוט להט כף יד הוא דומה מאתגר וגם נוטה לעורר תגובות משתנים מאותו מביא. שחזור גירוי יכול להיותלשפר באמצעות מפעיל כוח מבוקר מחשב כדי לספק כוחות מדויקים חיטוט (ומתיחה). לחיטוט, אנו משתמשים monofilament עם קוטר גדול יותר (לדוגמא, # 6.45, 1 מ"מ) המכסה RF מביא טיפוסי 24,28 באופן מלא יותר. מבוקרת מחשב מתיחה היקפית, בניגוד לגישות רקמת מתיחה שונות המכוונות לRF, מאפשר עיוות הומוגנית לאורך כל אורכו של colorectum, מה שהופך אפשרי המתאם עם התנפחות מעי גס בתצורה הגלילית המקורית שלה המבוסס על מתח דומה היקפי מכאני (כלומר, 0 - 170 למתוח MN הוא שווה ערך ל0-45 מ"מ לחץ intraluminal Hg 23). מאז כוח המתיחה אחיד בקצה אנטי-mesenteric, ולא ישירות לRF, הלחץ המכני המקומי עורר בRF מביא הוא לשחזור בין יישומים ברציפות של מתיחה. בנוסף, nifedipine Ca 2 + חוסם ערוץ L-הסוג הוסיף לאמבטיה לinhibit התכווצות שריר חלק ספונטני, תורמת לשמירה על תאימות בין מעי גס בדיקות מתיחת ramped 23. לבסוף, התגובות מביא לפרוטוקול מתיחת ramped הוכיחו להיות שחזור עם שונות קטנות בשני סף פונקצית תגובה לגירוי ותגובה (לדוגמא, איור 4). לפיכך, תגובות מביא למתיחה ramped היו בשימוש נרחב כהערכה אובייקטיבית של שינויים בתפקוד מביא בחקר מנגנונים עצביים של כאב בטן ורגישות יתר (למשל, 19-22,24,26,28-31).
הכנת colorectum העצבים היא כלי רב עוצמה ללימוד afferents הקרביים המעי הגס. עם זאת, יש לה גם כמה מגבלות. ראשית, את האקסונים של גופי התא של הנוירונים החושיים בגנגליון השורש הגבי הם transected בהכנה, המונעים המחקר של זהויות מולקולריות של גופי תא אלו (לדוגמא, תא בודד RT-PCR או TRanscriptome ניתוח של הסוגים השונים של afferents המעי הגס). שנית, יחס אות לרעש הנמוך של ההקלטה חד-הסיבים דורש נתיחה / כישורים אופטימליים כירורגית עצב פיצול והקלטת רעש נמוך, הגבלת יישום רחב יותר של פרוטוקול זה במעבדות אחרות באופן משמעותי. שלישית, בתכשיר זה במבחנה לא יכול להיות ישים לחקירות של גורמים מערכתיים המווסתים את תחושת בטן, כגון מערכת העצבים האוטונומית, במחזור הורמונים וציטוקינים, חיידקי מעיים, ויורד אפנון ממערכת העצבים המרכזית.
Subscription Required. Please recommend JoVE to your librarian.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Leica MZ16 stereo microscope | Leica Microsystems Inc. | ||
| Leica IC D camera | Leica Microsystems Inc. | ||
| Amplifier | World Precision instruments, Inc. | SYS-DAM80 | Low-noise differential amplifier |
| Two-compartment tissue chamber | Custom made | ||
| Power1401 | Cambridge Electronic Design Limited | Power1401 | Data acquisition, analog signal input/out |
| Spike2 v5.02 | Cambridge Electronic Design Limited | Software package that works with the Power1401 | |
| Audio monitor | Natus | Am 8 | |
| Square pulse stimulator | Natus | S48 | To deliver electrical stimuli |
| Photoelectric isolation unit | Natus | PSIU6 | Stimulus isolation to reduce noise |
| Concentric bipolar microelectrode | FHC Inc. | CBFFG75 | To deliver electrical stimuli |
| Dual-mode lever system | Aurora Scientific Inc. | Series 300C | To deliver mechanical stimuli |
| Forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11252-00 | Forceps with fine tips |
References
- Naliboff, B. D., et al. Evidence for two distinct perceptual alterations in irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 41, 505-512 (1997).
- Verne, G. N., Robinson, M. E., Vase, L., Price, D. D. Reversal of visceral and cutaneous hyperalgesia by local rectal anesthesia in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) patients. Pain. 105, 223-230 (2003).
- Verne, G. N., Sen, A., Price, D. D. Intrarectal lidocaine is an effective treatment for abdominal pain associated with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Journal of Pain. 6, 493-496 (2005).
- Chey, W. D., et al. Linaclotide for irritable bowel syndrome with constipation: a 26-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate efficacy and safety. Am J Gastroenterol. 107, 1702-1712 (2012).
- Rao, S., et al. A 12-week, randomized, controlled trial with a 4-week randomized withdrawal period to evaluate the efficacy and safety of linaclotide in irritable bowel syndrome with constipation. Am J Gastroenterol. 107, 1714-1724 (2012).
- Busby, R. W., et al. Pharmacologic properties, metabolism, and disposition of linaclotide, a novel therapeutic peptide approved for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with constipation and chronic idiopathic constipation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 344, 196-206 (2013).
- Mei, N. Intestinal chemosensitivity. Physiol Rev. 65, 211-237 (1985).
- Mei, N., Lucchini, S. Current data and ideas on digestive sensitivity. J Auton Nerv Syst. 41, 15-18 (1992).
- Su, X., Gebhart, G. F. Mechanosensitive pelvic nerve afferent fibers innervating the colon of the rat are polymodal in character. J Neurophysiol. 80, 2632-2644 (1998).
- McMahon, S. B., Morrison, J. F. Spinal neurones with long projections activated from the abdominal viscera of the cat. J Physiol. 322, 1-20 (1982).
- Cervero, F., Sann, H. Mechanically evoked responses of afferent fibres innervating the guinea-pig's ureter: an in vitro study. J Physiol. 412, 245-266 (1989).
- Sengupta, J. N., Gebhart, G. F. Mechanosensitive properties of pelvic nerve afferent fibers innervating the urinary bladder of the rat. J Neurophysiol. 72, 2420-2430 (1994).
- Sengupta, J. N., Gebhart, G. F. Characterization of mechanosensitive pelvic nerve afferent fibers innervating the colon of the rat. J Neurophysiol. 71, 2046-2060 (1994).
- Habler, H. J., Janig, W., Koltzenburg, M. Activation of unmyelinated afferent fibres by mechanical stimuli and inflammation of the urinary bladder in the cat. J Physiol. 425, 545-562 (1990).
- Habler, H. J., Janig, W., Koltzenburg, M. A novel type of unmyelinated chemosensitive nociceptor in the acutely inflamed urinary bladder. Agents Actions. 25, 219-221 (1988).
- Brierley, S. M., Jones, R. C. 3rd, Gebhart, G. F., Blackshaw, L. A. Splanchnic and pelvic mechanosensory afferents signal different qualities of colonic stimuli in mice. Gastroenterology. 127, 166-178 (2004).
- Meyer, R. A., Davis, K. D., Cohen, R. H., Treede, R. D., Campbell, J. N. Mechanically insensitive afferents (MIAs) in cutaneous nerves of monkey. Brain Res. 561, 252-261 (1991).
- Handwerker, H. O., Kilo, S., Reeh, P. W. Unresponsive afferent nerve fibres in the sural nerve of the rat. J Physiol. 435, 229-242 (1991).
- Feng, B., Gebhart, G. F. Characterization of silent afferents in the pelvic and splanchnic innervations of the mouse colorectum. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 300, G170-G180 (2011).
- Feng, B., La, J. H., Schwartz, E. S., Gebhart, G. F. Irritable bowel syndrome: methods, mechanisms, and pathophysiology. Neural and neuro-immune mechanisms of visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 302, G1085-G1098 (2012).
- Feng, B., et al. Long-term sensitization of mechanosensitive and -insensitive afferents in mice with persistent colorectal hypersensitivity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 302, G676-G683 (2012).
- Feng, B., et al. Altered colorectal afferent function associated with TNBS-induced visceral hypersensitivity in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 303, G817-G824 (2012).
- Feng, B., Brumovsky, P. R., Gebhart, G. F. Differential roles of stretch-sensitive pelvic nerve afferents innervating mouse distal colon and rectum. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 298, G402-G409 (2010).
- Feng, B., et al. Activation of guanylate cyclase-C attenuates stretch responses and sensitization of mouse colorectal afferents. J Neurosci. 33, 9831-9839 (2013).
- Jolliffe, I. T. Principal component analysis. , 2nd, Springer. New York, NY. (2002).
- La, J. H., Feng, B., Schwartz, E. S., Brumovsky, P. R., Gebhart, G. F. Luminal hypertonicity and acidity modulate colorectal afferents and induce persistent visceral hypersensitivity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 303, G802-G809 (2012).
- Christianson, J. A., et al. plasticity and modulation of visceral afferents. Brain Research Reviews. 60, 171-186 (2009).
- Kiyatkin, M. E., Feng, B., Schwartz, E. S., Gebhart, G. F. Combined genetic and pharmacological inhibition of TRPV1 and P2X3 attenuates colorectal hypersensitivity and afferent sensitization. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 305, G638-G648 (2013).
- Brumovsky, P. R., Feng, B., Xu, L., McCarthy, C. J., Gebhart, G. F. Cystitis increases colorectal afferent sensitivity in the mouse. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 297, G1250-G1258 (2009).
- Shinoda, M., Feng, B., Gebhart, G. F. Peripheral and central P2X receptor contributions to colon mechanosensitivity and hypersensitivity in the mouse. Gastroenterology. 137, 2096-2104 (2009).
- Tanaka, T., Shinoda, M., Feng, B., Albers, K. M., Gebhart, G. F. Modulation of visceral hypersensitivity by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family receptor α-3 in colorectal afferents. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 300, G418-G424 (2011).



