24.15: Second Uniqueness Theorem
Consider a region consisting of several individual conductors with a definite charge density in the region between these conductors. The second uniqueness theorem states that if the total charge on each conductor and the charge density in the in-between region are known, then the electric field can be uniquely determined.
In contrast, consider that the electric field is non-unique and apply Gauss's law in divergence form in the region between the conductors and the integral form to the surface enclosing each conductor. When integrated over the outermost boundary, the charge includes the total charge on all the conductors and the charge density in the in-between region.
If a third field is defined as the difference between the two fields, then the divergence of the third field and the integral form of the third field are zero. The product rule is used to obtain the expression for the divergence of the third field and its associated potential. The potential can be written in terms of the field, and applying that the divergence of the third field is zero gives the square of the magnitude of the electric field.

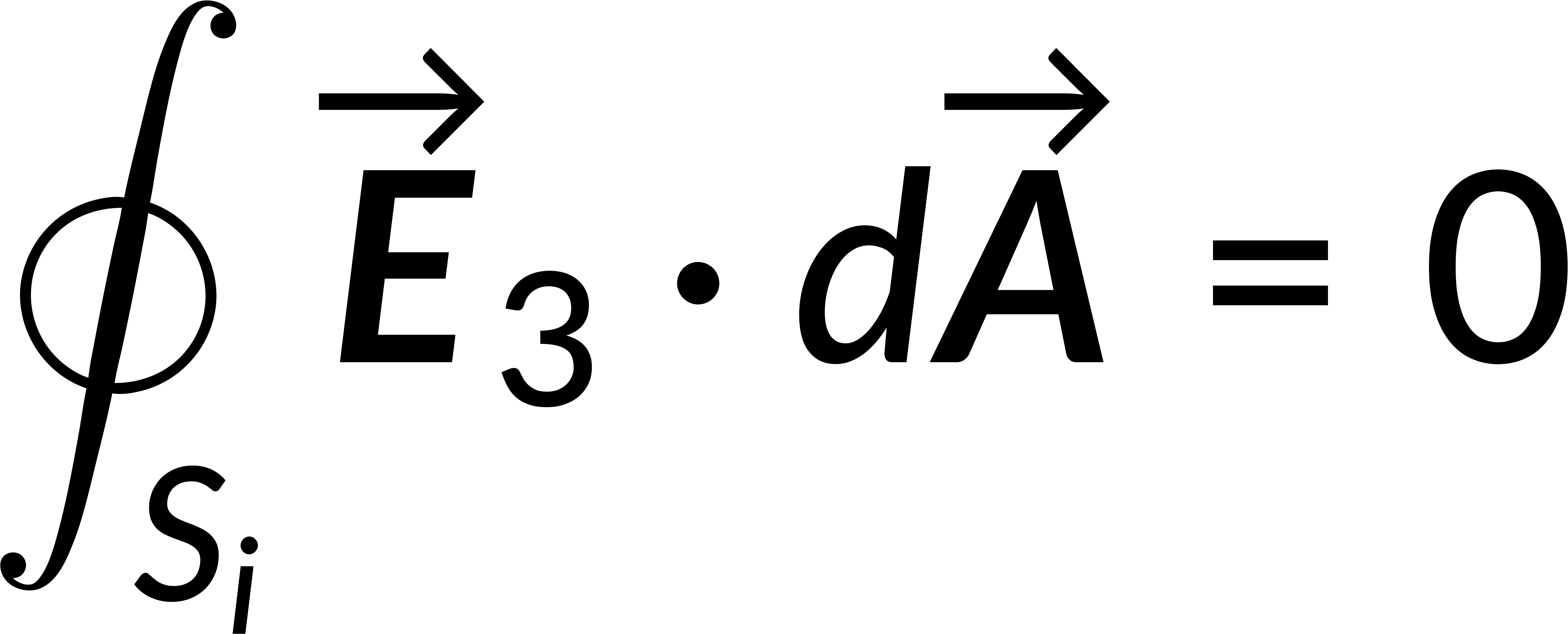

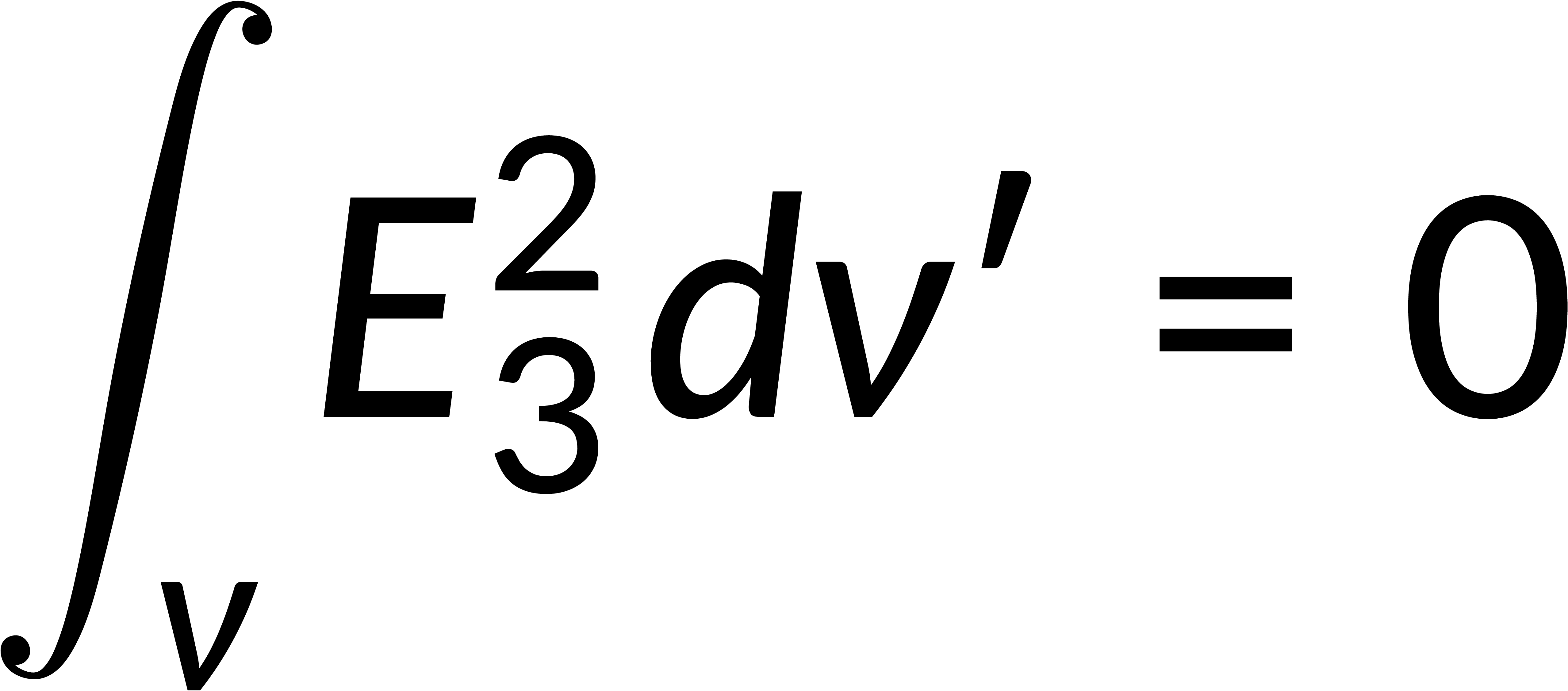
This expression is integrated over the region's volume, and the divergence theorem is applied to rewrite the volume integral as a surface integral. Recalling that the surface integral of the third field is zero implies that the magnitude of the third field is zero everywhere. This shows that the first two fields are equal, proving the solution's uniqueness.