Chapter 11
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces

Particles in a solid are tightly packed together (fixed shape) and often arranged in a regular pattern; in a liquid, they are close together with no…

Intermolecular forces (IMF) are electrostatic attractions arising from charge-charge interactions between molecules. The strength of the…

Intermolecular forces are attractive forces that exist between molecules. They dictate several bulk properties, such as melting points, boiling…

Surface Tension
The various IMFs between identical molecules of a substance are examples of cohesive forces. The molecules within a liquid are…

The physical form of a substance changes on changing its temperature. For example, raising the temperature of a liquid causes the liquid to vaporize…

When a liquid vaporizes in a closed container, gas molecules cannot escape. As these gas phase molecules move randomly about, they will occasionally…

Heating a crystalline solid increases the average energy of its atoms, molecules, or ions, and the solid gets hotter. At some point, the added energy…

Some solids can transition directly into the gaseous state, bypassing the liquid state, via a process known as sublimation. At room temperature and…

A phase diagram combines plots of pressure versus temperature for the liquid-gas, solid-liquid, and solid-gas phase-transition equilibria of a…

Solids in which the atoms, ions, or molecules are arranged in a definite repeating pattern are known as crystalline solids. Metals and ionic…

Crystalline solids are divided into four types: molecular, ionic, metallic, and covalent network based on the type of constituent units and their…

Ionic crystals consist of two or more different kinds of ions that usually have different sizes. The packing of these ions into a crystal structure…

When two or more atoms come together to form a molecule, their atomic orbitals combine and molecular orbitals of distinct energies result. In a…
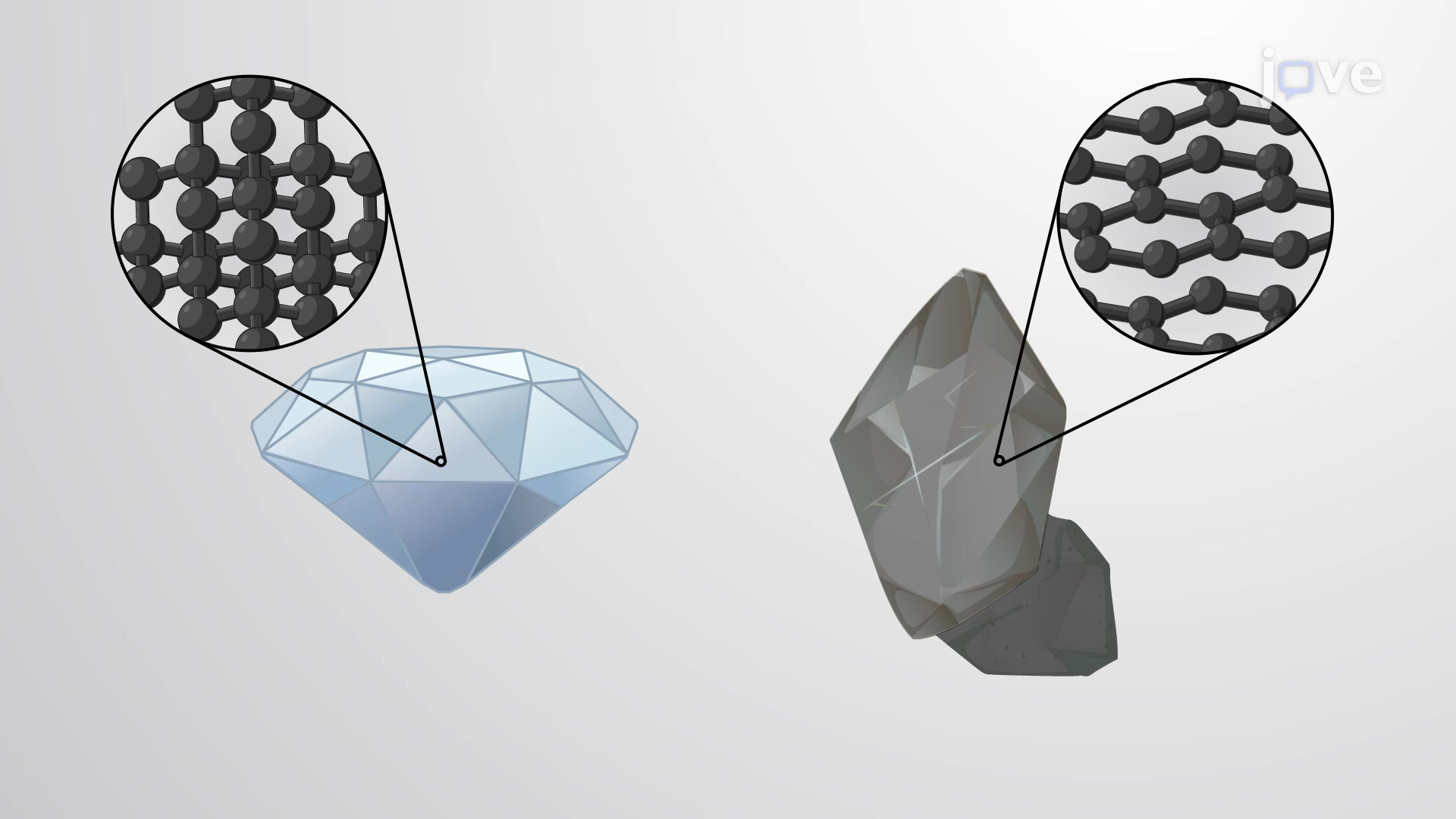
Network covalent solids contain a three-dimensional network of covalently bonded atoms as found in the crystal structures of nonmetals like diamond,…

Controlling interfacial tension is an effective method for manipulating the shape, position, and flow of fluids at sub-millimeter length scales,…

Characterization of Glycoproteins with the Immunoglobulin Fold by X-Ray Crystallography and Biophysical Techniques
Free SampleFree access at this time
Glycoproteins on the surface of cells play critical roles in cellular function, including signalling, adhesion and transport. On leukocytes, several…










