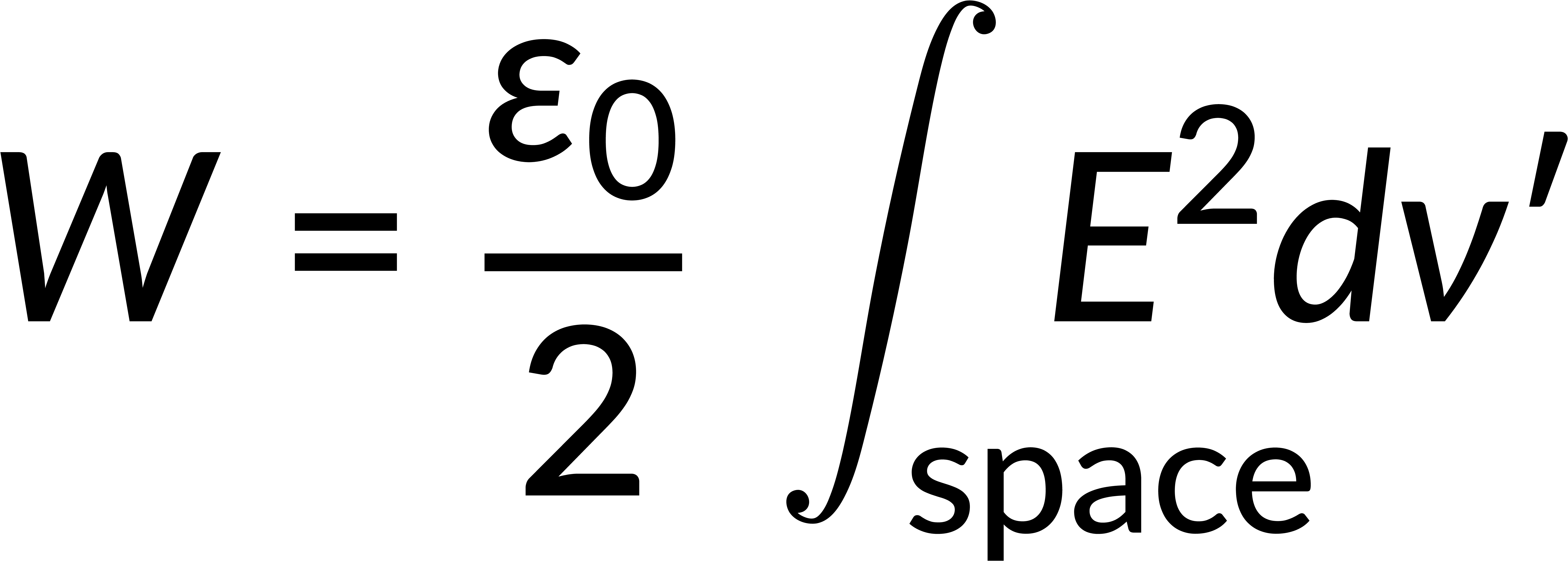24.13: Energy Associated With a Charge Distribution
The work done to bring a charge through a distance r is given by the potential difference between the initial and the final position. To assemble a collection of point charges, the total work done can be expressed in terms of the product of each pair of charges divided by their separation distance, defined with respect to a suitable origin. Solving this expression gives the energy stored in a point charge distribution.
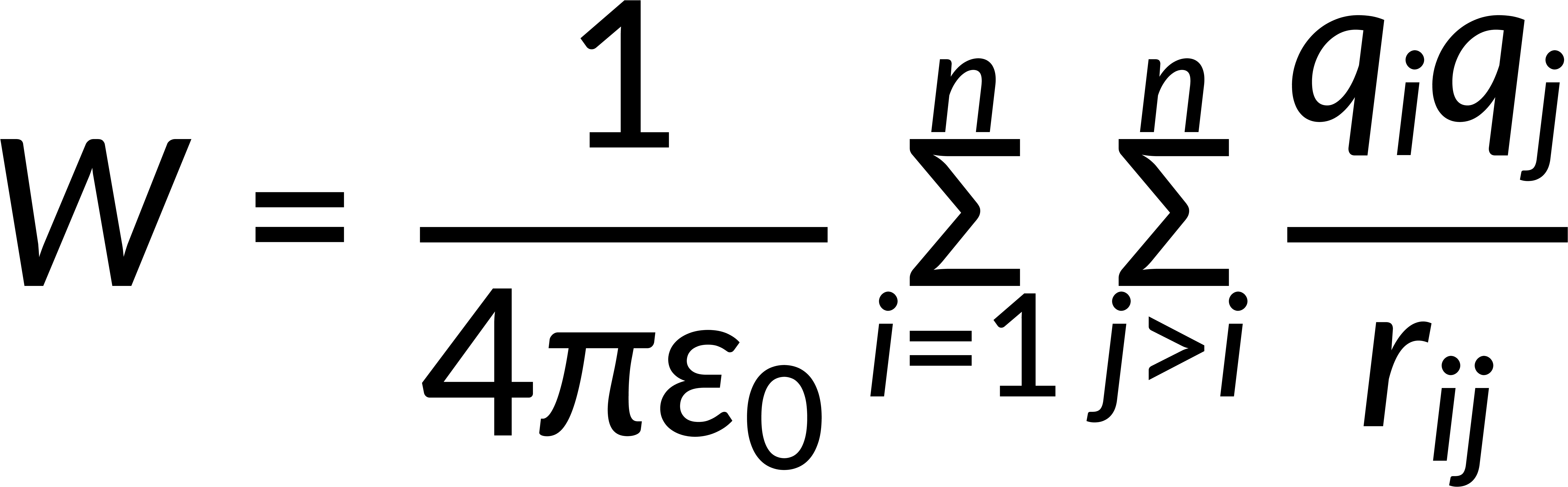
Consider an infinitesimal charge element in a configuration of continuous charge distribution enclosed in a definite volume. The product of the volume charge density and the volume of the element gives the total charge in this element. The energy stored in this configuration of continuous charge distribution is given by integrating volume charge density and the corresponding potential.
Applying Gauss's law in its differential form, the volume charge density can be written in terms of the electric field. Using the product rule in this expression gives the divergence of the electric field. The volume integral can be written as a surface integral using Gauss's divergence theorem. Rewriting the potential in terms of the electric field gives the energy stored in this configuration.
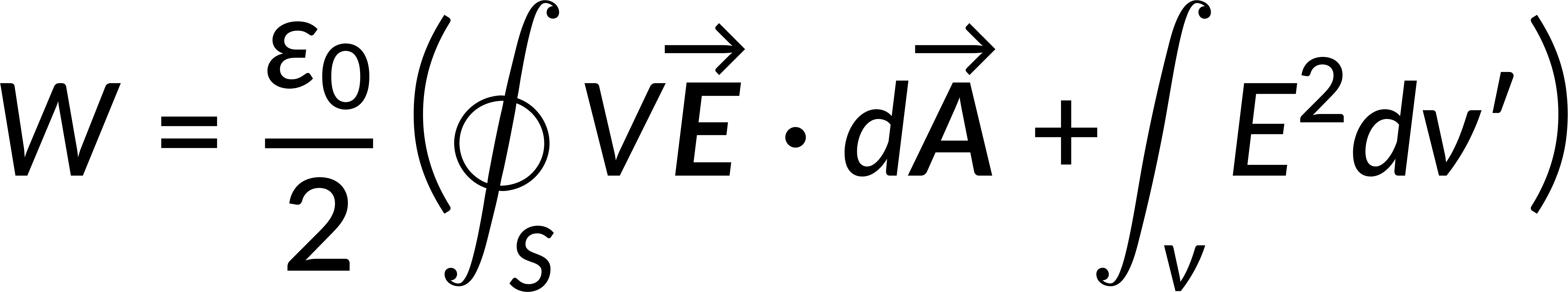
Recall that to obtain the expression for work done, the integration must be performed over the region where the charge is located. Even if the integration is performed over a larger volume, the work done remains conserved as the charge density in the extra volume is zero.
The surface integral of an electric field, which relates to electric potential energy, depends on factors beyond distance, such as charge distribution and system geometry. To calculate total energy, integration over all space, considering the entire volume, is necessary, as the electric field alone at the surface does not provide the complete picture.