Chapter 13
Membrane Transport and Active Transporters

The transport of solutes across the cell membrane is essential for metabolic processes, like maintaining cell size and volume, generating the action…

Transporters are essential membrane transport proteins with functions related to cell nutrition, homeostasis, communication, etc. Approximately 7% of…

In contrast to passive transport, active transport involves a substance being moved through membranes in a direction against its concentration or…

ATP-driven pumps, also known as transport ATPases, are integral membrane proteins. They have binding sites for ATP located on the membrane's…

V-type pumps are ATP-driven pumps found in the vacuolar membranes of plants, yeast, endosomal and lysosomal membranes of animal cells, plasma…

ATP-binding cassette or ABC transporter is the largest superfamily of integral membrane proteins. The transporters have transmembrane-binding domains…

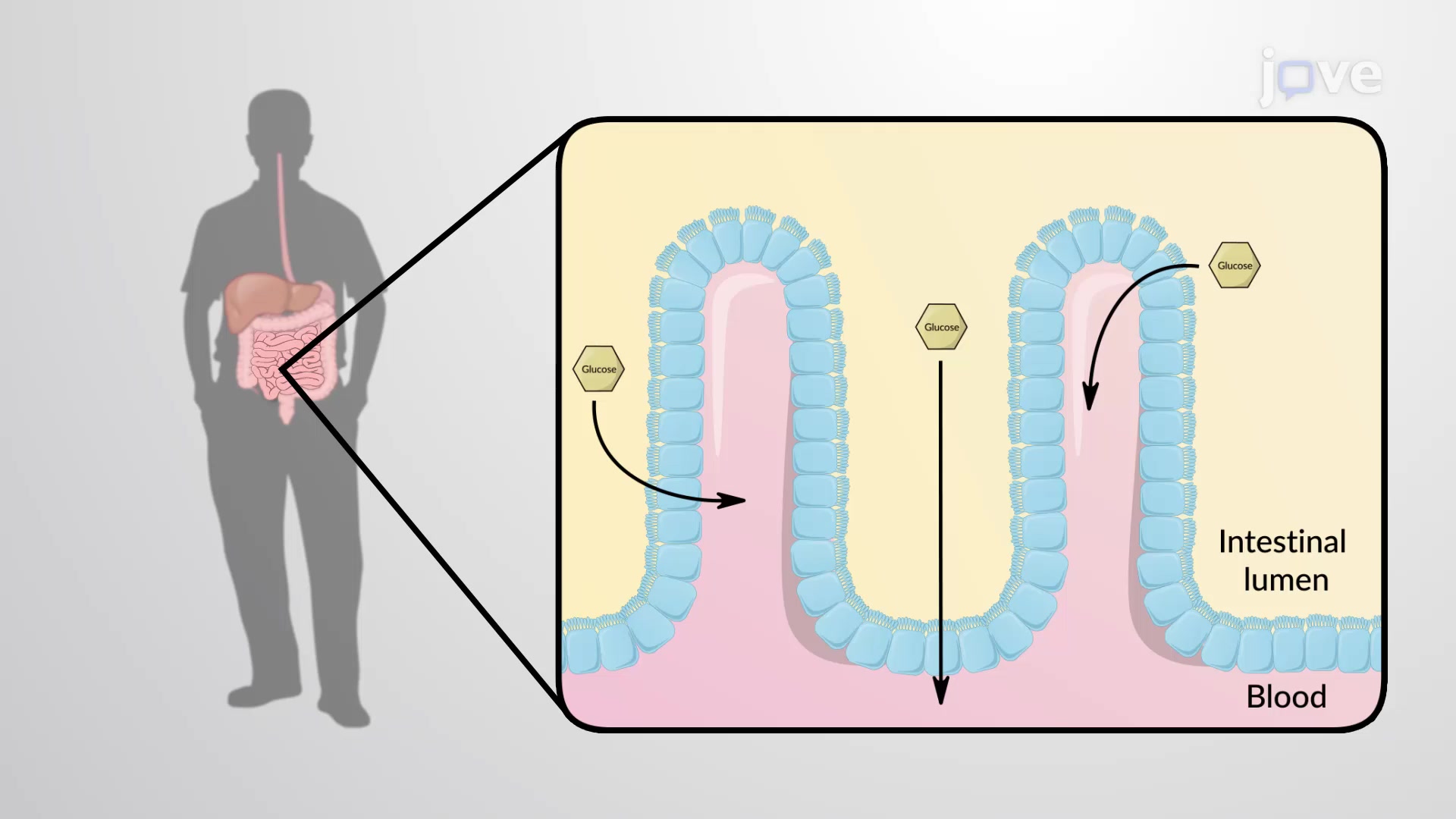
Glucose transporters facilitate the transport of glucose across the cell membrane. In addition to glucose, some glucose transporters can also aid the…

One example of how cells use the energy contained in electrochemical gradients is demonstrated by glucose transport into cells. The ion vital to this…

F1-ATPase is a membrane-extrinsic catalytic subcomplex of F-type ATP synthase, an enzyme that uses the proton motive force across biological…

The sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) is a P-type ATPase that has been crystallized in various conformations. Detailed functional…