ERRATUM NOTICE
Important: There has been an erratum issued for this article. Read more …
Summary
本研究报告了一种使用废培养基对人类胚胎进行染色体筛选的方案,该方案避免了胚胎活检并使用 NGS 进行染色体倍性鉴定。本文介绍了详细的过程,包括培养基的制备、全基因组扩增(WGA)、下一代测序(NGS)文库的制备和数据分析。
Abstract
在临床体外受精 (IVF) 中,PGT-A 的常用方法需要对滋养外胚层 (TE) 中的一些细胞进行活检。这是形成胎盘的谱系。然而,这种方法需要专业技能,具有侵入性,并且存在假阳性和假阴性,因为 TE 中的染色体数量和发育成胎儿的内细胞团 (ICM) 并不总是相同的。NICS是一种需要对从TE和ICM释放到培养基中的DNA进行测序的技术,可能为这些问题提供一条出路,但先前已被证明疗效有限。本研究报告了NICS的完整方案,包括培养基采样方法、全基因组扩增(WGA)和文库制备,以及通过分析软件进行NGS数据分析。考虑到不同胚胎实验室的冷冻保存时间不同,胚胎学家有两种收集胚胎培养基的方法,可以根据试管婴儿实验室的实际情况进行选择。
Introduction
辅助生殖技术(ART)越来越多地用于治疗不孕症。然而,ART如试管婴儿的成功率一直有限,流产率明显高于正常人群1。这些问题的主要原因是染色体异常,这通常存在于植入前人类胚胎中2。PGT-A是在植入前筛选胚胎染色体平衡的有效方法3,4。一些研究证明,PGT-A可以降低流产率,提高怀孕率5,6,7,8。然而,PGT-A需要复杂的技术专长,需要特定的培训和经验。侵入性胚胎活检程序也可能对胚胎造成损害9.研究表明,卵裂球活检会阻碍后续发育,活检TE的数量可能会影响植入率10。尽管胚胎活检的长期生物安全性问题尚未在人类中得到彻底评估,但动物研究表明其对胚胎发育的负面影响11,12,13。
先前的报道表明,在胚胎发育过程中,微量的DNA物质被分泌到培养基中,并且已经努力使用废胚胎培养基14,15,16,17,18进行全面的染色体筛选(CCS)。然而,检测的检出率和准确性尚未满足临床广泛使用的要求。本研究报告了 NICS 检测方法在提高检测率和 NICS 测试准确性方面的改进19.近年来,囊泡液 (BF) 已被研究为微创 PGT-A 的分析样本。然而,囊胚液样本中成功的全基因组扩增和可检测 DNA 的比例从 34.8% 到 82%20,21,22 不等。各种研究中报告的 BF 体积范围为 0.3 nL 至 1 μL。鉴于BF中DNA含量低,可以通过混合囊胚液和培养基来增加游离DNA的量,以提高检测的成功率和一致性。库兹涅佐夫等人。23和Li等24用激光处理透明带,向培养基中释放囊胚液,提高胚胎DNA总量,WGA后合并培养基/BF样品的扩增率分别为100%和97.5%。Jiao等25也用同样的方法获得了100%的扩增成功率。
本研究报告了一个详细的方案,包括废培养基样品制备、NGS 制备和数据分析。通过小心地从卵母细胞中去除卵丘细胞,本研究进行了卵胞浆内单精子注射(ICSI)和囊胚培养。收集第 4 天-第 5 天/第 6 天用过的培养基用于 WGA 和 NGS 文库制备。通过使用NICS技术,本研究在大约3 h内简化了WGA和NGS文库的制备步骤,并在大约9 h内获得了无创的CCS结果。
Subscription Required. Please recommend JoVE to your librarian.
Protocol
获得北京大学第三医院伦理委员会的伦理许可。
1. 准备工作
注意: 所需的材料和设备列在 材料表中。
- 试剂
- 在使用前,在37°C,5%CO2 和5%O2 中预热并平衡(平衡)20-30μL配子培养基/受精培养基和裂解/囊胚期培养基(覆盖有矿物油)和透明质酸酶(在密盖管中)过夜。
- 在通风橱的工作表面上将透明质酸酶预热至37°C。
- 根据制造商的说明准备玻璃化缓冲液和样品采集试剂。
- 工具
- 准备样品收集和转移移液器(内径~200至250μm),剥蚀/剥离移液器(内径为≥150μm,~130-140μm和~120μm)以及用于洗涤的移液器(内径~150μm)通过拉动玻璃巴斯德移液器以产生火焰抛光的开放细尖端。
注意:用于样品收集/转移、剥蚀和洗涤的移液器可直接购买。夹针和注射针也可以直接购买。
- 准备样品收集和转移移液器(内径~200至250μm),剥蚀/剥离移液器(内径为≥150μm,~130-140μm和~120μm)以及用于洗涤的移液器(内径~150μm)通过拉动玻璃巴斯德移液器以产生火焰抛光的开放细尖端。
2. 方案1:样本采集
- 卵母细胞-电晕-积云复合物(OCCCs)的预处理,然后用透明质酸酶消化
- 使用促卵泡激素 (FSH) 和人绝经期促性腺激素 (hMG) 制剂实现卵巢刺激。当先导卵泡>18毫米时,使用10,000IU绒毛膜促性腺激素(hCG)进行最终卵母细胞成熟。
- 触发射击后36小时进行卵母细胞提取。用矿物油覆盖的 2.5 mL 预热的 m-HTF 拾取卵母细胞并将其转移到组织培养皿中。
- 使用转移移液管将OCCC快速转移到含有1mL受精培养基的器官培养皿的中心孔中,然后在37°C下在5%CO 2和5%O 2培养箱中与卵母细胞孵育2-4小时。
- 通过将1mL预热的37°C预热透明质酸酶(80IU / mL)加入含有OCCC的器官培养皿的中心孔中,用透明质酸酶消化OCCCs(步骤2.1.3)。将透明质酸酶的终浓度保持在 40 IU/mL 并充分混合。
- 将OCCCs在37°C热平台上孵育2分钟。每30秒在显微镜下观察一次变化,直到只剩下1-2层颗粒细胞。
- 颗粒细胞剥蚀
- 在培养皿中快速转移消化的OCCC以进行卵母细胞处理,并在每个孔中用矿物油覆盖。
- 在显微镜下观察分离的颗粒细胞。轻轻吸出并释放卵母细胞 5 次,以去除卵母细胞周围残留的颗粒细胞。
- 在剩余的3个孔中重复上一步,以完全去除颗粒细胞。
注:上述步骤(2.1-2.3)可根据各实验室的常规操作进行。
- 卵母细胞的评估
- 使用显微镜评估颗粒细胞去除的完整性。如果细胞不能完全去除,则此时保留 5 个或更少的颗粒细胞是可以接受的。
注意:如果卵丘细胞仍附着在卵母细胞上,则可以在第3天晚些时候将残留物从卵裂阶段培养基转移到囊胚阶段培养基之前去除。
- 使用显微镜评估颗粒细胞去除的完整性。如果细胞不能完全去除,则此时保留 5 个或更少的颗粒细胞是可以接受的。
- 进行卵胞浆内单精子注射(ICSI)26后,使用转移移液器将卵母细胞转移到20-30μL卵裂胚胎培养基微滴(一个卵母细胞对应于一个微滴)中,并在37°C,5%CO2 和5%O2 培养箱中孵育。
- 将ICSI的日期记录为第0天。根据伊斯坦布尔共识研讨会对胚胎卵裂的第 1 天(约 18 小时)、第 2 天(约 45 小时)和第 3 天(约 68 小时)进行胚胎切割27 的胚胎评估进行评分。
- 胚胎清洗
- 在第2天,在37°C,5%CO2 和5%O2 培养箱中,为组织培养皿中覆盖有矿物油的每个胚胎制备20-30μL囊胚培养基微滴。
- 准备另外三个用矿物油覆盖的微滴,并在新的组织培养皿上贴上标签,用于洗涤1-3号。
- 将第3天的胚胎转移到洗涤微滴中。使用剥蚀移液管在每个液滴中轻轻吸出并释放胚胎 3 次。
注意:此过程还可以帮助去除附着在胚胎上的残留颗粒细胞。 - 在第3天在显微镜下观察和评估胚胎,然后将培养基从卵裂阶段培养基更改为囊胚培养基进行形态学评分。如果卵丘细胞仍然附着在胚胎上,则用剥离器移液管在另一个预热和平衡的囊胚培养基液滴中适当地上下移液,该液滴覆盖有矿物油,直到卵丘细胞完全去除。
注意:在胚胎从卵裂阶段培养基板转移到囊胚期培养基板之前,必须在第 3 天完全去除所有附着的卵丘细胞。任何剩余的积云细胞都会干扰最终分析并给出假阴性结果。
- 培养基收集的两种选择
注意:试管婴儿中心可以根据中心的资源、需求和偏好,从两种培养基收集方法中选择一种。- 选项1:胚胎清洗和培养
注意:此选项适用于在第 5 天早上进行玻璃化检查的 IVF 实验室。- 将胚胎转移到预热(37°C)的培养基微滴中,并在第4天下午通过移液在3个微滴中轻轻洗涤每个胚胎。
- 将每个胚胎转移到独特的预热(37°C)单微滴培养基中,用于样品收集。单滴培养基的体积不能超过 25 μL。
- 在第5天/第6天在37°C,5%CO2和5%O2下进行囊胚胚胎培养。
- 选项2:胚胎清洗和培养
注意:此选项适用于在第 5 天下午或第 6 天进行玻璃化检查的 IVF 实验室。- 将胚胎转移到预热(37°C)的10-15μL培养基的微滴中,并在第5天通过移液在3个微滴中轻轻洗涤每个胚胎。
- 将每个胚胎转移到独特的预热(37°C)单微滴培养基中,用于样品收集。单滴培养基的体积不能超过 15 μL。
- 在第5天/第6天在37°C和5%CO2下进行囊胚胚胎培养。
- 选项1:胚胎清洗和培养
- 样品采集
- 在距离激光束目标点相当远的地方轻轻调整ICM,该激光束聚焦在滋养外胚层的细胞连接处,在滋养外胚层上产生一个小孔,以将液体从胚腔中释放出来。然后按照常规工艺将胚胎移至冷冻溶液中进行冷冻保存。
- 将每个培养胚胎的培养基转移到含有 5 μL 细胞裂解缓冲液的无 RNase/DNase PCR 管中。
- 收集相同量的培养基,而不用于胚胎培养,作为阴性对照。立即将所有收集的样品冷冻在液氮中,然后在收集后储存在-80°C,直到进行NICS测定。
- 按照方案中的说明进行玻璃化。
3. 协议2:文库建设
- 培养基裂解
- 用 199 μL 新鲜培养基稀释 1 μL 阳性对照(10 ng 人 gDNA)。充分混合并短暂离心管(200× g ,持续5秒)。
- 将 10 μL 第 5 天第 6 天囊胚培养基、稀释的阳性对照和新鲜培养基转移到新的 0.2 mL PCR 管中。
- 向每个PCR管中加入1μL MT酶混合物,并通过移液彻底混合,并立即以200× g离心2-3秒。
- 将步骤3.1.3中的PCR管放入预热的NICS样品制备站中,并按如下方式运行裂解程序:在75°C下10分钟;95°C下4分钟;保持在22°C。
注:样品制备站可与标准PCR仪相媲美。- 单击 裂解 图标进入设置屏幕。
- 选择 管 作为控制模式;输入 10 μL 样品体积;为 Hotlid 控制选择 开 ,然后输入 105 °C 作为温度。为“在第一个段暂停”选择 “否 ”。单击“ 确定 ”继续。
- 等到“ 停留时间 ”显示“--:-- :--,表示程序结束,然后单击 ”停止 “终止程序。
- 该过程完成后停止程序。立即继续执行下一步。
- 文库前准备
- 解冻预配置缓冲液至RT.通过移液彻底混合,并立即以200× g离心2-3秒。
- 制备用于预库反应的预混液如下:将 2 μL Pre-Lib 酶混合物加入 60 μL Pre-Lib 缓冲液中,充分混合反应并短暂离心。
- 将 60 μL 预库反应混合物加入到上一步的每个预处理培养基样品中。通过移液彻底混合,并立即以200× g离心2-3秒。
- 将步骤3.2.3中的PCR管置于样品制备站中,并按如下方式运行预库程序:95°C2分钟;15°C循环40 s、22 °C循环40 s、33 °C循环30 s、65 °C循环30 s、72 °C循环40 s、95 °C循环10 s、63 °C循环10 s;并保持在4°C。
- 单击 Pre_Lib 图标进入设置屏幕。
- 选择 管 作为控制模式;输入 70 μL 样品体积;为热盖控制选择 开 ,然后输入 105 °C 作为温度。为“在第一个段暂停”选择 “否 ”。单击“ 确定 ”继续。
- 等待“ 停留时间 ”显示“--:-- :--”,表示程序结束,单击“停止”终止程序。
- 该过程完成后停止程序。立即继续执行下一步。
- 文库制备
- 解冻文库缓冲液至RT.通过移液彻底混合,并立即以200× g离心2-3秒。
- 制备用于文库反应的预混液如下:将 1.6 μL 文库酶混合物加入 60 μL 文库缓冲液中,充分混合反应并短暂离心。
- 向步骤 3.2.3 中的每种预库产物中加入 60 μL 文库反应混合物和 2 μL 条形码引物。充分混合反应并短暂离心。
- 将步骤3.2.3中的PCR管放入热循环仪中,并按如下方式运行文库制备程序:94°C30秒;94 °C 25 s、62 °C 30 s 和 72 °C 45 s 的 17 次循环);然后保持在4°C。
- 单击 Lib_Prep 图标进入设置屏幕。
- 选择 管 作为控制模式;输入 130 μL 样品体积;为 Hotlid 控制选择 开 ,然后输入 105 °C 作为相应的温度。为“在第一个段暂停”选择 “否 ”。单击“ 确定 ”继续。
- 等待“ 停留时间 ”显示“--:-- :--”,表示程序结束,单击“停止”终止程序。
- 文库净化
- 在纯化步骤之前,将Magbeads从2-8°C的储存中取出至少20分钟。涡旋并混合Magbeads20秒。将足够的纯化步骤珠子分配到新的 1.5 mL 微量离心管中,并将珠子加热至 RT。
- 将 1x Magbeads 添加到每个文库中。通过上下移液≥10次混合,并在室温下孵育5分钟。
注:例如,将 100 μL Magbeads 加入 100 μL 文库样品中。 - 孵育后,短暂离心试管并放在磁性支架上。
- 等待约5分钟,直到溶液变得清晰。将试管放在磁性支架上的同时,小心地吸出溶液并丢弃。
- 向试管中加入 200 μL 新鲜制备的 80% 乙醇。在室温下孵育30秒,小心地除去上清液。再重复一次。
- 尽可能彻底地去除乙醇。在室温下将磁性支架上的珠子风干约5-10分钟。
- 从磁性支架上取下试管,加入 17.5 μL 洗脱缓冲液,涡旋试管以重悬珠子。短暂离心试管并在室温下孵育5分钟。
- 将试管放在磁性支架上,等待溶液变清。小心地将 15 μL 上清液转移到新管中。
- 文库定量
- 根据 qubit dsDNA HS 检测试剂盒28 的用户指南,使用荧光计定量纯化的文库。文库的产量范围为 ~15 至 300 ng。
- 库池化
- 使用每个文库样品 10 ng 进行混合。
- 测 序
- 请参阅测序用户指南 (15027617 v01)29。
- 在平台上单端纯化 50 bp 的文库序列,每个样本产生约 200 万个读长,建议测序深度为 0.03 ×。
- 数据分析
- 在登录页面输入用户名和密码
- 登录系统后,单击 “分析 ”,将出现一个新页面。单击 NICS-A 选项卡下的 Create Submission 。然后,选择 NGS 作为平台,选择公司,选择 NICSInst作为试剂,在项目ID下的框中输入项目信息,设置分析首选项并上传文件。成功上传所有测序文件后,单击 “提交 ”开始分析(图3A)。
- 单击 “查看提交” 以显示已提交项目的列表。分析完成后,项目的状态将变为“已完成”,并且报表字段中将出现“显示”按钮。单击 “显示 ”按钮查看NICS分析的汇总表(图3B)。
- 单击 “导出 报告”按钮以保存报告(图3C)。
注意:每次分析将导出三种类型的文件。一个图形文件,包括每条染色体和全基因组的所有拷贝数变异 (CNV) 图,将存储在“图形”文件夹下;包含此分析运行的样本 QC 详细信息的电子表格;包含用户自定义的 NICS 报告的文档文件;以及包含此分析运行的示例摘要信息的电子表格。
Subscription Required. Please recommend JoVE to your librarian.
Representative Results
本研究将所提出的方法应用于患者。在应用NICS分析之前,已获得IRB的批准和知情同意。本研究从患者身上获取了 6 个囊胚,并在第 4 天至第 5 天培养基上对所有 6 个胚胎进行了 NICS检测。采用NICS法在5条染色体中检测到由父母平衡易位引起的染色体异常;因此,它们不能用于转移(图4A-E)。两个胚胎的NICS结果显示相同的核型45,XN和-18(×1)都是18号染色体缺失(图4A,B)。核型46,XN,-1p(pter→p21.1,×1)只是染色体1 pter→p21.1区域缺失的短臂(图4D)。
NICS结果显示核型46,XN,+1p(pter→p21.2,×3)和-18(q21.32→qter,×1),表明18号染色体q21.32→qter区的长臂和1号染色体pter→p21.2区的短臂均重复(图4E)。尽管核型 46、XN、+5q (×4) 和 -8 (×1, mos) 是 5 号染色体重复并显示 8 个镶嵌差异,但 NICS 测定可以筛选所有 24 条染色体的非整倍体。该过程为转移单个正常核型囊胚提供了一种新方法。

图 1.卵丘细胞的去除完整性。 (A)具有卵丘细胞的卵母细胞。(B) 没有卵丘细胞附着的卵母细胞。 请点击这里查看此图的较大版本.

图2.在转移到BM之前,从D3的胚胎中取出积云细胞。 在培养基从初始卵裂胚胎培养基板更换为囊胚培养基板之前,必须在胚胎达到 8 细胞阶段后的第 3 天去除所有附着的卵丘细胞。任何未去除的卵丘细胞都会干扰最终分析,产生假阴性结果。 请点击这里查看此图的较大版本.

图3.数据分析。 (A) 用户应用程序有不同的选项。对于测序平台公司,用户可以选择Illumina、Ion Torrent或MGI。用户可以选择是否报告性别信息。完成上述参数设置后,点击文件上传下的框,选择合适的测序文件进行上传。对于 Illumina,选择扩展名为 fastq.gz 的文件。点击 提交,在上传成功后开始分析。(B) 汇总表视图。汇总表包含以下信息: 样本名称:列出每个 NICS 样本的名称;数据QC:表示测序文件是否通过NICS分析的QC;AI 评级:每个 NICS 样本的评级(A、B 或 C);AI_Rating 解读:胚胎植入潜力评估;AI 分级:每个 NICS 样本的分数;CNV图(全基因组):查看所有染色体的CNV图谱;(C) “保存报告”页面。单击“结果摘要”旁边的 “导出报告”按钮。选择要在最终报告中显示的信息,然后单击 导出。报告将保存到计算机的 “下载”文件夹中。 请点击这里查看此图的较大版本.

图4.使用NICS对患者进行胚胎筛选和选择。 共有6个胚胎成功发育到囊胚期,并收集每个胚胎的第4-5天培养基进行NICS测定。(A)和(B)是两个囊胚胚胎的NICS结果,显示相同的核型45,XN,-18(×1)都是18号染色体缺失。(C)显示核型46,XN,+5q(×4),-8(×1,mos)为5号染色体重复和8号染色体镶嵌。(D)显示核型46,XN,-1p(pter→p21.1,×1)仅为1号染色体pter→p21.1区的短臂缺失,而(E)显示染色体核型46,XN,+1p(pter→p21.2,×3),-18(q21.32→qter,×1)为1号染色体pter→p21.2区域的短臂,18号染色体的长臂q21.32→qter区(F)显示染色体组成平衡。x 轴表示红色和蓝色的 22 个常染色体,y 轴表示每个常染色体的拷贝数。灰点是每个 bin 窗口的拷贝数响应的标尺刻度,拷贝数的正常核型必须为 2。 请点击这里查看此图的较大版本.
表 S1.DNA检测的成功率 选项 1 和选项 2。请按此下载此表格。
表 S2.NICS 和 PGT-A 在不同选项中的一致性。请按此下载此表格。
Subscription Required. Please recommend JoVE to your librarian.
Discussion
修改和故障排除
如果NICS结果被亲本遗传物质污染,请确保去除所有日冕状积云细胞,并确保进行ICSI受精。避免了不正确的培养基储存或模板制备过程,这可能会降解DNA。使用DNase和RNase去污试剂对工作空间进行了彻底净化。为了避免其他胚胎的污染,一个胚胎总是在单滴培养基中培养,以避免从第4天开始的交叉污染。当延迟胚胎在最终培养液滴中的放置时,污染现象最小化30,31,32,33。为了尽量减少母体污染,Kuznyetsov34 修改了从第 0 天到第 4 天的胚胎培养程序,包括通过移液和冲洗小心去除残留的电晕细胞。
Lane等30 表明,从第4天到第5天服用胚胎培养基时,整倍体检测的准确性提高,胚胎倍性一致性达到95%以上,性染色体一致性达到100%。Lledo等[33 ]发现,当胚胎从第4天培养到第6天时,第3-5天培养基与TE样品之间的吻合率分别为74.6%和92.0%。
我们的内部数据也支持这一结论, 如表S1所示。与传统的第3-5天培养方法相比,由于第4天或第5天培养基的再次变化,颗粒细胞被进一步去除。我们提供的内部数据(表S1)表明,与PGT-A相比,我们的两种方法(选项1和选项2)具有良好的一致性,这比没有彻底去除CC的采样方法更好。
IF扩增产物出现在阴性对照中,外部DNA材料可能污染了试剂或工作空间。工作空间应用DNA/RNA去除试剂清洗,使用无核酸酶材料,首次使用后应分装试剂。
表S1和表S2讨论了选项1和选项2之间成功率的差异。
NICS检测的局限性
NICS 有两个主要限制。1)在ICSI之前,必须去除所有卵丘细胞(通常是母体来源,通常是正常的染色体组成)。如果去除不完全,卵丘细胞可能会在胚胎发育过程中释放DNA,外部DNA被扩增,这可能是假阴性检测的原因。2)很难去除附着在透明带上的精子,强烈建议使用ICSI进行NICS程序。虽然在第 3 天定期更换切割培养基可能会减少由于卵丘细胞和冗余精子造成的污染的可能性,但如果将 NICS 用于临床 IVF,则必须将这种污染降至最低。然而,已经开发了一种检测试管婴儿胚胎中NICS的方法,包括识别外源DNA的功能,这将在不久的将来得到证明。
本研究没有比较不同培养基之间的差异,因为大规模临床试验比较了培养基。8 个中心使用 4 种不同的培养基,顺序和连续培养基,以及 2 种不同百分比的白蛋白补充(5% 和 10%),这些差异对胚胎 cfDNA 结果的准确性没有显着影响31。这些发现支持胚胎cfDNA分析在特定协议下工作时对每个IVF实验室的潜在适用性。
与现有方法相关的意义
NICS方法避免了胚胎活检,从而大大提高了使用的安全性。与囊胚相比,NICS是一种简单、省时、灵敏、可重复的植入前筛查技术,适用于非整倍体概率高的辅助生殖人群。与囊胚活检程序需要大量专业知识的侵入性活检不同,NICS可以广泛应用,因为它仅遵循IVF19 的常规操作,并且在某些国家不需要PGS / PGD资格。
未来应用
NICS具有广泛适用于临床IVF染色体筛查的潜力,不仅适用于ICSI,也适用于IVF胚胎。虽然强烈推荐使用ICSI,但需要去除附着在透明带上的精子的方法,以防止精子的影响。
形态学评估是一种传统的胚胎评估方法,但在大多数情况下,染色体异常的胚胎在形态上可能与染色体正常(整倍体)胚胎相似。将形态良好的倍体胚胎移植到子宫中时,将形态学评估与NICS测定相结合可能会提高持续妊娠率和活产率。将进行一项随机临床试验,以评估使用 NICS 技术进行单胚胎移植的临床疗效。
协议中的关键步骤
受精前必须从卵母细胞中取出所有日冕辐射积云细胞。卵母细胞通过卵胞浆内单精子注射(ICSI)受精。避免在培养基中添加人源性蛋白质/补充剂。在第 4 天更换培养基,并在第 5 天至第 6 天囊胚完全扩增时收集培养基。从第4天开始,胚胎在培养基的单个液滴中培养。收集培养基时,更换样品之间的移液器以避免污染。
Subscription Required. Please recommend JoVE to your librarian.
Disclosures
Yaxin Yao、Jieliang Ma、Jing Wang和Sijia Lu是Yikon Genomics Co., Ltd.的员工。
Acknowledgments
作者感谢 Shiping Bo 和 Shujie Ma 在 NGS 数据分析方面的帮助。基金资助:本工作由国家重点研发计划(批准号:2018YFC1003100)资助。
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1.5 mL EP tube, 0.2 mL PCR tube | Axygen | MCT-150-C, PCR-02-C | DNase/RNase free, Low Binding PCR tubes and 1.5 mL micro-centrifuge tubes are recommended. |
| 10 µL, 200 µL, 1000 µL DNase /RNase Free Tips | Axygen | T-300-R-S, T-200-Y-R-S, T-1000-B-R-S | This can be replaced by other brand/For sample transfer |
| 100 % ethanol | Sinopharm Chemical | 10009218 | This can be replaced by other brand/For DNA library purification |
| Barcode Primer1-48 | Yikon Genomics | Reagent in NICSInst library preparation kit | For library amplificaton |
| BD Falcon Organ Culture Dish, Sterile | BD Bioscience | 363037 | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo culture |
| BD Falcon Tissue culture Dishes (Easy Grip) , Sterile | BD Bioscience | 353001 | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo culture |
| BD Falcon Tissue culture Dishes, Sterile | BD Bioscience | 353002 | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo culture |
| Cell Lysis Buffer | Yikon Genomics | Reagent in NICSInst library preparation kit | For culture medium pre-treatment |
| Cell Lysis Enzyme | Yikon Genomics | Reagent in NICSInst library preparation kit | For culture medium pre-treatment |
| ChromGo software | Yikon Genomics | Data analysis | |
| CMPure Magbeads | Yikon Genomics | Reagent in NICSInst library preparation kit | For library purification |
| Cryotop open systerm | KITAZATO BioPharma | 81110 | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo vitrification |
| Distill water | Yikon Genomics | Reagent in NICSInst library preparation kit | To dissolve DNA |
| ES (Vitrification kit) | KITAZATO BioPharma | Reagent inVitrification kit | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo vitrification |
| HOLDNIG | ORIGIO | MPH-MED-35 | This can be replaced by other brand/For ICSI |
| Hyaluronidase solution, 80 U/mL | SAGE | ART4007-A | This can be replaced by other brand/Digest oocyte-corona-cumulus complex |
| ICSI | ORIGIO | MPH-35-35 | This can be replaced by other brand/For ICSI |
| Illumina MiSeq® System | Illumina | SY-410-1001 | For library sequencing |
| Incubator | Labotect | Inkubator C16 | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo culture |
| Library buffer | Yikon Genomics | Reagent in NICSInst library preparation kit | For library amplificaton |
| Library Enzyme Mix | Yikon Genomics | Reagent in NICSInst library preparation kit | For library amplificaton |
| Magnetic Stand | DynaMagTM-2 | 12321D | For library purification |
| Microscope | OLYMPUS | 1X71 | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo observation |
| Mini-centrifuge | ESSENSCIEN | ELF6 | For separation |
| MT Enzyme Mix | Yikon Genomics | Reagent in NICSInst library preparation kit | For culture medium pre-treatment |
| NICSInst library preparation kit | Yikon Genomics | KT1000800324 | Whole genome amplification and library construction |
| NICSInst Sample Prep Station | Yikon Genomics | ME1001003 | Amplificate DNA |
| Nunc IVF 4-Well Dish | Thermo Scientific | 144444 | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo washing and blastocyst culture |
| Pasteur Pipette | Oirgio | MXL3-IND-135 | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo tansfer |
| Pasteur pipettes | ORIGIO | PP-9-1000 | This can be replaced by other brand/For IVF laboratory |
| Pre-Lib Buffer | Yikon Genomics | Reagent in NICSInst library preparation kit | Pre-library preparation |
| Pre-Lib Enzyme | Yikon Genomics | Reagent in NICSInst library preparation kit | Pre-library preparation |
| Qubit® 3.0 Fluorometer | Thermo Scientific | Q33216 | For library quantification |
| Quinn's Advantage Blastocyst Medium | SAGE | ART-1029 | For embryo blastocyst stage culture |
| Quinn's Advantage Cleavage Medium | SAGE | ART-1026 | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo cleavage stage culture |
| Quinn's Advantage Fertilization Medium | SAGE | ART-1020 | This can be replaced by other brand/For oocyte and sperm fertilization |
| Quinn's Advantage m-HTF Medium with HEPES | SAGE | ART-1023 | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo clutrure |
| Quinn's Advantage SPS Serum protein Substitute Kit | SAGE | ART-3010 | This can be replaced by other brand/To denude the oocyte |
| Quinn's Advantage Tissue culture mineral oil | SAGE | ART-4008P | This can be replaced by other brand/To cover the culture medium |
| STRIPPER TIPS | ORIGIO | MXL3-IND-135 | This can be replaced by other brand/For denudating granulosa cells |
| Vitrification Cryotop Open systerm | KIZTAZATO | 81111 | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo vitrification |
| Vitrification kit | KITAZATO BioPharma | VT101 | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo vitrification |
| Vortexer | Qilinbeier | DNYS8 | Sample mix |
| VS (Vitrification kit) | KITAZATO BioPharma | Reagent inVitrification kit | This can be replaced by other brand/For embryo vitrification |
| ZILOS-tk Laser System | Hamilton Thorne | CLASS 1 laser | This can be replaced by other brand/For artificial blastocoele collapse |
References
- Barlow, P. Early pregnancy loss and obstetrical risk after in-vitro fertilization and embryo replacement. Human Reproduction. 3 (5), 671-675 (1988).
- Munne, S. Chromosome abnormalities and their relationship to morphology and development of human embryos. Reproductive BioMedicine Online. 12 (2), 234-253 (2006).
- Harton, G. L. Diminished effect of maternal age on implantation after preimplantation genetic diagnosis with array comparative genomic hybridization. Fertility and Sterility. 100 (6), 1695-1703 (2013).
- Hodes-Wertz, B. Idiopathic recurrent miscarriage is caused mostly by aneuploid embryos. Fertility and Sterility. 98 (3), 675-680 (2012).
- Keltz, M. D. Preimplantation genetic screening (PGS) with Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) following day 3 single cell blastomere biopsy markedly improves IVF outcomes while lowering multiple pregnancies and miscarriages. Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics. 30 (10), 1333-1339 (2013).
- Scott, R. T. Jr Blastocyst biopsy with comprehensive chromosome screening and fresh embryo transfer significantly increases in vitro fertilization implantation and delivery rates: a randomized controlled trial. Fertility and Sterility. 100 (3), 697-703 (2013).
- Forman, E. J. In vitro fertilization with single euploid blastocyst transfer: a randomized controlled trial. Fertility and Sterility. 100 (1), 100-107 (2013).
- Yang, Z. Selection of single blastocysts for fresh transfer via standard morphology assessment alone and with array CGH for good prognosis IVF patients: results from a randomized pilot study. Molecular Cytogenetics. 5 (1), 24 (2012).
- Cimadomo, D. The Impact of Biopsy on Human Embryo Developmental Potential during Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis. BioMed Research International. 2016, 7193075 (2016).
- Scott, R. T. Jr, Upham, K. M., Forman, E. J., Zhao, T., Treff, N. R. Cleavage-stage biopsy significantly impairs human embryonic implantation potential while blastocyst biopsy does not: a randomized and paired clinical trial. Fertility and Sterility. 100 (3), 624-630 (2013).
- Wu, Y. Blastomere biopsy influences epigenetic reprogramming during early embryo development, which impacts neural development and function in resulting mice. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 71 (9), 1761-1774 (2014).
- Zhao, H. C. Aberrant epigenetic modification in murine brain tissues of offspring from preimplantation genetic diagnosis blastomere biopsies. Biology of Reproduction. 89 (5), 117 (2013).
- Zeng, Y. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) influences adrenal development and response to cold stress in resulting mice. Cell and Tissue Research. 354 (3), 729-741 (2013).
- Palini, S. Genomic DNA in human blastocoele fluid. Reproductive BioMedicine Online. 26 (6), 603-610 (2013).
- Gianaroli, L. Blastocentesis: a source of DNA for preimplantation genetic testing. Results from a pilot study. Fertility and Sterility. 102 (6), 1692-1699 (2014).
- Stigliani, S., Anserini, P., Venturini, P. L., Scaruffi, P. Mitochondrial DNA content in embryo culture medium is significantly associated with human embryo fragmentation. Human Reproduction. 28 (10), 2652-2660 (2013).
- Stigliani, S. Mitochondrial DNA in Day 3 embryo culture medium is a novel, non-invasive biomarker of blastocyst potential and implantation outcome. Molecular Human Reproduction. 20 (12), 1238-1246 (2014).
- Wu, H. Medium-Based Noninvasive Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis for Human α-Thalassemias-SEA. Medicine. 94 (12), e669 (2015).
- Xu, J. Noninvasive chromosome screening of human embryos by genome sequencing of embryo culture medium for in vitro fertilization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 113 (42), 11907-11912 (2016).
- Capalbo, A. Diagnostic efficacy of blastocoel fluid and spent media as sources of DNA for preimplantation genetic testing in standard clinical conditions. Fertility and Sterility. 110 (5), 870-879 (2018).
- Tobler, K. J. Blastocoel fluid from differentiated blastocysts harbors embryonic genomic material capable of a whole-genome deoxyribonucleic acid amplification and comprehensive chromosome microarray analysis. Fertility and Sterility. 104 (2), 418-425 (2015).
- Magli, M. C. Preimplantation genetic testing: polar bodies, blastomeres, trophectoderm cells, or blastocoelic fluid? Fertility and Sterility. 105 (3), 676-683 (2016).
- Kuznyetsov, V. Evaluation of a novel non-invasive preimplantation genetic screening approach. PLoS One. 13 (5), e0197262 (2018).
- Li, P. Preimplantation Genetic Screening with Spent Culture Medium/Blastocoel Fluid for in Vitro Fertilization. Scientific Reports. 8 (1), 9275 (2018).
- Jiao, J. Minimally invasive preimplantation genetic testing using blastocyst culture medium. Human Reproduction. 34 (7), 1369-1379 (2019).
- Palermo, G. D. Births after intracytoplasmic injection of sperm obtained by testicular extraction from men with nonmosaic Klinefelter's syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine. 338 (9), 588-590 (1998).
- Alpha Scientists in Reproductive, M., & Embryology, E. S. I. G. o. The Istanbul consensus workshop on embryo assessment: proceedings of an expert meeting. Human Reproduction. 26 (6), 1270-1283 (2011).
- Thermo Fisher Scientific. Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit. , Available from: https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/Q32851?ICID=search-product (2015).
- Miseq system use guide. , Available from: https://support.illumina.com/downloads/miseq_system user _ guide 15027617.html (2016).
- Lane, M. Ability to detect aneuploidy from cell free DNA collected from media is dependent on the stage of development of the embryo. Fertility and Sterility. 108 (3), (2017).
- Rubio, C. Multicenter prospective study of concordance between embryonic cell-free DNA and trophectoderm biopsies from 1301 human blastocysts. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 223 (5), 751-751 (2020).
- Rubio, C. Embryonic cell-free DNA versus trophectoderm biopsy for aneuploidy testing: concordance rate and clinical implications. Fertility and Sterility. 112 (3), 510-519 (2019).
- Lledo, B. Consistent results of non-invasive PGT-A of human embryos using two different techniques for chromosomal analysis. Reproductive BioMedicine Online. 42 (3), 555-563 (2021).
- Kuznyetsov, V. Minimally Invasive Cell-Free Human Embryo Aneuploidy Testing (miPGT-A) Utilizing Combined Spent Embryo Culture Medium and Blastocoel Fluid -Towards Development of a Clinical Assay. Scientific Reports. 10 (1), 7244 (2020).
Tags
染色体筛查、人类胚胎植入前胚胎、废培养基、样本采集、染色体倍性分析、体外受精 (IVF)、非整倍体植入前基因检测 (PGT-A)、滋养外胚层 (TE)、细胞内质量 (ICM)、假阳性和假阴性、NICS 技术、DNA 测序、培养基采样、全基因组扩增 (WGA)、文库制备、NGS 数据分析、冷冻保存、试管婴儿实验室Erratum
Formal Correction: Erratum: Chromosome Screening of Human Preimplantation Embryos by Using Spent Culture Medium: Sample Collection and Chromosomal Ploidy Analysis
Posted by JoVE Editors on 10/01/2021.
Citeable Link.
An erratum was issued for: Chromosome Screening of Human Preimplantation Embryos by Using Spent Culture Medium: Sample Collection and Chromosomal Ploidy Analysis. The Protocol and Representaive Results sections were updated.
In the Protocol, step 3.8.2 was updated from:
After logging into the system, click Create Submission under the NICS tab. Then, select the sequencing platform, choose ChromInst for the reagent, enter the project information in the box under Project ID, set the analysis preferences and upload the files. Once all sequencing files are successfully uploaded, click Submit to start the analysis (Figure 3A).
to:
After logging into the system, click Create Submission under the NICS-A tab. Then, choose NGS for the platform, select corporation, choose ChromInst for the reagent, enter the project information in the box under Project ID, set the analysis preferences and upload the files. Once all sequencing files are successfully uploaded, click Submit to start the analysis (Figure 3A).
In the Representative Results, Figure 3 was updated from:
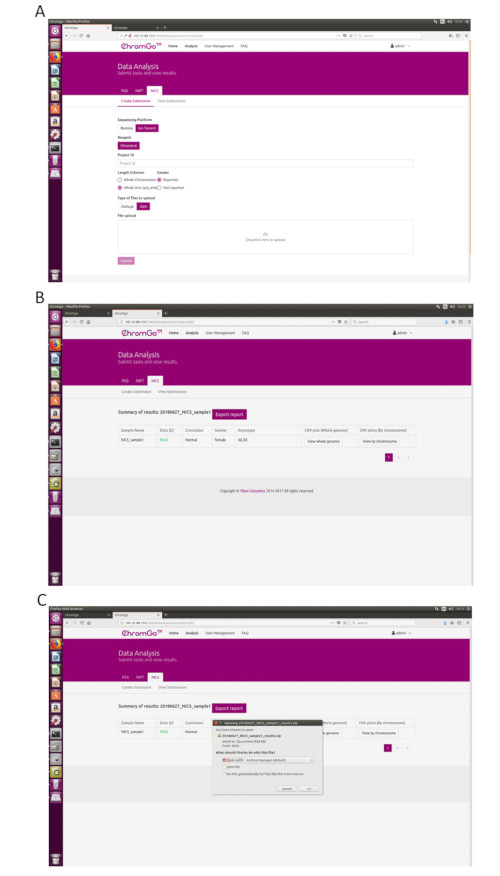
Figure 3. Data Analysis. (A) The page of Create Submission. There are different options for the user application. For sequencing platform, users can choose Illumina or Ion Torrent. For analysis criterion, there are two length detection resolution for selection, the whole chromosome and whole arm level. The users also can choose whether the mosaicism or gender information is reported. Finished the above parameter setting,click on the box under File upload and choose the appropriate sequencing files to upload. For Illumina, choose the files with an extension of fastq.gz. For Ion Torrent platform, choose files with an extension of bam. Click Submit to start the analysis after successfully upload. (B) The view of summary table. The summary table consists of following information: Sample Name: The name of each NICS sample is listed; Data QC: Indicates whether the sequencing file passes the QC for NICS analysis; Conclusion: Indicates whether the NICS analysis is normal or abnormal, "N/A" indicates no conclusive result is available; Gender: If the user chooses to report the sex information, this column will appear in the summary table; Karyotype: Shows the analysis results; CNV plot (Whole Genome): View the CNV profiles of all chromosomes; CNV plot (By Chromosome): View the CNV profiles of each chromosome. (C) The Save Report Page. Click Export report button next to the Summary of Results. Select the information you want to show on the final report and click Export. Select Save File in the appearing dialog window and then click OK. The reports will be saved to the Download folder of the computer. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
to:
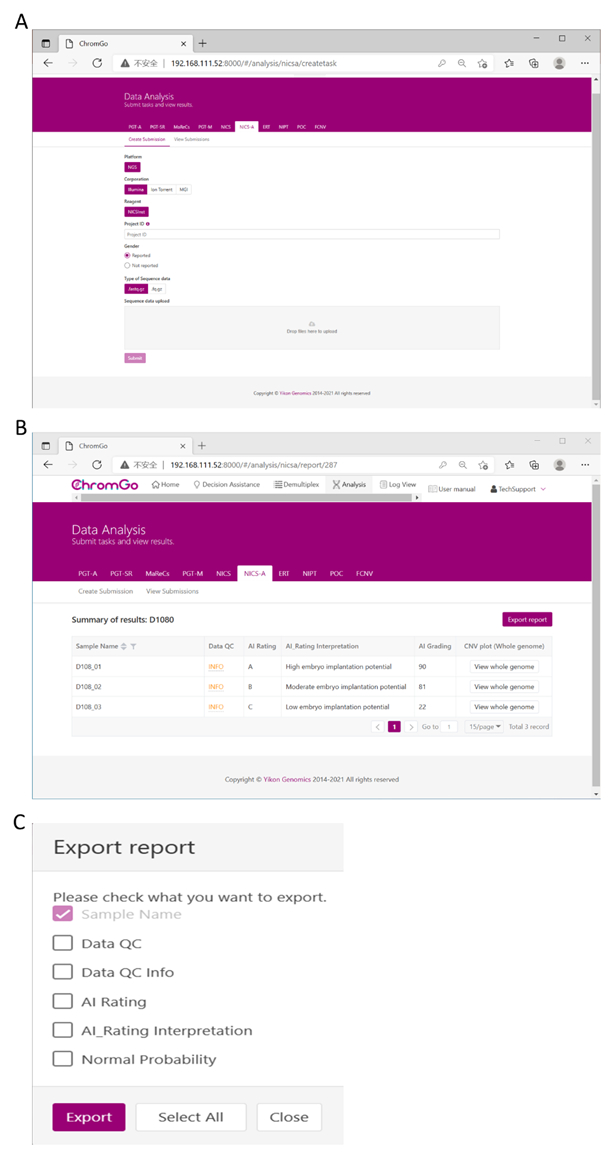
Figure 3. Data Analysis. (A) There are different options for the user application. For sequencing platform corporation, users can choose Illumina, Ion Torrent or MGI. The users can choose whether the gender information is reported. Finished the above parameter setting, click on the box under File upload and choose the appropriate sequencing files to upload. For Illumina, choose the files with an extension of fastq.gz. Click Submit to start the analysis after successfully upload. (B) The view of summary table. The summary table consists of following information: Sample Name: The name of each NICS sample is listed; Data QC: Indicates whether the sequencing file passes the QC for NICS analysis; AI Rating: The rating (A, B or C) for each NICS sample; AI_Rating Interpretation: Evaluation of embryo implantation potential; AI Grading: The score for each NICS sample; CNV plot (Whole Genome): View the CNV profiles of all chromosomes; (C) The Save Report Page. Click Export report button next to the Summary of Results. Select the information you want to show on the final report and click Export. The reports will be saved to the Download folder of your computer. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.



