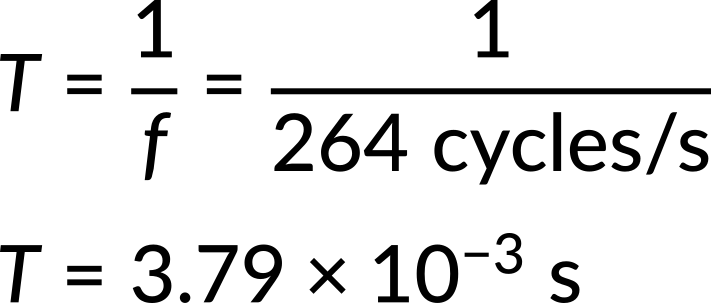15.1: Simple Harmonic Motion
Simple harmonic motion is the name given to oscillatory motion for a system where the net force can be described by Hooke's law. If the net force can be described by Hooke's law and there is no damping (by friction or other non-conservative forces), then a simple harmonic oscillator will oscillate with equal displacement on either side of the equilibrium position. To derive an equation for period and frequency, the equation of motion is used. The period of a simple harmonic oscillator is given by

and, because the frequency and period have inverse relation, the frequency of a simple harmonic oscillator is
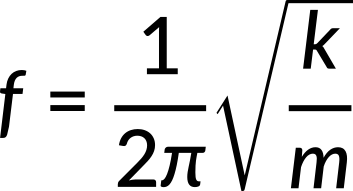
Note that neither period nor frequency has any dependence on amplitude, and the SI unit for frequency is Hertz.
Now, consider one example of each. (a) A medical imaging device produces ultrasound by oscillating with a period of 0.400 μs. What is the frequency of this oscillation? (b) The frequency of middle C on a typical musical instrument is 264 Hz. What is the time for one complete oscillation?
Both can be answered using the inverse relationship between period and frequency. Substituting the given value of period in the frequency expression, the frequency of oscillation is found.
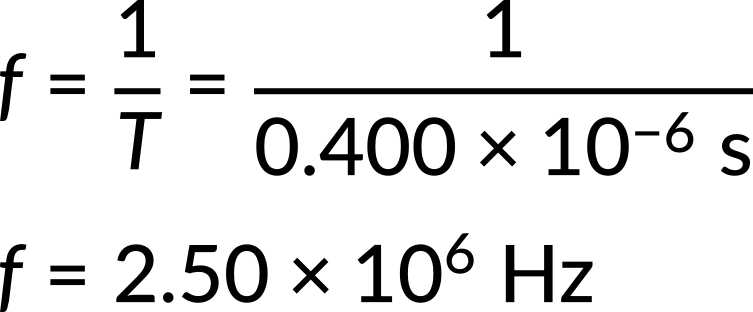
Substituting the given value for the frequency into the time period expression, the time for one complete oscillation is obtained.