Source: Kerry M. Dooley and Michael G. Benton, Department of Chemical Engineering, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA
Processing of biochemicals involves unit operations such as crystallization, ultracentrifugation, membrane filtration, and preparative chromatography, all of which have in common the need to separate large from small molecules, or solid from liquid. Of these, crystallization is the most important from a tonnage standpoint. For that reason, it is commonly employed in the pharmaceutical, chemical and food processing industries. Important biochemical examples include chiral separations,1 purification of antibiotics,2 separation of amino acids from precursors,3 and many other pharmaceutical,4-5 food additive,6-7 and agrochemical purifications.8 The control of crystal morphology and size distribution is critical to process economics, as these factors affect the costs of downstream processing operations such as drying, filtration, and solids conveying. For more information about crystallization, consult a specialized textbook or a Unit Operations textbook.9
The crystallizer unit (Figure 1) enables study of: (a) the effects of key parameters, such as supersaturation and cooling/heating rates, on solids content, morphology and crystal size distribution; (b) and the on-line control of crystallization processes. Supersaturation can be controlled by altering conditions such as agitation rate and temperature. The different classifications of crystallization include cooling, evaporative, pH swing and chemical modification. In this experiment,an offline microscope will measure from crystals ranging in size from 10-1000 μm, a typical size range for biologicals.
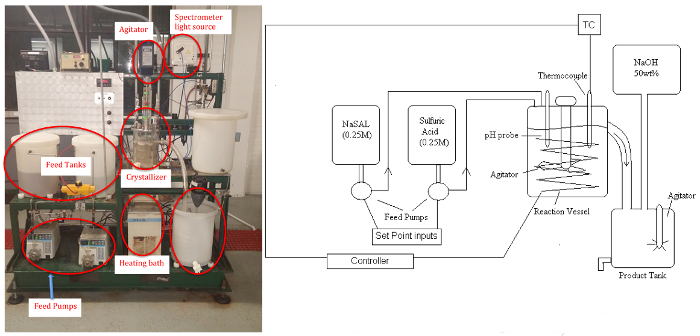
Figure 1: P&ID schematic (left)and picture (right)of Crystallizer. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
This experiment will demonstrate a "chemical modification",or "pH-swing" crystallization, to generate salicylic acid (SAL) (precursor of aspirin) crystals from the rapid reaction of aqueous solutions of basic sodium salicylate (NaSAL), which are basic, and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) at anywhere from 40 - 80°C.11
Na+SAL + 0.5 H2SO4 SAL (ppt) + Na+ + 0.5 SO42-
The byproduct sodium sulfate remains soluble. The apparatus consists of two feed tanks, three variable speed (peristaltic) pumps, the crystallizer (stirred tank to approximate uniform temperature and concentration, ~5 L), a circulating bath for temperature control, power controller, product tank, and a makeup tank for feed regeneration with NaOH solution (if desired). Samples will be analyzed by a UV-Vis spectrometer for the residual soluble salicylate ion, and the salicylic acid crystal product will be dried and weighed.A pH probe can be used to determine steady-state when reaction conditions are altered.
Chemical Engineering

