1.7:
מדידה: יחידות סטנדרטיות
1.7:
מדידה: יחידות סטנדרטיות
Every measurement provides three kinds of information: the size or magnitude of the measurement (a number), a standard of comparison for the measurement (a unit), and an indication of the uncertainty of the measurement. While the number and unit are explicitly represented when a quantity is written, the uncertainty is an aspect of the errors in the measurement results.
The number in the measurement can be represented in different ways, including decimal form and scientific notation, which is also known as exponential notation. For example, the maximum take-off weight of a Boeing 777-200ER airliner is 298,000 kilograms, which can also be written as 2.98 × 105 kg.
Units, such as liters, pounds, and centimeters, are standards of comparison for measurements. A 2-liter bottle of a soft drink contains a volume of beverage that is twice that of the accepted volume of 1 liter. Without units, a number can be meaningless, confusing, or possibly life-threatening. Suppose a doctor prescribes phenobarbital to control a patient’s seizures and states a dosage of “100” without specifying units. Not only will this be confusing to the medical professional giving the dose, but the consequences can be dire: 100 mg given three times per day can be effective as an anticonvulsant, but a single dose of 100 g is more than 10 times the lethal amount.
The International System of Units (SI Units)
The measurement units for seven fundamental properties (“base units”): length, mass, time, temperature, electric current, amount of substance, and luminous intensity, have been fixed by international agreement. They are called the International System of Units or SI Units. Units for other properties may be derived from these seven base units. Everyday measurement units are often defined as fractions or multiples of other units. Milk is commonly packaged in containers of 1 gallon (4 quarts), 1 quart (0.25 gallons), and one pint (0.5 quarts. This same approach is used with SI units, but these fractions or multiples are always powers of 10. Fractional or multiple SI units are named using a prefix and the name of the base unit. For example, a length of 1000 meters is also called a kilometer because the prefix kilo means “one thousand,” which in scientific notation is 103 (1 kilometer = 1000 m = 103 m).
Standard SI Units
The initial units of the metric system, which eventually evolved into the SI system, were established in France during the French Revolution. The original standards for the meter and the kilogram were adopted there in 1799 and eventually by other countries. The following are the four SI base units commonly used in chemistry.
1. Length
The standard unit of length in the SI system is the meter (m). A meter is defined as the distance light travels in a vacuum in 1/299,792,458 of a second. Longer distances are often reported in kilometers (1 km = 1000 m = 103 m), whereas shorter distances can be reported in centimeters (1 cm = 0.01 m = 10−2 m) or millimeters (1 mm = 0.001 m = 10−3 m).
2. Mass
The standard unit of mass in the SI system is the kilogram (kg). A kilogram is defined by the mass of a reference object – a metal cylinder made from platinum-iridium alloy with a height and diameter of 39 mm. Any object with the same mass as this reference is said to have a mass of 1 kilogram. The gram (g) is exactly equal to 1/1000 of the mass of the kilogram (10−3 kg).
The term “weight” is often used interchangeably with “mass.” However, the two quantities are different. While the mass of an object measures the quantity of matter within it, its weight measures the gravitational force exerted on its matter. For instance, if we could weigh ourselves on the moon, which has weaker gravity than Earth, we would weigh less than we did on Earth. However, mass—the quantity of matter in our body—would stay the same.
3. Temperature
The SI unit of temperature is the kelvin (K), although the degree Celsius (°C) is also allowed in the SI system, with both the word “degree” and the degree symbol used for Celsius measurements. Celsius degrees are the same magnitude as those of kelvin, but the two scales place their zeros in different places. Water freezes at 273.15 K (0 °C) and boils at 373.15 K (100 °C) by definition, and normal human body temperature is approximately 310 K (37 °C). The Fahrenheit (°F) scale is another commonly used unit for measuring temperature. On the Fahrenheit scale, water freezes at 32 °F and boils at 212 °F, and the normal human body temperature is 96 °F.
While Fahrenheit and Celsius scales allow for negative temperatures, the Kelvin scale, also called the absolute scale, does not. On the Kelvin scale, 0 K is the lowest temperature, which is known as absolute zero.
The temperature scales are interconvertible using the following conversion formulas:

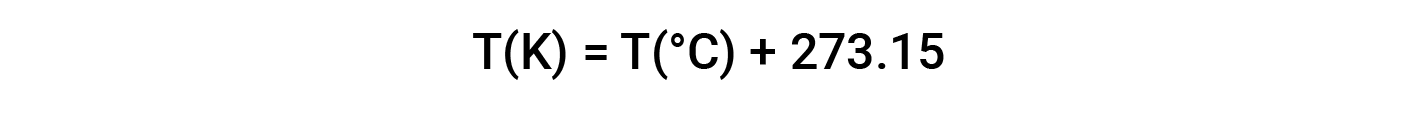
4. Time
The SI base unit of time is the second (s). Small and large time intervals can be expressed with the appropriate prefixes. For example:
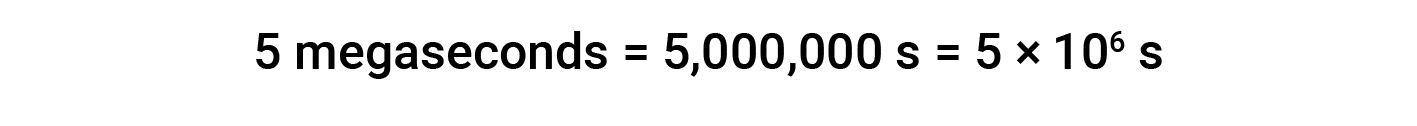
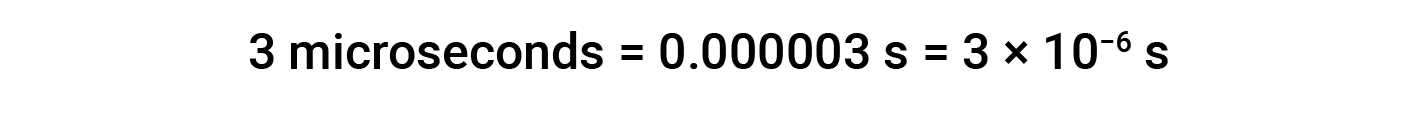
Alternatively, hours, days, and years can be used.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 1.4: Measurements.
