Overview
Source: Jaideep S. Talwalkar, MD, Internal Medicine and Pediatrics, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
The physical examination requires the use of all of the provider's senses to gain information about the patient. The sense of touch is utilized to obtain diagnostic information through palpation.
The specific parts of the examiner's hand used for palpation differ based on the body part being examined. Because of their dense sensory innervation, the finger pads are useful for fine discrimination (e.g., defining the borders of masses, lymph nodes) (Figure 1). The dorsal surface of the hand provides a rough sense of relative temperature (Figure 2). The palmar surfaces of the fingers and hands are most useful for surveying large areas of the body (e.g., abdomen) (Figure 3). Vibration is best appreciated with the ulnar surface of the hands and 5th fingers (e.g., tactile fremitus) (Figure 4).
While palpation is fundamental to the diagnostic aspect of the physical exam, it is also important to acknowledge the role that touch plays in communicating caring and comfort during the patient encounter. Patients generally perceive touch from a healthcare provider in a positive light, and their perceptions of a healthcare provider can be shaped by the skilled use of touch during clinical encounters.1 Physical contact has been associated with alterations in hormonal and neurotransmitter levels, specifically decreases in cortisol and increases in serotonin.2
Therefore, through the careful use of palpation, and touch in general, during the physical examination, the clinician has the opportunity to gain important diagnostic information, while developing rapport and promoting healing.
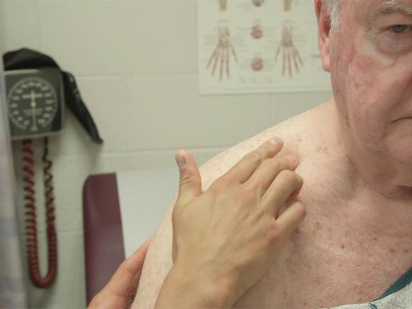
Figure 1. Lymph node examination with finger pads.
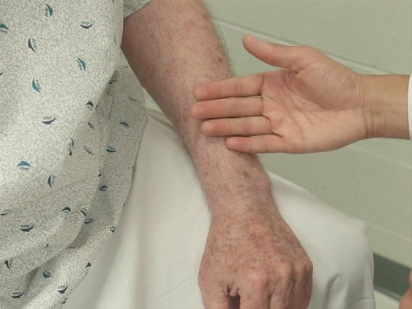
Figure 2. Using the dorsum of hand to assess for warmth.
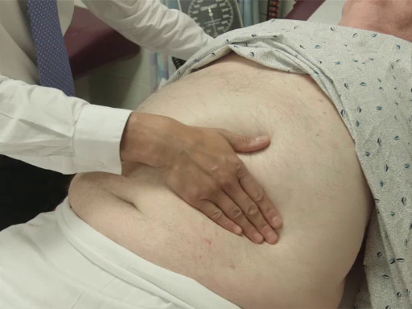
Figure 3. Abdominal palpation with palmar surface of fingers and hands.
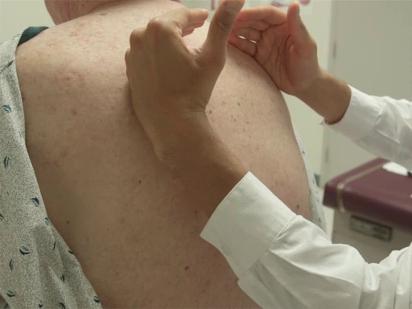
Figure 4. Using the ulnar surface of the hand to assess for tactile fremitus.
Procedure
1. Before the patient encounter
- Keep fingernails clean, groomed, and trimmed.
- Wash your hands with soap and water or topical disinfectant solution.
- Warm your hands as able (e.g., with warm water or by rubbing them together) before patient contact.
- If any specific infection control precautions are needed for the clinical encounter (e.g., contact precautions), explain to the patient why you are wearing protective equipment. Be aware that gowns, gloves, and masks can present a barrier to building a relationship with the patient.3
2. Components of the exam
- Familiarize oneself with the specific palpation techniques for each regional/anatomic component of the exam; refer to each of the individual videos for exploration of how palpation is utilized.
- Perform the palpation directly on the patient's skin. Employ draping techniques to optimize access, while balancing patient modesty. Refer to the videos on draping for specific details.
3. General considerations
- In order to slowly invite oneself into the patient's personal space and gauge the patient's comfort with the clinician's touch, many providers start the examination with the hands. Perform gentle palpation of the nailbeds with your fingertips (to assess for capillary refill and pallor) and palpation of the radial pulse with your finger pads to initiate the first contact in a non-threatening way.
- Use the finger pads when performing most of palpation, with the following notable exceptions:
- Use the fingertips to palpate the nailbeds, liver edge, and cervix.
- Use the ulnar surface of the hands when assessing tactile fremitus.
- Use the palmar surface of the fingers and/or hands for assessing chest expansion, precordium for PMI/heaves/lifts/thrills, performing light and deep palpation of the abdomen, and strength testing against resistance.
- Use the dorsal surface of the hands for assessing the relative temperature of the skin (typically in comparison to another portion of the patient's body).
- Be aware of the pressure used for palpation, which varies based on the structures being examined. For example, excessive pressure may occlude a pulse, causing discomfort and limiting utility. Insufficient pressure may limit one's ability to palpate deep structures (e.g., aorta).
- Be deliberate about the duration when applying pressure, which varies based on the structures being examined. For example, tense lower extremity pitting edema can be missed, if the examiner does not apply steady pressure for at least a few seconds. Similarly, a blanching rash may not be identified as such without ample duration of pressure. Conversely, excessive duration of palpation in a patient with peritoneal signs causes undue discomfort without increasing diagnostic yield.
- Consider palpating areas of known discomfort toward the end of the examination, making it clear to patients this is done in the interest of their comfort. For example, if a patient has acute right knee pain, initiating the exam on the left lower extremity, followed by examination of the right ankle and hip, may make the patient less guarded when the painful right knee is examined.
- Express empathy while acknowledging that certain parts of the examination may cause the patient discomfort. Patients expect to be examined, but ask permission and provide a warning if you are about to do something that is likely to worsen a patient's pain (e.g., palpation of the abdomen in a patient with suspected appendicitis).
During a physical exam, the clinician uses the sense of touch through palpation to obtain useful diagnostic information. It is an assessment technique in which the examiner uses the surface of the fingers and hands to feel and examine an organ or body part. While palpation is fundamental to the diagnostic aspect of the physical exam, it is also important to acknowledge the role that touch plays in communicating caring and comfort during the patient encounter.
This video will illustrate the different palpation techniques, and discuss the approach and considerations for this procedure.
First, let's discuss the different types of palpation techniques that are based on the specific parts of the examiner's hand used to perform the procedure. Finger pads are used for palpation of most of the body parts. Because of their dense sensory innervation, the finger pads are useful for fine discrimination, for example defining the borders of masses, or while examining the lymph nodes. Fingertips are used for palpating specific structures like the nailbeds, liver edge, and cervix. In addition to fingertips and finger pads, physicians also use the ulnar surface of the hands and fifth fingers to appreciate vibration when performing specialized test like tactile fremitus. One should use the palmar surface of the fingers and hands for assessing functions like chest expansion, palpation of the precordium, light and deep abdominal palpation, and muscle strength testing. Lastly, the dorsal surface of the hands is used for getting rough sense of relative temperature, typically in comparison to another portion of the patient's body.
Now that you know about different palpation techniques, let's discuss the general approach to palpation during any clinical exam.
Before every patient encounter, make sure that your fingernails are clean, groomed, and trimmed. Wash your hands with soap and water or apply topical disinfectant solution. Warm your hands either with warm water or by rubbing them together. If any specific infection control precautions are needed, then wear the protective equipment and explain to the patient why it's necessary. Remember: gowns, gloves, and masks can present a barrier to building a relationship with the patient.
In order to gauge the patient's comfort with the clinician's touch, you may start the examination with the hands. First, perform palpation of the nailbeds with your fingertips to assess for capillary refill and pallor. Then, palpate the radial pulse with your finger pads. After that, move to the anatomic region of interest, in this case the abdominal region. Employ draping techniques to optimize access, while balancing patient's modesty. Next, ask the patient to point to the area of discomfort. Consider palpating it towards the end, making it clear to patients this is done in the interest of their comfort, "I'm going to examine this area last in order just to make it more comfortable for you."
In general, be aware of the pressure used for palpation, which varies based on the structures being examined. For example, insufficient pressure may limit one's ability to palpate deep structures, and excessive pressure may occlude a pulse, causing discomfort and limiting utility. Be deliberate about the palpation duration as well, which again differs based on the structure under examination. For example, while examining the lower extremities, the palpation needs to be performed for sufficient amount of time to reveal pitting edema, if present. This kind of information can be missed if palpation duration is insufficient. In addition, express empathy while acknowledging that examination of certain parts may cause the patient discomfort. Although patient expects to be examined, always ask permission and provide a warning if you are about to do something that may worsen the pain. At the end of the exam, drape the patient back and thank them for their cooperation.
You've just watched JoVE's introduction to palpation. This demonstration covered the types and general considerations related to palpation during a physical exam. Through the careful use of this technique, the clinician has the opportunity to gain important diagnostic information, while developing rapport and promoting healing. As always, thanks for watching!
Subscription Required. Please recommend JoVE to your librarian.
Applications and Summary
This demonstration covered the general considerations related to palpation during the physical examination. While specific techniques vary based on each individual portion of the exam, many general principles related to palpation hold throughout the exam. Attention to patient safety and comfort is achieved through hand-washing, proper grooming, warming of the hands, infection control precautions, and sensitive draping. The correct part of the fingers and hands should be used for different types of palpation, with finger pads being used most commonly during the exam. The clinician should be deliberate about the amount and duration of pressure being applied during palpation; these variables change based on the part of the body being examined and specific patient circumstances. Finally, the clinician should remember the important role that touch plays in the patient encounter in terms of therapeutic value and the clinician-patient relationship. The most direct physical contact during the encounter occurs through palpation, which provides an opportunity to secure the bond the clinician has started to develop during history taking.
Subscription Required. Please recommend JoVE to your librarian.
References
- McCann, K., McKenna, H.P. An examination of touch between nurses and elderly patients in a continuing care setting in Northern Ireland. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 18, 838-46 (1993).
- Field, T. Violence and touch deprivation in adolescents. Adolescence. 37 (148), 735-749 (2002).
- Verrees, M. Touch me. JAMA. 276 (16), 1285-1286 (1996).




