4.3:
Reaktionsausbeute
4.3:
Reaktionsausbeute
The theoretical yield of a reaction is the amount of product estimated to form based on the stoichiometry of the balanced chemical equation. The theoretical yield assumes the complete conversion of the limiting reactant into the desired product. The amount of product that is obtained by performing the reaction is called the actual yield, and it may be less than or (very rarely) equal to the theoretical yield.
Percent Yield
In the case of chemical reactions, the actual yield of the product is often less than the theoretical yield predicted based on the reaction’s stoichiometry. When reactions are performed under a given set of conditions, an inevitable loss in mass is expected due to several reasons. Some reactions are naturally inefficient, generating other undesirable products through side reactions. Others are incomplete due to their reversible nature, accompanied by a state of equilibrium between the reactants and products. Sometimes the loss in product mass is due to inadequate recovery of the desired product from the reaction mixture during purification techniques such as crystallization, distillation, filtration, and chromatography. In cases where product loss is experienced, percent yield is used to measure the extent to which a reaction’s theoretical yield is achieved.

Actual and theoretical yields may be expressed as masses or molar amounts (or any other appropriate property, e.g., volume, if the product is a gas). As long as both yields are expressed using the same units, these units will cancel when percent yield is calculated.
Calculating Percent Yield
Consider the combustion of nitric oxide to nitrogen dioxide.
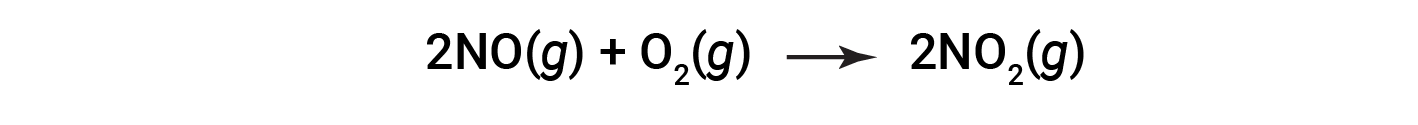
At the end of the reaction, 180 grams of nitrogen dioxide is obtained from 150 grams of nitric oxide and an excess of oxygen. What is the percent yield?
The actual yield of the reaction is 180 grams. Knowing that nitric oxide is the limiting reactant, the moles of theoretical yield are obtained based on the stoichiometry of NO and NO2. First, the mass of NO is converted to moles of NO. Then, the stoichiometric ratio of NO:NO2 (1:1) is applied, which suggests that 5 moles of NO2 will be formed from 5 moles of NO. Third, the moles of NO2 are converted to mass.

In the final step, percent yield is calculated based on the ratio of the actual yield to the theoretical yield.

This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 4.4: Reaction Yields.
