4.12:
Acids, Bases and Neutralization Reactions
The human stomach is a muscular organ containing gastric juices, including hydrochloric acid, which help digest food. Certain kinds of foods raise the acidity levels of our stomach, causing acid reflux.
Consuming alkaline food, or a base like an antacid, neutralizes the excess acid, relieving the burning sensation. This is an example of an acid-base reaction.
The simplest acids are substances that contain dissociable hydrogen atoms. In aqueous solutions, they release positively charged hydrogen ions, or protons, along with the corresponding anions. The protons react with water molecules to form hydronium ions.
For example, an aqueous solution of nitric acid contains hydronium ions and nitrate ions. Other commonly known acids are hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and phosphoric acid.
Acids are monoprotic or polyprotic depending on the number of dissociable hydrogen atoms per molecule.
Hydrochloric acid and nitric acid, with one dissociable hydrogen each, are both examples of monoprotic acids, while sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid are polyprotic. Sulfuric acid is diprotic and releases its two protons sequentially, whereas phosphoric acid is triprotic and dissociates sequentially in three steps.
The simplest bases are compounds that yield negatively charged hydroxide ions in aqueous solutions. Easily identifiable bases contain hydroxyl groups; for example, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, and calcium hydroxide.
Such bases, when added to water, dissociate into hydroxide ions and the corresponding metal cations.
Non-hydroxide bases like ammonia react with water by accepting protons from water molecules to produce ammonium ions and hydroxide ions.
In general, an acid and a base react to form water and a salt. Acid–base reactions are also called neutralization reactions when the moles of protons supplied by the acid and the moles of hydroxide ions supplied by the base are equal.
For example, when equal amounts of aqueous nitric acid and aqueous potassium hydroxide are mixed, the amounts of hydronium and hydroxide ions supplied to the solution are also equal.
The hydronium and hydroxide ions, therefore, completely neutralize each other by combining to form water, leaving no hydronium or hydroxide ions behind. Additionally, the nitrate anions and potassium cations pair up to form a salt — potassium nitrate.
Certain neutralization reactions are gas-evolution reactions. For example, hydrochloric acid and potassium sulfite react to form potassium chloride, water, and sulfur dioxide gas through the sulfite–bisulfite equilibrium system.
4.12:
Acids, Bases and Neutralization Reactions
An acid-base reaction is one in which a hydrogen ion, H+, is transferred from one chemical species to another. Such reactions are of central importance to numerous natural and technological processes, ranging from the chemical transformations within cells or lakes and oceans to the industrial-scale production of fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and other substances essential to the society.
There are several ways of defining an acid. In the context of aqueous solutions, an acid is a substance that dissolves to produce hydrogen ions.

This is the Arrhenius definition of an acid, named after Swedish chemist Svante Arrhenius (1859–1927). A hydrogen ion, represented by the symbol H+, is called a proton. In solution, the protons chemically combine with water molecules, through the lone pairs on oxygen, to form hydronium ions, H3O+.
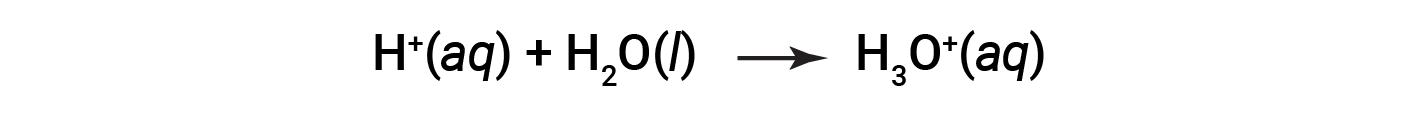
The chemical equation for the ionization of an acid is written as

Acids that react completely with water in this manner are called strong acids. HCl, HNO3, and HBr are a few examples.
Most acids encountered in daily life are weak acids. The citric acid in fruits, acetic acid in vinegar, and lactic acid in milk are a few examples. A familiar example of a weak acid is acetic acid, the main ingredient in food vinegar. When dissolved in water under typical conditions, only about 1% of acetic acid molecules are present in the ionized form, CH3CO2−.

The use of a double-arrow in the above equation denotes the partial reaction aspect of this process.
A base is a substance that will dissolve in water to yield hydroxide ions, OH−. The most common bases are ionic compounds composed of alkali or alkaline earth metal cations (groups 1 and 2) combined with the hydroxide ion—for example, NaOH and Ca(OH)2. Unlike acid-compounds discussed previously, these compounds do not react chemically with water; instead, they dissolve and dissociate, releasing hydroxide ions directly into the solution. For example, KOH and Ba(OH)2 dissolve in water and dissociate completely to produce cations (K+ and Ba2+, respectively) and hydroxide ions, OH−. These bases, along with other hydroxides that completely dissociate in water, are considered strong bases.
Consider the dissolution of sodium hydroxide in water as an example:

This equation confirms that sodium hydroxide is a base. When dissolved in water, NaOH dissociates to yield Na+ and OH− ions. This is also true for any other ionic compound containing hydroxide ions. Since the dissociation process is essentially complete when ionic compounds dissolve in water under typical conditions, NaOH and other ionic hydroxides are all classified as strong bases.
Unlike ionic hydroxides, some compounds produce hydroxide ions when dissolved by chemically reacting with water molecules. In all cases, these compounds react only partially and so are classified as weak bases. These types of compounds are also abundant in nature and are important commodities in various technologies. For example, global production of the weak base ammonia is typically well over 100 metric tons annually because it is widely used as an agricultural fertilizer, a raw material for chemical synthesis of other compounds, and an active ingredient in household cleaners. When dissolved in water, ammonia reacts partially to yield hydroxide ions, as shown here:

This is, by definition, an acid-base reaction involving the transfer of H+ ions from water molecules to ammonia molecules. Under typical conditions, only about 1% of the dissolved ammonia is present as NH4+ ions.
A neutralization reaction is a specific type of acid-base reaction in which the reactants are an acid and a base (but not water), and the products are often salt and water:

To illustrate a neutralization reaction, consider what happens when a typical antacid such as milk of magnesia (an aqueous suspension of solid Mg(OH)2) is ingested to ease symptoms associated with excess stomach acid (HCl):

Note that, in addition to water, this reaction produces a salt, magnesium chloride. The H+ (aq) from the acid (strong or weak) combines with the OH− (aq) from the base (or produced by the reaction of a weak base with water) to form H2O (l). For example, the reaction between aqueous solutions of HCl (strong acid) and NaOH (strong base) is written as follows:

Both HCl and NaOH undergo 100% ionization. The complete ionic equation, therefore, may be written as:
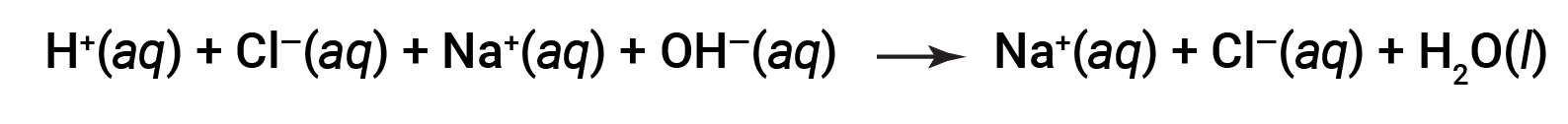
Cl– and Na+ are called the spectator ions, which cancel out, giving the net ionic equation as:
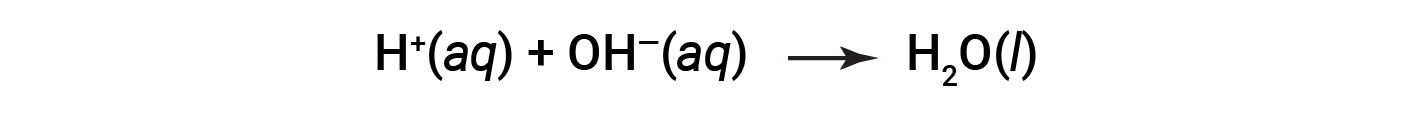
This text is adapted from OpenStax Chemistry 2e, Section: 4.2: Classifying Chemical Reactions.
