3.8:
Formelmasse- und Molkonzepte von Verbindungen
3.8:
Formelmasse- und Molkonzepte von Verbindungen
Formula Mass of Covalent Compounds
Chemical formulas represent the elemental makeup of substances. For covalent compounds, the formula represents the numbers and types of atoms composing a single molecule of the substance; therefore, the formula mass may be correctly referred to as a molecular mass. The molecular formula of chloroform (CHCl3), a covalent compound, indicates that a single molecule contains one carbon atom, one hydrogen atom, and three chlorine atoms. The average molecular mass of a chloroform molecule is equal to the sum of the average atomic masses of these atoms:
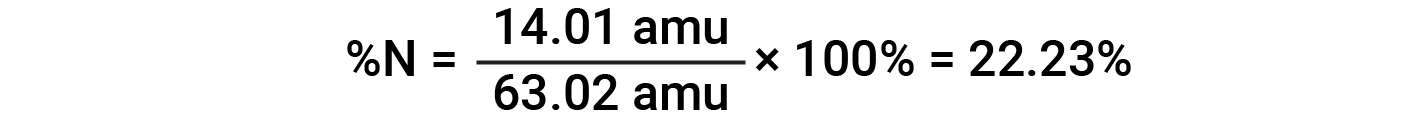
Formula Mass of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are composed of discrete cations and anions that are combined in ratios to yield electrically neutral bulk matter. The formula mass for an ionic compound is calculated in the same way as the formula mass for covalent compounds: by summing the average atomic masses of all the atoms in the compound’s formula. However, the formula for an ionic compound does not represent the composition of a discrete molecule, so it may not correctly be referred to as the ‘molecular mass’.
For example, common table salt or sodium chloride (NaCl) is an ionic compound composed of sodium cations (Na+) and chloride anions (Cl−) combined in a 1:1 ratio. The formula mass for this compound is computed by adding the average atomic masses of its constituent elements:
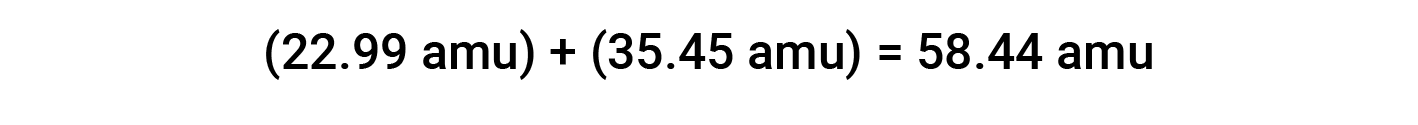
When computing the formula mass of an ionic compound, the average masses of neutral sodium and chlorine atoms were used, rather than the masses for sodium cations and chloride anions. Even though a sodium cation has a slightly smaller mass than a sodium atom (since it is missing an electron), this difference will be offset by the fact that a chloride anion is slightly more massive than a chlorine atom (due to the extra electron). Moreover, the mass of an electron is negligibly small with respect to the mass of a typical atom.
Mass Percent Composition
The elemental makeup of a compound defines its chemical identity, and chemical formulas are the most concise way of representing this elemental makeup. Percentage by mass of each element in the compound is called the mass percent of that particular element. Percent composition can be calculated by dividing the mass of each element by the overall mass of the compound and then convert to a percentage.
Percent composition is useful for evaluating the relative abundance of a given element in different compounds of known formulas. As long as the molecular or empirical formula of the compound in question is known, the percent composition may be derived from the atomic or molar masses of the compound's elements.
For example, one molecule of nitric acid (HNO3) contains one nitrogen atom weighing 14.01 amu, one hydrogen atom weighing 1.008 amu, and three oxygen atoms weighing (3 × 16.00 amu) = 48.00 amu. The formula mass of nitric acid is therefore (14.01 amu + 1.008 amu + 48.00 amu) = 63.02 amu, and it’s percent composition is:
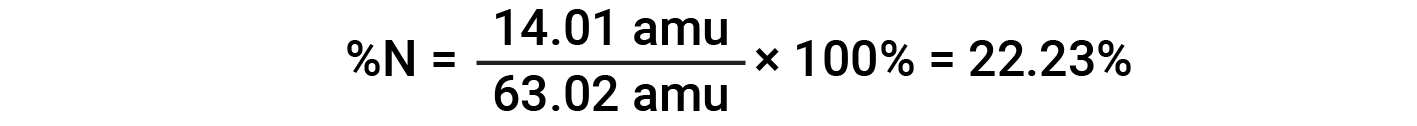
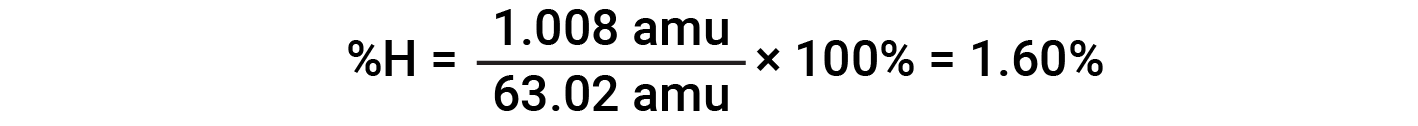
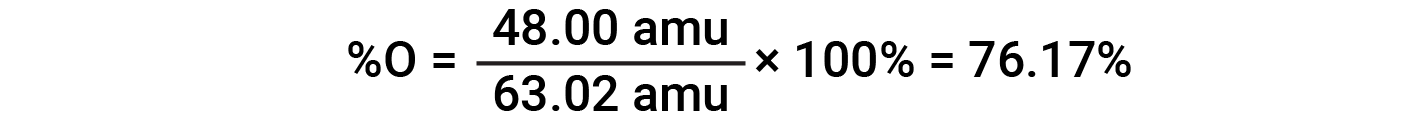
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 3.1: Formula Mass and the Mole Concept and Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 3.2: Determining Empirical and Molecular Formulas.
