7.2:
Das elektromagnetische Spektrum
7.2:
Das elektromagnetische Spektrum
The electromagnetic spectrum consists of all the types of electromagnetic radiation arranged according to their frequency and wavelength. Each of the various colors of visible light has specific frequencies and wavelengths associated with them, and you can see that visible light makes up only a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Because the technologies developed to work in various parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are different, for reasons of convenience and historical legacies, different units are typically used for different parts of the spectrum. For example, radio waves are usually specified as frequencies (typically in units of MHz), while the visible region is usually specified in wavelengths (typically in units of nm or angstroms).
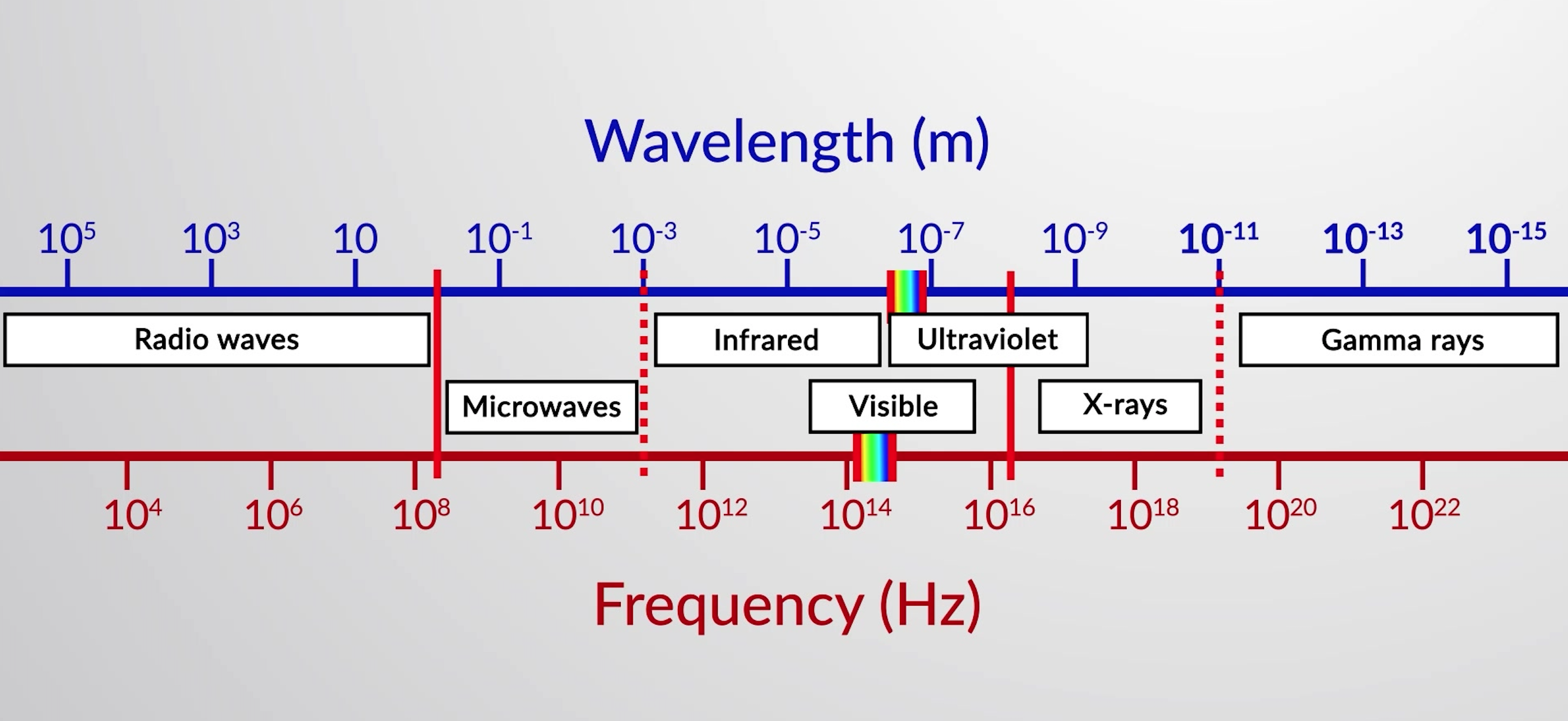
Figure 1: Portions of the electromagnetic spectrum are shown in order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength.
The types of electromagnetic waves are radio waves, microwaves, ultraviolet, visible, infrared, x-rays, and gamma rays.
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths, the lowest frequencies, and carry the least amount of energy. They are used in cell phone technology, radio and television broadcasts, air-traffic control, etc.
Microwaves have shorter wavelengths as compared to the radio waves. They are absorbed by water and are used to heat and cook food.
Next is infrared radiation, which is emitted by warm objects. For example, the Earth absorbs radiant energy from the sun and emits infrared radiation. Some of the infrared radiation is absorbed and re-emitted by the atmosphere to maintain the average temperature of the Earth through the greenhouse effect. Night vision goggles sense the infrared radiations emitted by our bodies.
Visible light is only a tiny portion of electromagnetic radiations ranging from 740 to 390 nm. Human eyes can only see this small range of wavelengths. Visible light mainly consists of seven color components, including red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
Ultraviolet radiation has wavelengths ranging from 400 to 10 nm. Sunlight is the most familiar source of UV radiation. It carries enough energy that, with excessive exposure, it causes sunburns.
X-rays can pass through many substances, making them an important imaging tool. Dentists use x-rays for diagnostic purposes, and airport security uses them to visualize components in a suitcase.
Gamma rays have smaller wavelengths, high frequencies, and energies. Gamma rays are released by nuclear reactions and naturally occurring radioactive elements.
X-rays and gamma rays are the most energetic forms of electromagnetic radiation. Their high energies can ionize atoms and molecules. The ionizing radiation can cause permanent change or damage to biological molecules. They are used to destroy cancer cells.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 6.1: Electromagnetic Energy.
