17.9:
שינויי אנרגיה חופשית עבור מצבים לא סטנדרטיים
17.9:
שינויי אנרגיה חופשית עבור מצבים לא סטנדרטיים
The free energy change for a process taking place with reactants and products present under nonstandard conditions (pressures other than 1 bar; concentrations other than 1 M) is related to the standard free energy change according to this equation:
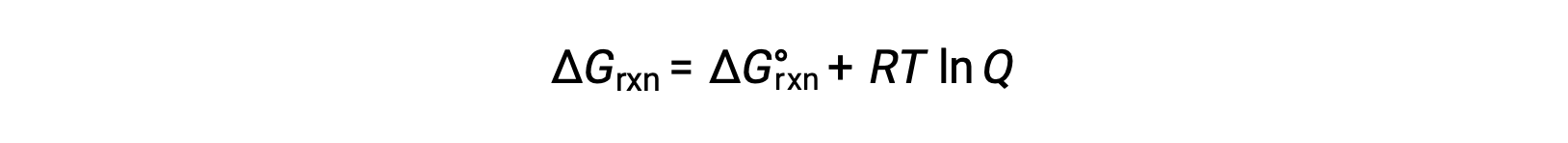
where R is the gas constant (8.314 J/K·mol), T is the absolute temperature in kelvin, and Q is the reaction quotient. This equation may be used to predict the spontaneity of a process under any given set of conditions.
Reaction Quotient (Q)
The status of a reversible reaction is conveniently assessed by evaluating its reaction quotient, Q. For a reversible reaction described by
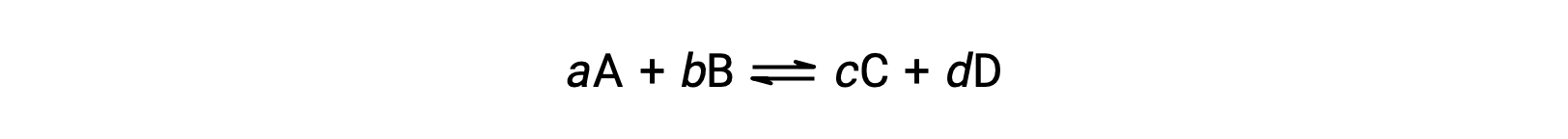
the reaction quotient is derived directly from the stoichiometry of the balanced equation as
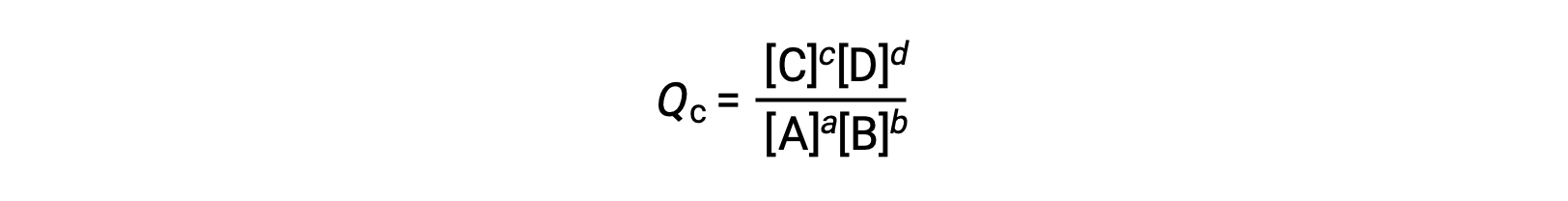
where the subscript c denotes the use of molar concentrations in the expression. The concentration-based reaction quotient, Qc, is used for condensed phase equilibria. If the reactants and products are gaseous, a reaction quotient may be similarly derived using partial pressures:
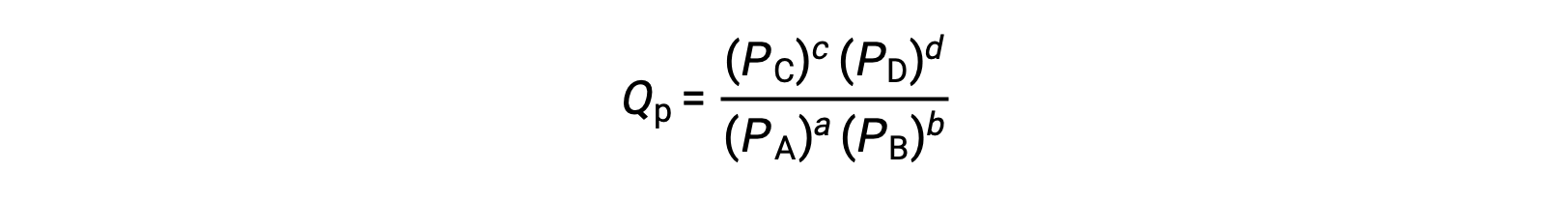
Under standard conditions, the reactant and product solution concentrations are 1 M, or the pressure of gases is 1 bar, and Q is equal to 1. Therefore, under standard conditions
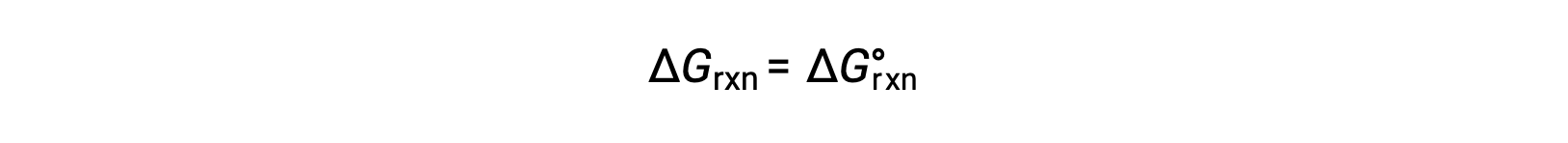
Under nonstandard conditions, Q must be calculated.
The numerical value of Q varies as a reaction proceeds towards equilibrium; therefore, it can serve as a useful indicator of the reaction’s status. To illustrate this point, consider the oxidation of sulfur dioxide:
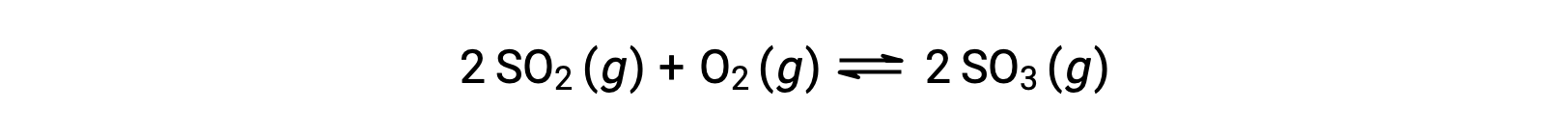
Consider two different experimental scenarios, one in which this reaction is initiated with a mixture of reactants only, SO2 and O2, and another that begins with only the product, SO3. For the reaction that begins with a mixture of reactants only, Q is initially equal to zero:
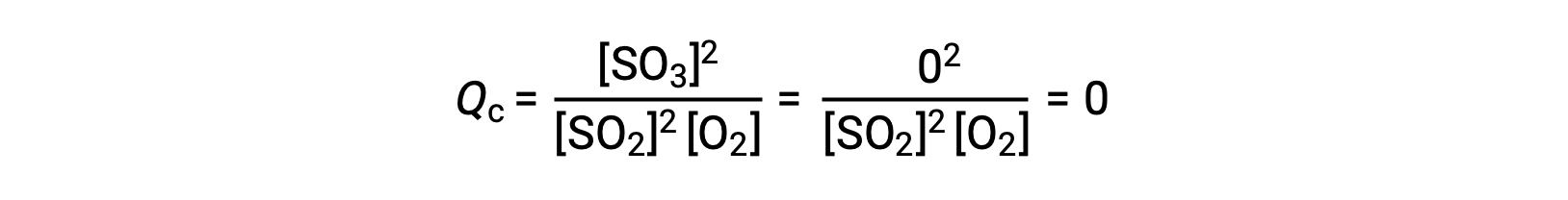
As the reaction proceeds toward equilibrium in the forward direction, reactant concentrations decrease (as does the denominator of Qc), product concentration increases (as does the numerator of Qc), and the reaction quotient consequently increases. When equilibrium is achieved, the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant, as does the value of Qc.
If the reaction begins with only the product present, the value of Qc is initially undefined (immeasurably large or infinite):
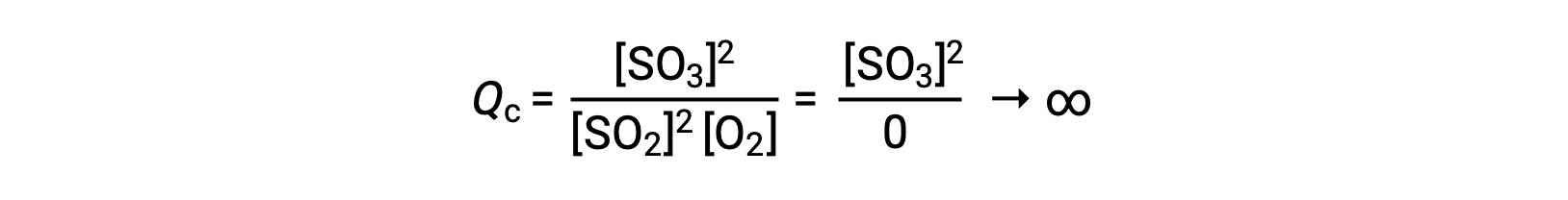
In this case, the reaction proceeds toward equilibrium in the reverse direction. The product concentration and the numerator of Qc decrease with time, the reactant concentrations and the denominator of Qc increase, and the reaction quotient consequently decreases until it becomes constant at equilibrium.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Chapter 16.4: Free Energy and Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Chapter 13.2: Equilibrium Constants.
