The pursuit of sophisticated results just got easier.
It’s part of the job. Novel results compel researchers to pursue unfamiliar, interdisciplinary experiments.
Introduction — About 5 years ago, Dr. Theresa Casey and her colleagues at Dr. Karen Plaut’s Lab at Purdue University faced a predicament.

-Dr. Theresa Casey
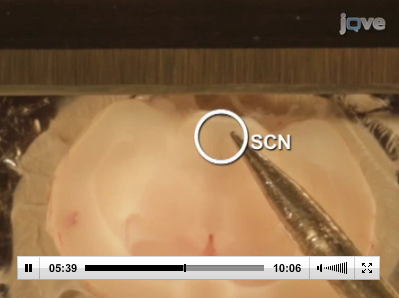
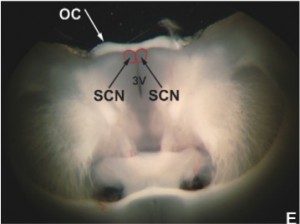
They had just made a discovery about how the circadian system plays a prominent role in the development of the mammary gland and lactation. And while their research team was prepared to begin exploring this relationship, as physiologists, Dr. Casey and her colleagues lacked the clinical neuroscience experience needed to properly study the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) — a group of cells in the hypothalamus region of the brain governing circadian rhythms like the sleep/wake and reproductive cycles — in mice.
Problem — Dr. Casey has been doing research for over 20 years, and she has seen the SCN surgery preformed before. But even so, she needed to see the procedure in order to learn it again. While Casey had a collaborator in Buffalo, NY who knew the SCN surgery her lab needed to preform, she estimated that the round-trip flight alone would cost around $500. Factoring in the cost of a hotel for a couple of days, food expenses, etc., she estimated that a decision to travel to learn the technique could cost the Plaut lab over $1,000.
Solution — So Dr. Casey and her colleagues found an alternative solution — a JoVE video demonstrating dissection of the SCN from the hypothalamus.
Referencing how much time she and her colleagues saved learning the new procedure with JoVE, she said, “It took us about three days to master what we were doing. …Once you can see how someone else does something, or see how someone does something different than you, it makes your work better.”
Results — Using JoVE allowed the Plaut lab to learn the SCN procedure they needed to continue their research.
- Time saved in forgoing travel and team-training equated to $6,300 saved in lost wages.
- $1,100 saved on travel and lodging.
- An estimated $7,700 was saved in reagents.

How has your lab used JoVE videos? Let us know in a comment below, or reach out directly via press@jove.com.