6.3:
Internal Energy
In a chemical process, the difference between the internal energies of reactants and products, represented by ΔU, is used to determine whether the system gained or lost energy during the reaction.
If ΔU is greater than zero, the final internal energy was higher than the initial internal energy and the system gained energy during the reaction.
If ΔU is less than zero, the final internal energy is lower than the initial internal energy, meaning the system lost energy.
According to the first law of thermodynamics, any change in a system’s energy must be balanced by an equal and opposite change in its surroundings.
Thus, the change in a system’s internal energy is equal to the energy transferred as heat, symbolized by “q”, plus the energy transferred as work symbolized by “w”, during the process.
In chemistry, the signs for heat and work depend on whether the system gains or loses energy.
Consider the transformation of carbon dioxide to elemental carbon and oxygen. The reactant has lower internal energy than the products, meaning ΔU is positive. Energy is transferred from the surroundings to the system increasing its internal energy.
Alternatively, during the reaction between sulfur and oxygen gas to make sulfur dioxide, energy is transferred to the surroundings. Here, the products have a lower internal energy than the reactants, and ΔU is negative.
Hence, ΔU only depends on the initial and final internal energy states of the system and the magnitude of heat and work exchanged with the surroundings.
6.3:
Internal Energy
The total of all possible kinds of energy present in a substance is called the internal energy (U), sometimes symbolized as E. Suppose a system with initial internal energy, Uinitial, undergoes a change in energy (transfer of work or heat), and the final internal energy of the system is Ufinal. Change in internal energy equals the difference between Ufinal and Uinitial.
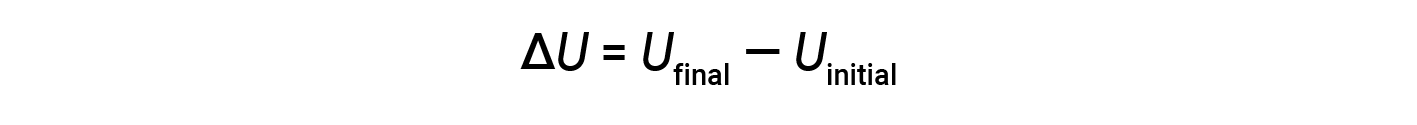
Although the values for Ufinal and Uinitial cannot be determined for a system, the first law of thermodynamics only requires the value of ΔU, which can be determined even without knowing the values of Ufinal and Uinitial. A positive value of ΔU results when Ufinal > Uinitial, and indicates that the system has gained energy from the surroundings. A negative value of ΔU is obtained when Ufinal < Uinitial, and indicates that the system has lost energy to the surroundings.
Heat (thermal energy) and work (mechanical energy) are the two different ways a system can exchange energy with its surroundings. Energy is transferred into a system when it absorbs heat (q) from the surroundings or when the surroundings do work (w) on the system.
For example, energy is transferred into room-temperature metal wire if it is immersed in hot water (the wire absorbs heat from the water), or when the wire is rapidly bent back and forth (the wire becomes warmer because of the work done on it). Both processes increase the internal energy of the wire, which is reflected in an increase in the wire’s temperature. Conversely, energy is transferred out of a system when heat is lost from the system or when the system does work on the surroundings. For example, the burning of rocket fuel releases a tremendous amount of heat and also performs work on the surroundings by applying a force over a distance (causing a space shuttle to lift off from the ground). Both processes decrease the internal energy of the system.
The relationship between internal energy, heat, and work can be represented by the equation:
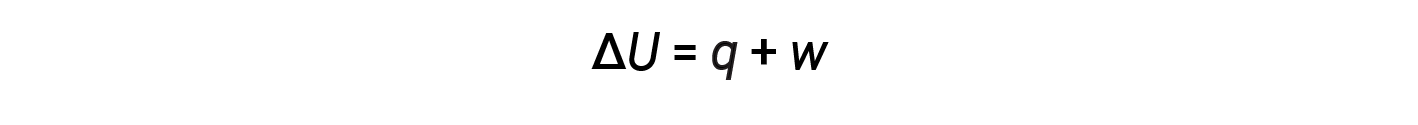
This is one version of the first law of thermodynamics, and it shows that the internal energy of a system changes through heat flow into or out of the system or work is done on or by the system. The signs for heat and work depend on whether the system gains or loses energy. Positive q is heat flow into the system from the surrounding, while negative q is heat flow out of the system. The work, w, is positive if it is done on the system and negative if it is done by the system.
When q and w are both positive (>0), ΔU is always positive (>0), and the internal energy of the system increases. When q and w are both negative (<0), ΔU is always negative (<0), and the internal energy of the system decreases. If q and w have different sign conventions, then the sign of ΔU depends on the relative magnitudes of q and w.
The SI unit of energy, heat, and work is the joule (J).
This text is adapted from OpenStax Chemistry 2e, Section 5.3: Enthalpy.
