9.1:
רדיאקטיביות ומשוואות גרעיניות
9.1:
רדיאקטיביות ומשוואות גרעיניות
Nuclear chemistry is the study of reactions that involve changes in nuclear structure. The nucleus of an atom is composed of protons and, except for hydrogen, neutrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number (Z) of the element, and the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons is the mass number (A). Atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers are isotopes of the same element.
A nuclide of an element has a specific number of protons and neutrons and is in a specific nuclear energy state. The notation for a nuclide is 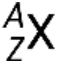 , where X is the symbol for the element, A is the mass number, and Z is the atomic number. There are also several shorthand notations for nuclides, many of which omit the atomic number. For example,
, where X is the symbol for the element, A is the mass number, and Z is the atomic number. There are also several shorthand notations for nuclides, many of which omit the atomic number. For example, 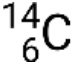 may be written carbon-14, C-14, or 14C.
may be written carbon-14, C-14, or 14C.
If the nuclide is in a temporary excited state, this is typically denoted with an asterisk. If it is in a longer-lived excited state, called a metastable state, this is denoted by adding ‘m’ to the mass number. For example, the isotope technetium-99 exists as ground-state 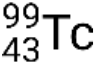 and metastable
and metastable 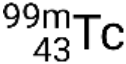 . If there is more than one metastable state for a given isotope, they are numbered in increasing energy order. For example, the isotope tantalum-180 has five nuclides: ground-state
. If there is more than one metastable state for a given isotope, they are numbered in increasing energy order. For example, the isotope tantalum-180 has five nuclides: ground-state 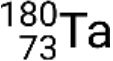 and metastable states
and metastable states 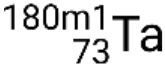 ,
, 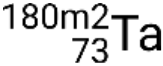 ,
,  , and
, and 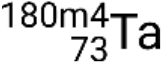 .
.
Nuclear reactions are the transformations of one or more nuclides into another, which occur via changes in the atomic numbers, mass numbers, or nuclear energy states of nuclei. To describe a nuclear reaction, we use an equation that identifies the nuclides and particles involved in the reaction. As with chemical reactions, nuclear reactions obey conservation of mass: the sum of the mass numbers of the reactants equals the sum of the mass numbers of the products.
Many different particles or photons can be involved in nuclear reactions. The most common include alpha particles (α or 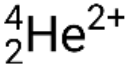 ), which are high-energy helium-4 nuclei; beta particles (β), which include electrons (e− or β−) and positrons (e+ or β+); gamma rays (γ); neutrons (
), which are high-energy helium-4 nuclei; beta particles (β), which include electrons (e− or β−) and positrons (e+ or β+); gamma rays (γ); neutrons (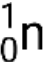 ); and protons (p+ or
); and protons (p+ or 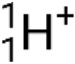 ).
).
Some nuclides remain intact indefinitely, or are stable, whereas others spontaneously transform into other nuclides, or are unstable. The spontaneous change of an unstable nuclide into another is radioactive decay. The unstable nuclide is called the parent nuclide, and the nuclide that results from the decay is known as the daughter nuclide. The daughter nuclide may be stable, or it may decay itself.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 21.1: Nuclear Structure and Stability and Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 21.2: Nuclear Equations.
Additional Sources
IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book"). Compiled by A. D. McNaught and A. Wilkinson. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford (1997). Online version (2019-) created by S. J. Chalk. https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook. Accessed 2021-01-10
International Atomic Energy Agency, Nuclear Data Section. Live Chart of Nuclides. https://www-nds.iaea.org/relnsd/vcharthtml/VChartHTML.html. Accessed 2021-01-10
