6.9:
Kalorimetrie bei konstantem Volumen
6.9:
Kalorimetrie bei konstantem Volumen
Calorimeters are useful to determine the heat released or absorbed by a chemical reaction. Coffee cup calorimeters are designed to operate at constant (atmospheric) pressure and are convenient to measure heat flow (or enthalpy change) accompanying processes that occur in solution at constant pressure. A different type of calorimeter that operates at constant volume, colloquially known as a bomb calorimeter, is used to measure the energy produced by reactions that yield large amounts of heat and gaseous products, such as combustion reactions. (The term “bomb” comes from the observation that these reactions can be vigorous enough to resemble explosions that would damage other calorimeters.)
The first law of thermodynamics suggests that the change in internal energy (ΔE) of a reaction is the sum of heat (q) and work (w).
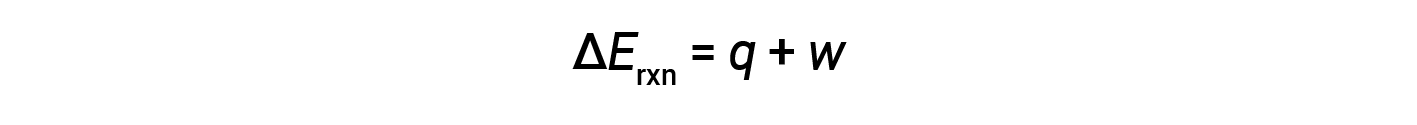
In gaseous reactions, the work done is pressure-volume type, thereby resulting in changes in the volume of the reaction.
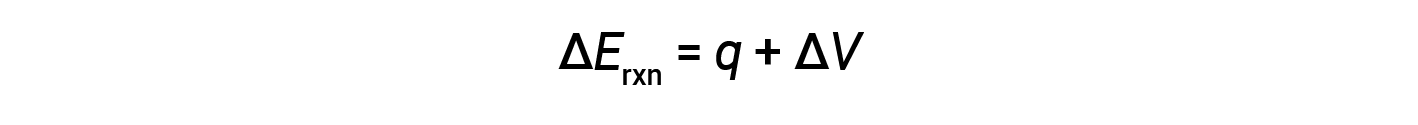
Bomb calorimeters are designed to operate at constant volume, such that the volume of the reaction is not allowed to change (ΔV = 0).
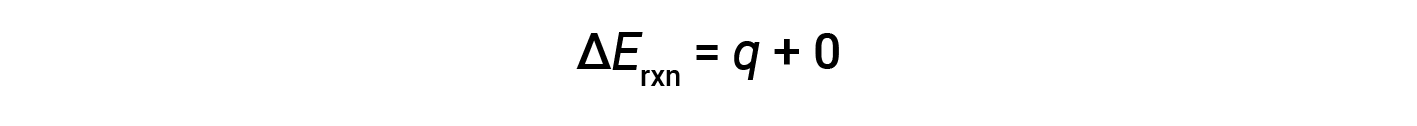
Therefore, the work done is zero, and the heat (qv) measured using a bomb calorimeter is equivalent to the change in internal energy of the reaction.
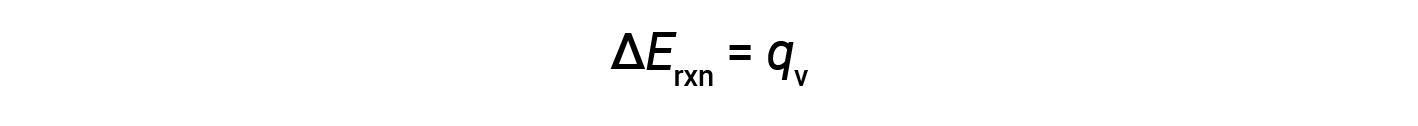
A bomb calorimeter consists of a robust steel container that contains the reactants and is itself submerged in water. The sample is placed in the bomb, which is then filled with oxygen at high pressure. A small electrical spark is used to ignite the sample. The energy produced by the reaction is absorbed by the steel bomb and the surrounding water. The temperature increase (ΔT) is measured and, along with the known heat capacity of the calorimeter (Ccal), is used to calculate the heat absorbed by the entire calorimeter assembly (qcal).
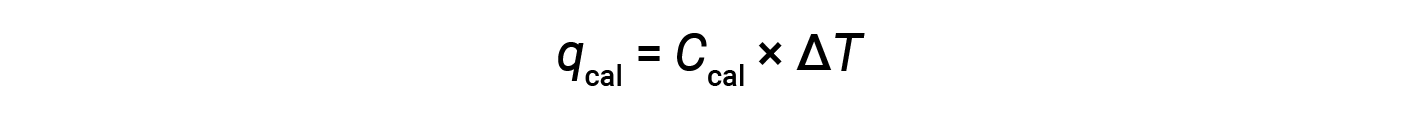
Since the calorimeter is insulated and no heat is lost to the environment, heat gained by the calorimeter equals the heat released by the reaction.
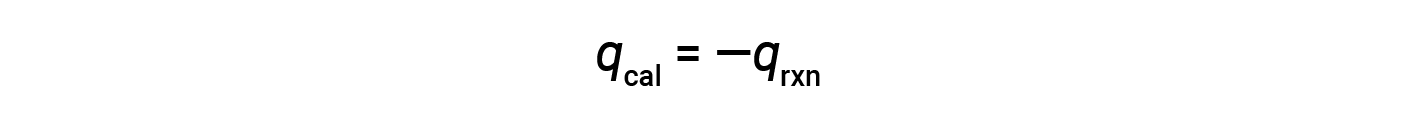
Due to constant volume conditions, the heat evolved in the reaction corresponds to the internal energy change.
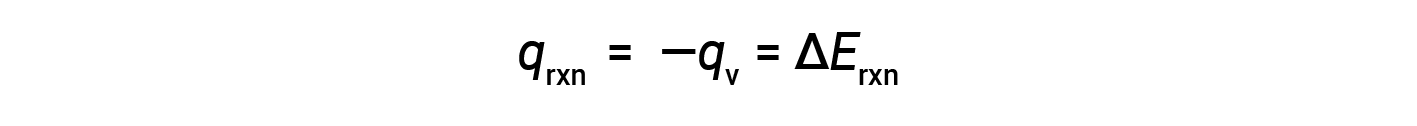
This is the internal energy change for the specific amount of reactant undergoing combustion. ΔErxn per mole of a particular reactant is obtained by dividing the value by the number of moles that actually reacted.
Bomb calorimeters require calibration to determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter and ensure accurate results. The calibration is accomplished using a reaction with a known q, such as a measured quantity of benzoic acid ignited by a spark from a nickel fuse wire that is weighed before and after the reaction. The temperature change produced by the known reaction is used to determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter. The calibration is generally performed each time before the calorimeter is used to gather research data.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 5.2: Calorimetry.
Suggested Reading
- Hornyak, Frederick M. "A flashbulb bomb calorimeter." Journal of Chemical Education 38, no. 2 (1961): 97.
- Watkins, Geo B. "Total Carbon in Coal Determined by Analysis of Gas from Bomb Calorimeter." Industrial & Engineering Chemistry 19, no. 9 (1927): 1052-1054.
- Olney, David J. "Bomb calorimeter simulation." (1990): 922.
