17.10:
אנרגיה חופשית ושיווי משקל
17.10:
אנרגיה חופשית ושיווי משקל
The free energy change for a process may be viewed as a measure of its driving force. A negative value for ΔG represents a driving force for the process in the forward direction, while a positive value represents a driving force for the process in the reverse direction. When ΔGrxn is zero, the forward and reverse driving forces are equal, and the process occurs in both directions at the same rate (the system is at equilibrium).
Recall that Q is the numerical value of the mass action expression for the system, and its value may be used to identify the direction in which a reaction will proceed in order to achieve equilibrium. When Q is lesser than the equilibrium constant, K, the reaction will proceed in the forward direction until equilibrium is reached and Q = K. Conversely, if Q > K, the process will proceed in the reverse direction until equilibrium is achieved.
The free energy change for a process taking place with reactants and products present under nonstandard conditions (pressures other than 1 bar; concentrations other than 1 M) is related to the standard free energy change according to this equation:
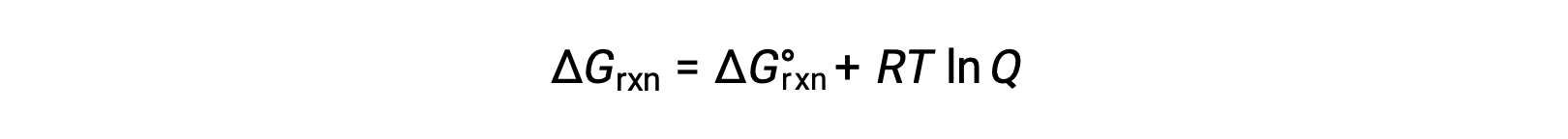
R is the gas constant (8.314 J/K mol), T is the kelvin or absolute temperature, and Q is the reaction quotient. For gas-phase equilibria, the pressure-based reaction quotient, Qp, is used. The concentration-based reaction quotient, Qc, is used for condensed phase equilibria. This equation may be used to predict the spontaneity of a process under any given set of conditions
For a system at equilibrium, Q = K and ΔGrxn = 0, and the previous equation may be written as
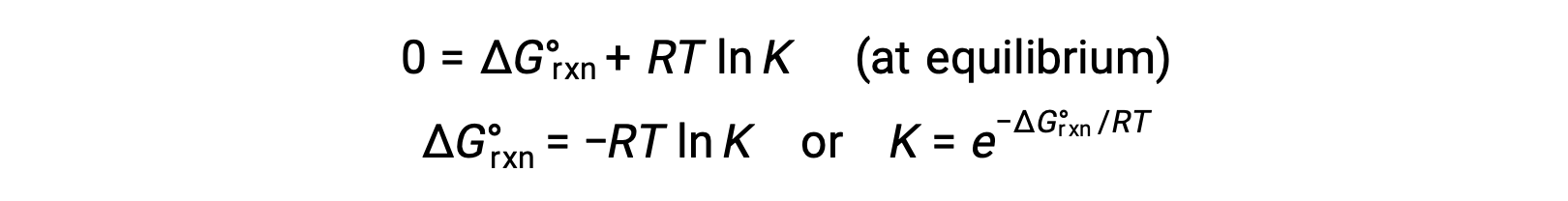
This form of the equation provides a useful link between these two essential thermodynamic properties, and it can be used to derive equilibrium constants from standard free energy changes and vice versa. The relations between standard free energy changes and equilibrium constants are summarized below.
If K > 1, ΔGºrxn < 0 and the products are more abundant in the reaction mixture.
If K < 1, ΔGºrxn > 0 and the reactants are more abundant in the reaction mixture.
K = 1, ΔGºrxn = 0 and the reactants and products are comparably abundant in the reaction mixture.
The standard free energy for a reaction change depends on temperature:
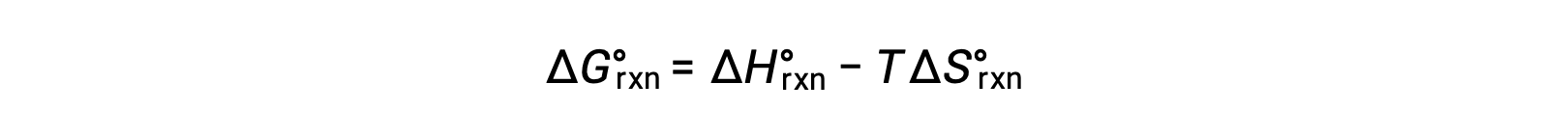
The standard free energy change for a reaction is related to the equilibrium constant for a reaction:
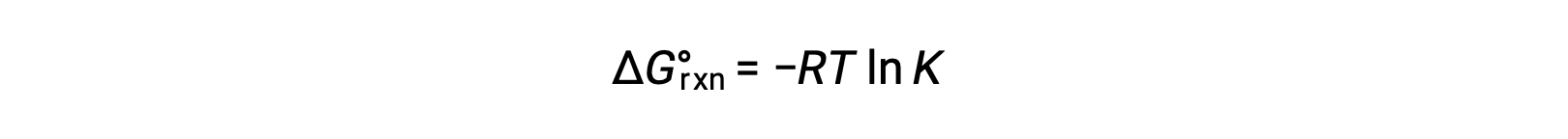
Combining the two expressions:
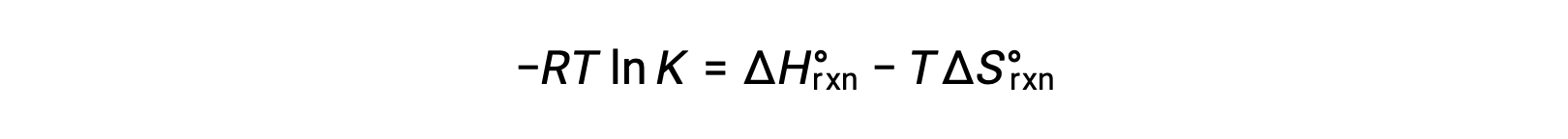
Dividing both sides by RT gives

Rearranging gives
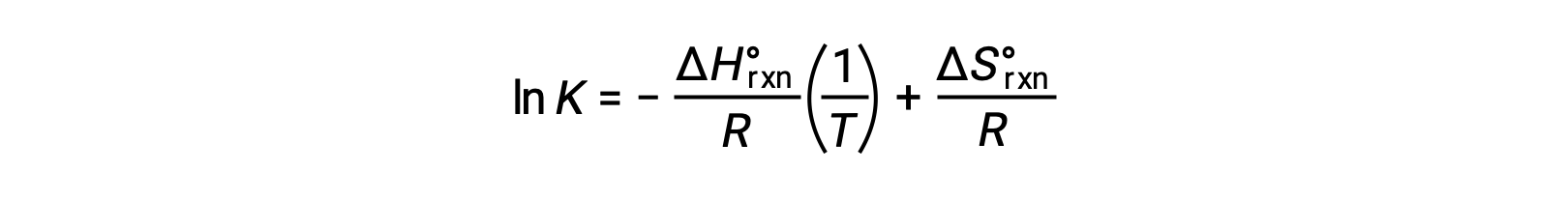
The equation takes the form of a straight line y = mx + b. A plot of ln K plotted against 1/T yields a straight line with a slope of −ΔHºrxn/R and a y-intercept of ΔSºrxn/R. The equation can also be expressed in a two-point form:
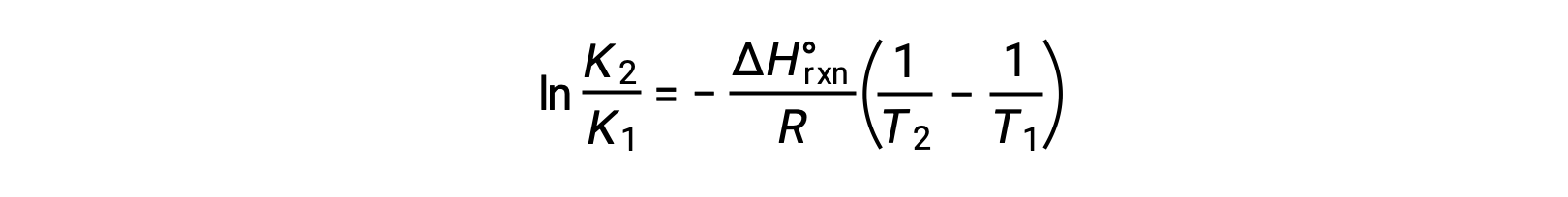
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Chapter 16.4: Free Energy.
