10.5:
Structurele Isomerie
10.5:
Structurele Isomerie
Isomerism in Complexes
Isomers are different chemical species that have the same chemical formula. Structural isomerism of coordination compounds can be divided into two subcategories, the linkage isomers and coordination-sphere isomers.
Linkage isomers occur when the coordination compound contains a ligand that can bind to the transition metal center through two different atoms. For example, the CN− ligand can bind through the carbon atom or through the nitrogen atom. Similarly, SCN− can be bound through the sulfur or nitrogen atom. A few different ligands capable of linkage isomerism are shown in Figure 1. The nomenclature of ligands capable of linkage isomerism depends on which donor atom is bonded with the metal ion. For example, a CN− ligand bound through the carbon atom is called cyano, while the same ligand bound through a nitrogen atom is called isocyano.
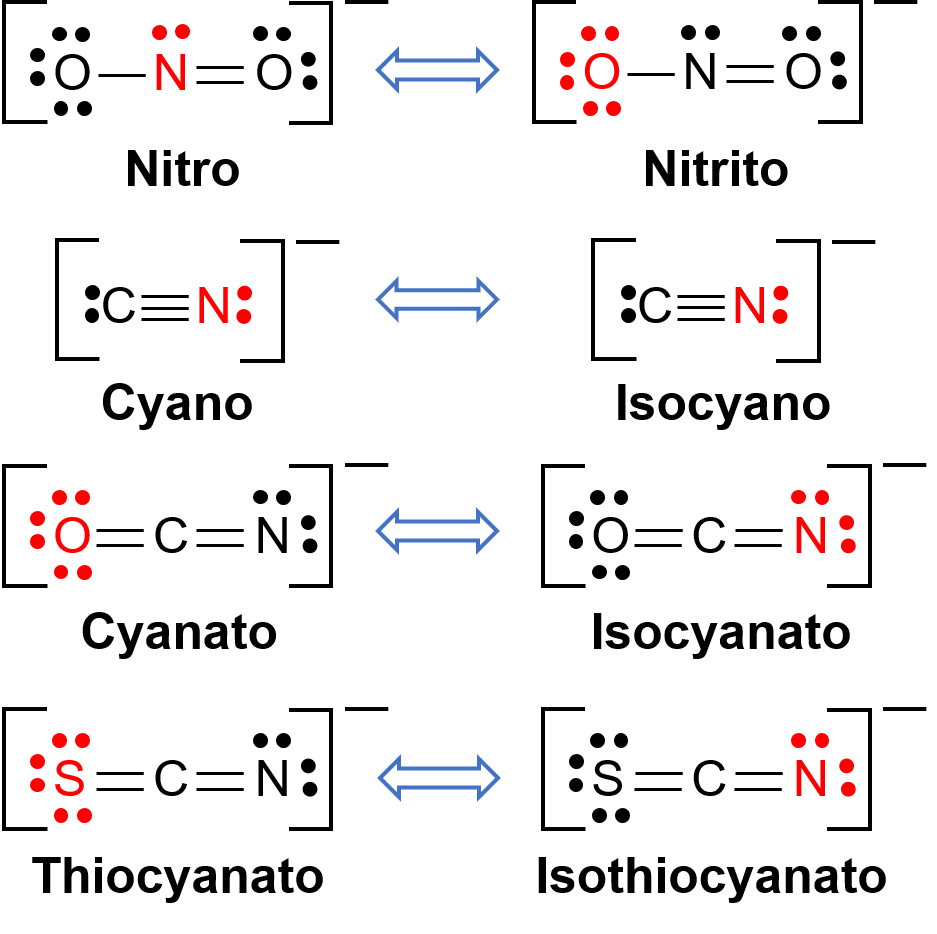
Figure 1. List of different ligands capable of linkage isomerism. In the ligand molecule, the atom in the red binds to the central metal atom.
Coordination-sphere isomers (or ionization isomers) occur when one anionic ligand in the inner coordination sphere is replaced with the counter ion from the outer coordination sphere. A simple example of two coordination-sphere isomers are [CoCl6][Br] and [CoCl5Br][Cl].
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section19.2: Coordination Chemistry of Transition Metals.
