変形性膝関節症のウサギモデルにおける推拿介入
Summary
プロトコルは膝の変形性関節症のウサギ モデルにおけるTuinaの介在のための方法を記述する。
Abstract
変形性膝関節症(KOA)は、主に膝関節の軟骨と周囲の軟部組織の変性変化を特徴としています。KOAの治療における推拿の有効性が確認されていますが、根本的なメカニズムを調査する必要があります。本研究は、科学的に実現可能なKOAウサギモデルを確立し、そのメカニズムを明らかにすることを目的としています。このために、生後6か月の正常グレードのオスのニュージーランドウサギ18匹を偽ウサギ、モデルウサギ、およびトゥイナグループにランダムに分け、各グループに6匹のウサギを配置しました。KOAモデルは、膝関節腔内に4%パパイン溶液を注入することによって確立されました。推拿群は、膝関節回転矯正法と組み合わせた推拿を4週間介入した。標準的な把持と固定のみが、偽群およびモデル群で実施されました。1週間の介入の終わりに、膝関節の可動域(ROM)が観察され、軟骨ヘマトキシリン-エオシン(HE)染色が行われました。この研究は、Tuinaが軟骨細胞のアポトーシスを阻害し、軟骨組織を修復し、膝関節ROMを回復させる可能性があることを示しています。結論として、この研究は、KOAモデルウサギに対する推拿治療の科学的実現可能性を実証し、KOAおよび同様の膝関節関連疾患の研究におけるその潜在的な応用を強調しています。
Introduction
変形性膝関節症(KOA)は、膝関節の変性疾患であり、主に膝の痛み、腫れ、変形、動きの制限によって現れ、障害率が高く、女性で有病率が高く、2019年には世界で5億2,781万人の変形性関節症患者がおり、その世界的な有病率はOAの世界の総有病率の60.6%を占めています1.臨床的には、KOAの治療は通常、非外科的治療と外科的治療に分けられます。非外科的療法には、理学療法、薬物療法、多血小板血漿注射療法などがあります2,3。推拿は、漢方薬における一般的で、安全で、信頼性が高く、効果的な治療法です。この研究では、膝関節回転矯正法と組み合わせた Tuina を使用して KOA を治療します。回転混練や圧搾法などの推拗技術は、筋肉組織のバランスを取り、痛みを軽減し、炎症因子レベルを調整し、組織の代謝を改善し、関節軟骨の変性を抑制することができます4,5。膝関節回転矯正法は、下肢の骨と関節のアライメントを調整し、膝関節のギャップを改善し、正常な力線を回復し、下肢のバイオメカニクスのバランスをとることができます6,7,8,9。レジスタンスエクササイズは、筋肉量と筋力を高め、軟骨組織の再生を促進することができます10,11。予備調査はこのTuinaのプロトコルが損傷した軟骨組織の軟骨細胞の変性そして修理の行為のより速い開始そして重要な阻止のKOAの処置の口頭グルコサミンの硫酸塩のカプセルよりかなり有効であることが分った12。KOAの治療では、推拿療法と比較して、非ステロイド性抗炎症薬は副作用と不十分な長期的有効性、比較的高い外科的リスクとコスト、および術後の問題と人工周囲合併症を伴う外科的治療のための特定の適応を必要とします13,14,15.薬物療法や手術と比較した場合、KOAの推拿治療には、副作用の軽減、リスクの低減、安全性の向上、費用対効果、効果の長期化など、いくつかの利点があります。さらに、膝関節の痛み、腫れ、飛び出し、動きの制限を効果的に緩和できます6,13,16,17。
しかし、KOAの治療のための推拿のメカニズムを明らかにする必要があり、KOAの治療プロトコルの改善と完成を制限します。そのため、KOAにおける推拿介入のメカニズムを動物実験で調べることは有効な方法である。ウサギは、ラットと比較して、従順な気質と大きな膝関節を持っています。解剖学的構造と軟骨の生化学的指標は人間のものと似ているため、Tuina18による膝関節疾患のメカニズムを研究するのに適した主題です。ウサギの膝関節腔にパパインを注射して確立したKOAモデルは、モデリング時間が短く、外傷が少なく、成功率が高く、生存率が高く、KOA19と同様の病理学的メカニズムという利点があります。本研究は、KOAにおける推拗化のための科学的に実現可能な動物実験プロトコルを確立し、推拿のメカニズムを調査することを目的としています。
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
実験プロトコルの設計は、KOAの治療における推拿のメカニズムを調査するために特に重要です。KOAモデリングは、ワイシヤンでパパイン注射によりウサギで行われました。ワイシヤンは膝蓋靭帯の外側陰窩に位置しており、見つけやすく、膝屈曲時の大腿骨と脛骨の間の関節空間が大きいため、膝関節腔への注入が容易で、周囲の組織への損傷を防ぐことができるため、KOAモデル<sup class="xref…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
この研究は、山東省伝統漢方科学技術プロジェクト(2021Q080)とQilu School of Traditional Chinese Medicine Academic School Inheritance Project[Lu-Wei-Letter (2022) 93]の支援を受けました。
Materials
| 0.9 % sodium chloride injection | Sichuan Keren Pharmaceutical Co. | Z22121903 | |
| -20°C refrigerator | Haier | BD-328WL | |
| 4 % fixative solution | Solarbio | P1110 | |
| 4°C refrigerator | Haier | SC-315DS | |
| Anhydrous ethanol | Sinopharm | ||
| Automatic tissue dewatering machine | Dakowei (Shenzhen) Medical Equipment Co. | HP30 | |
| Blast drying oven | Shanghai Yiheng Scientific Instruments Co. | DHG-9070A | |
| Coverslip | Biyuntian | FCGF50 | |
| Electric thermostat water bath | Shanghai Yiheng Scientific Instruments Co. | HWS-26 | |
| Embedding freezing table | Changzhou Paishijie Medical Equipment Co. | BM450 | |
| Embedding machine | Changzhou Paishijie Medical Equipment Co. | BM450A | |
| Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid decalcification solution | Servicebio | G1105-500ML | |
| Fluorescent inverted microscope | Leica | Leica DM IL LED | |
| Hematoxylin-eosin staining kit | Cisco Jet | EE0012 | |
| Hydrochloric acid | Laiyang Economic and Technological Development Zone Fine Chemical Plant | ||
| Medical joint goniometer | KOSLO | ||
| Neutral gum | Cisco Jet | EE0013 | |
| Normal-grade male New Zealand rabbit | Jinan Xilingjiao Breeding and Breeding Center | SCXK (Lu) 2020 0004 | |
| Papain(3000 U/mg) | Bioss | D10366 | |
| Pathological tissue bleaching and drying instrument | Changzhou Paishijie Medical Equipment Co. | PH60 | |
| Pet electric clippers | Codos | CP-3180 | |
| Rabbit fixing box | any brand | ||
| Rotating Slicer | Leica | 531CM-Y43 | |
| Tuina technique parameter determination instrument | Shanghai DuKang Instrument Equipment Co. Ltd. | ZTC-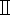 |
|
| Ventilator | TALY ELECTRIC | C32 | |
| Xylene | Fuyu Reagent |
References
- Long, H. B., et al. Prevalence trends of site-specific osteoarthritis from 1990 to 2019: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. Arthritis & Rheumatology. 74 (7), 1172-1183 (2022).
- Tschopp, M., et al. A randomized trial of intra-articular injection therapy for knee osteoarthritis. Investigative Radiology. 58 (5), 355-362 (2023).
- Buchanan, W. W., Kean, C. A., Kean, W. F., Rainsford, K. D. Osteoarthritis. Inflammopharmacology. , (2023).
- Wang, W. Y., et al. A randomized, parallel control and multicenter clinical trial of evidence-based traditional Chinese medicine massage treatment VS External Diclofenac Diethylamine Emulgel for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Trials. 23 (1), 555 (2022).
- Wang, M. N., et al. Mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in treating knee osteoarthritis. Journal of Pain Research. 13, 1421-1429 (2020).
- Katz, J. N., Arant, K. R., Loeser, R. F. Diagnosis and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: A review. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 325 (6), 568-578 (2021).
- Chang, A., et al. The relationship between toe-out angle during gait and progression of medial tibiofemoral osteoarthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 66, 1271-1275 (2007).
- Jenkyn, T. R., Hunt, M. A., Jones, I. C., Giffin, J. R., Birmingham, T. B. Toe-out gait in patients with knee osteoarthritis partially transforms external knee adduction moment into flexion moment during early stance phase of gait: a tri-planar kinetic mechanism. Journal of Biomechanics. 41 (2), 276-283 (2008).
- Brouwer, G. M., et al. Association between valgus and varus alignment and the development and progression of radiographic osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 56 (4), 1204-1211 (2007).
- Liao, C. D., et al. Effects of protein supplementation combined with resistance exercise training on walking speed recovery in older adults with knee osteoarthritis and sarcopenia. Nutrients. 15 (7), 1552 (2023).
- Thudium, C. S., et al. Cartilage tissue turnover increases with high-compared to low-intensity resistance training in patients with knee OA. Arthritis Research & Therapy. 25 (1), 22 (2023).
- Zheng, L. J., et al. Shutiao Jingjin massage can stabilize intracellular environment of rabbit chondrocytes following knee osteoarthritis-induced cartilage injury. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 27, (2023).
- Liu, K. Q., et al. Efficacy and safety of Tuina (Chinese therapeutic massage) for knee osteoarthritis: A randomized, controlled, and crossover design clinical trial. Frontiers in Medicine. 10, 997116 (2023).
- Wang, Z., et al. Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis of Acupuncture Combined with Massage in Treating Knee Osteoarthritis. BioMed Research International. 2022, 4048550 (2022).
- Li, Y. Y., et al. Therapeutic effect of acupotomy at Sanheyang for cartilage collagen damage in moderate knee osteoarthritis: a rabbit model. Journal of Inflammation Research. 16, 2241-2254 (2023).
- Guo, G. X., et al. Cerebral mechanism of Tuina analgesia in management of knee osteoarthritis using multimodal MRI: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 23 (1), 694 (2022).
- Perlman, A., et al. Efficacy and safety of massage for osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 34 (3), 379-386 (2019).
- Chen, B. J., et al. Aerobic exercise combined with glucosamine hydrochloride capsules inhibited the apoptosis of chondrocytes in rabbit knee osteoarthritis by affecting TRPV5 expression. Gene. 830, 146465 (2022).
- Rasheed, M. S., Ansari, S. F., Shahzadi, I. Formulation, characterization of glucosamine loaded transfersomes and in vivo evaluation using papain induced arthritis model. Scientific Reports. 12 (1), 19813 (2002).
- Li, Z. R. Experimental acupuncturology. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2003, 314-319 (2003).
- Hu, Y. L. Manual of practical animal acupuncture. Beijing: China Press of Agriculture. 2003, 286-298 (2014).
- Liu, J., et al. Effects of "knot-loosing" of acupotomy on motor function and morphological changes of knee joint in knee osteoarthritis rabbits. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 46 (2), 129-135 (2021).
- Li, Q., et al. The protective effects and mechanism of Ruyi Zhenbao Pill, a Tibetan medicinal compound, in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 308, 116255 (2023).
- Kwon, M., Nam, D., Kim, J. Pathological characteristics of monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. 20 (3), 435-446 (2023).
- Wang, J. G., Tang, C. L. Experimental Tuina science. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Chinese. , (2017).
- Fang, M., Song, B. L. Tuina science. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine. , (2016).
- Jin, X. Y., Yu, Y. Y., Lin, Y. Y., Yang, J. P., Chen, Z. H. Tendon-regulating and bone-setting manipulation promotes the recovery of synovial inflammation in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis via the TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway. Annals of Translational Medicine. 11 (6), 245 (2023).
- Wang, M., Liu, C., Xiao, W. Intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid for the reduction in joint adhesion formation in a rabbit model of knee injury. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy: Official Journal of the ESSKA. 22 (7), 1536-1540 (2014).
- Xu, C., et al. Bacterial cellulose membranes used as artificial substitutes for dural defection in rabbits. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 15 (6), 10855-10867 (2014).
- Leary, S., et al. AVMA guidelines for the euthanasia of animals: 2020 edition. Schaumburg: American Veterinary Medical Association. 2020, (2020).
- Amirtham, S. M., Ozbey, O., Kachroo, U., Ramasamy, B., Vinod, E. Optimization of immunohistochemical detection of collagen type II in osteochondral sections by comparing decalcification and antigen retrieval agent combinations. Clinical Anatomy. 33 (3), 343-349 (2020).
- Niazvand, F., et al. Curcumin-loaded poly lactic-co-glycolic acid nanoparticles effects on mono-iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Veterinary Research Forum: An International Quarterly Journal. 8 (2), 155-161 (2017).
- Liu, A., et al. Intra-articular injection of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells loaded with graphene oxide granular lubrication ameliorates inflammatory responses and osteoporosis of the subchondral bone in rabbits of modified papain-induced osteoarthritis. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 12, 822294 (2022).
- Hall, M. M. The accuracy and efficacy of palpation versus image-guided peripheral injections in sports medicine. Current Sports Medicine Reports. 12 (5), 296-303 (2013).
- Xing, L., et al. Traditional Chinese medicine ointment combined with Tuina therapy in treatment of pain and swelling after total knee arthroplasty. World Journal of Orthopedics. 13 (10), 932-939 (2022).
- Xu, H., et al. The effectiveness of Tuina in relieving pain, negative emotions, and disability in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Pain Medicine. 24 (3), 244-257 (2023).
- Ding, N., et al. Mast cells are important regulator of acupoint sensitization via the secretion of tryptase, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and histamine. The Public Library of Science One. 13 (3), e0194022 (2018).
- Cai, F. H., Li, F. L., Zhang, Y. C., Li, P. Q., Xiao, B. Research on electroacupuncture parameters for knee osteoarthritis based on data mining. European Journal of Medical Research. 27 (1), 162 (2022).
- Mei, Z. G., Cheng, C. G., Zheng, J. F. Observations on curative effect of high-frequency electric sparkle and point-injection therapy on knee osteoarthritis. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 31 (4), 311-315 (2011).
- Xiao, G., et al. Effect of manipulation on cartilage in rats with knee osteoarthritis based on the Rho-associated protein kinase/LIM kinase 1/Cofilin signaling pathways. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 42 (2), 194-199 (2022).
- Wu, M. X., et al. Clinical study on the treatment of knee osteoarthritis of Shen-Sui insufficiency syndrome type by electroacupuncture. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine. 16 (4), 291-297 (2010).
- Richards, R. E., Andersen, M. S., Harlaar, J., van den Noort, J. C. Relationship between knee joint contact forces and external knee joint moments in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis: effects of gait modifications. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 26 (9), 1203-1214 (2018).
- Shull, P. B., et al. Toe-in gait reduces the first peak knee adduction moment in patients with medial compartment knee osteoarthritis. Journal of Biomechanics. 46 (1), 122-128 (2013).
- Adouni, M., Shirazi-Adl, A. Partitioning of knee joint internal forces in gait is dictated by the knee adduction angle and not by the knee adduction moment. Journal of Biomechanics. 47 (7), 1696-1703 (2014).
- Kutzner, I., Trepczynski, A., Heller, M. O., Bergmann, G. Knee adduction moment and medial contact force–facts about their correlation during gait. The Public Library of Science One. 8 (12), e81036 (2013).
- Camacho-Cardenosa, A., et al. Resistance circuit training combined with hypoxia stimulates bone system of older adults: a randomized trial. Experimental Gerontology. 169, 111983 (2022).
- Babur, M. N., Siddiqi, F. A., Tassadaq, N., Arshad Tareen, M. A., Osama, M. Effects of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate supplementation in addition to resistance exercise training and manual therapy in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association. 72 (7), 1272-1277 (2022).
- Wang, H. N., et al. Effect of low-load resistance training with different degrees of blood flow restriction in patients with knee osteoarthritis: study protocol for a randomized trial. Trials. 23 (1), 6 (2022).
- Cheon, Y. H., et al. Relationship between decreased lower extremity muscle mass and knee pain severity in both the general population and patients with knee osteoarthritis: Findings from the KNHANES V 1-2. The Public Library of Science One. 12 (3), e0173036 (2017).
- Murton, A. J., Greenhaff, P. L. Resistance exercise and the mechanisms of muscle mass regulation in humans: acute effects on muscle protein turnover and the gaps in our understanding of chronic resistance exercise training adaptation. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 45 (10), 2209-2214 (2013).

