19.2: Types of Radioactivity
The most common types of radioactivity are α decay, β decay, γ decay, neutron emission, and electron capture.
Alpha (α) decay is the emission of an α particle from the nucleus. For example, polonium-210 undergoes α decay:
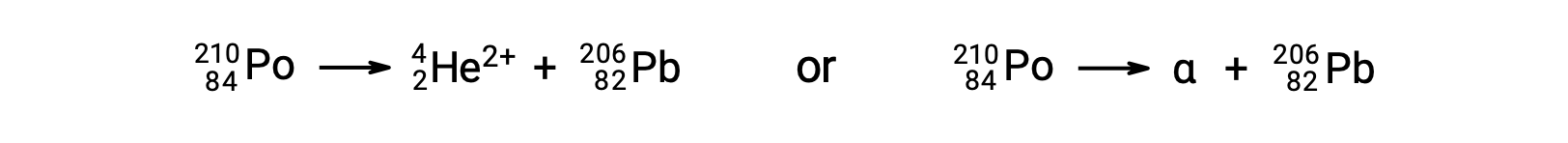
Alpha decay occurs primarily in heavy nuclei (A > 200, Z > 83). Loss of an α particle gives a daughter nuclide with a mass number four units smaller and an atomic number two units smaller than those of the parent nuclide.
Beta (β) decay is the emission of an electron or positron from a nucleus. Iodine-131 is an example of a nuclide that undergoes β− decay:
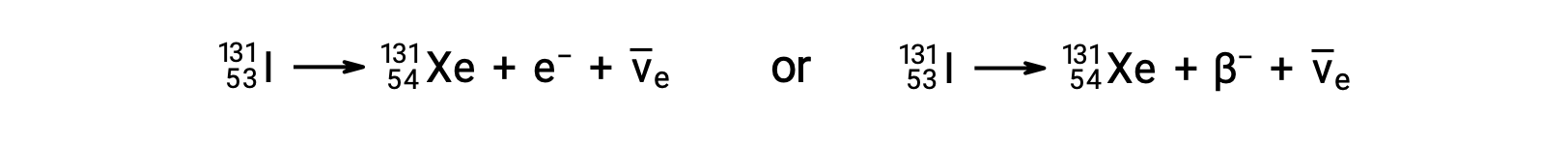
The electron emitted is from the atomic nucleus and is not one of the electrons surrounding the nucleus. Emission of an electron does not change the mass number of the nuclide but does increase the number of its protons and decrease the number of its neutrons. An antineutrino (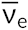 ) is also emitted owing to conservation of energy.
) is also emitted owing to conservation of energy.
Oxygen-15 is an example of a nuclide that undergoes positron emission, or β+ decay:
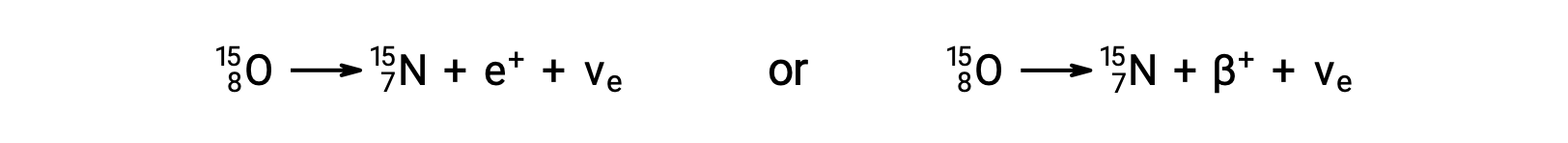
Positron decay is the conversion of a proton into a neutron with the emission of a positron. A neutrino (νe) is also emitted owing to conservation of energy.
Gamma emission (γ emission) is observed when a nuclide is formed in an excited state and then decays to its ground state with the emission of a γ ray, a quantum of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. The presence of a nucleus in an excited state is often indicated by an asterisk (*). Cobalt-60 emits γ radiation and is used in many applications, including cancer treatment:

There is no change in mass number or atomic number during the emission of a γ ray. However, γ emission may accompany one of the other modes of decay that would result in a change in mass number or atomic number.
Neutron emission is the ejection of a neutron from the nucleus. It can happen spontaneously, like the decay of beryllium-13 to beryllium-12, or in response to bombardment by gamma rays or particles. The atomic number remains unchanged during this process, whereas the mass number decreases by 1.
Electron capture occurs when one of the inner electrons in an atom is captured by the atom’s nucleus. For example, potassium-40 undergoes electron capture:
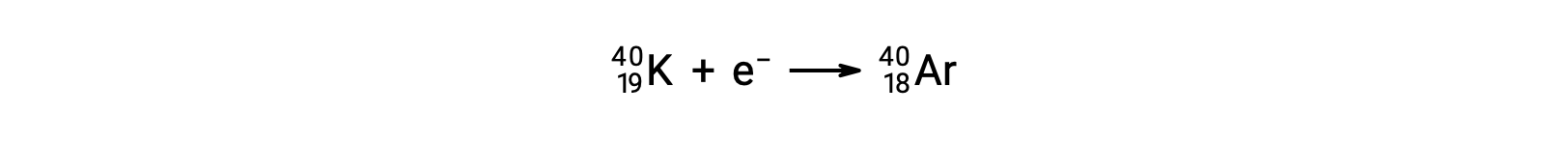
Electron capture occurs when an inner-shell electron combines with a proton and is converted into a neutron. The loss of an inner-shell electron leaves a vacancy that will be filled by one of the outer electrons. As the outer electron drops into the vacancy, it will emit energy. In most cases, the energy emitted will be in the form of an X-ray. Electron capture has the same effect on the nucleus as positron emission does: the atomic number is decreased by one and the mass number does not change.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 21.3: Radioactive Decay.


