A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
JoVE Journal
Medicine
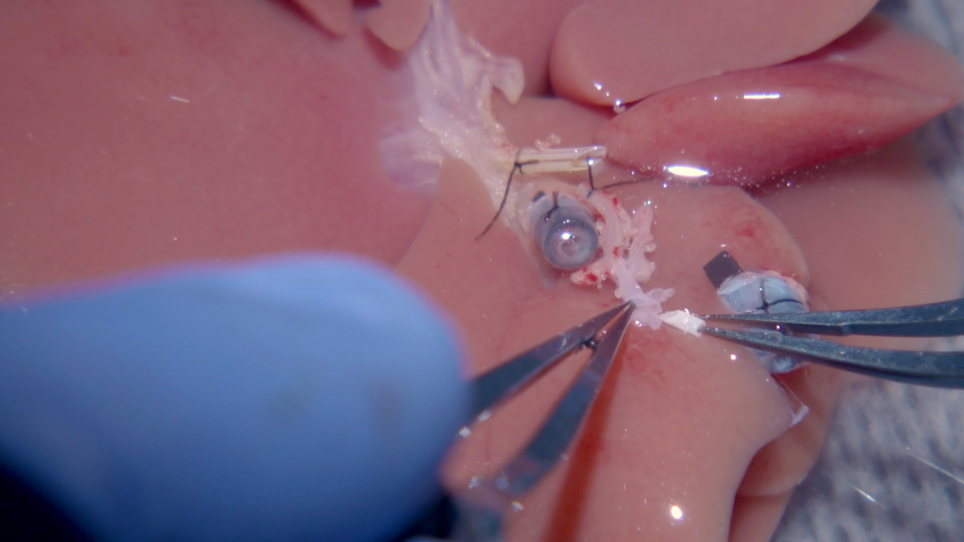
A Rat Model of Orthotopic Liver Transplantation Using a Novel Magnetic Anastomosis Technique for Suprahepatic Vena Cava Reconstruction
1Shaanxi Provincial Center for Regenerative Medicine and Surgical Engineering,First Affiliated Hospital, Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2Institute of Advanced Surgical Technology and Engineering,First Affiliated Hospital, Xi’an Jiaotong University, 3Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery,First Affiliated Hospital, Xi’an Jiaotong University, 4Organ Transplantation Center,Tianjin First Center Hospital
Chapters
- 00:00Title
- 00:37Donor Operation
- 05:17Graft Preparation
- 08:01Recipient Operation
- 13:50Results: The SHVC Anastomosis by the Magentic Rings and Survival of Recipient Rats
- 14:07Conclusion
Suprahepatic vena kava (SHVC) yeniden inşası sıçan orthotopic karaciğer nakli zor bir adım kalır. Bu makalede, bir roman manyetik anastomoz tekniği kullanarak Sıçanlarda SHVC yeniden inşası için adım adım bir protokol gösteriyoruz.