18.4:
Standard Electrode Potentials
Consider two containers having different fluid levels. When connected, the liquid flows from the higher to the lower level. By measuring the individual fluid levels, the flow direction can be predicted.
Comparatively, in a galvanic cell, knowing individual electrode potentials helps predict the oxidant, reductant, and flow of electrons. Here, each half-cell has its corresponding electrode potential. However, the individual electrode potential cannot be measured directly but only the potential difference between the two half-cells. So how is it calculated?
To determine individual electrode potentials, one electrode is assigned a potential of zero, and the other electrode’s potentials are measured relative to it.
The electrode with a potential of zero is the hydrogen electrode under standard-state conditions, also called the standard hydrogen electrode, or SHE. The SHE is operated at 25 °C, consisting of an inert platinum electrode partially submerged in 1 molar hydrochloric acid and exposed to a stream of hydrogen gas at 1 atmosphere.
When a zinc electrode is connected to the SHE, its mass reduces, indicating its oxidation to Zn2+ ions. Simultaneous increased production of hydrogen gas signifies a reduction of hydrogen ions.
Thus, zinc is the anode, and SHE the cathode. Zinc’s standard electrode potential of −0.76 V indicates a greater oxidative potential than the SHE.
However, when a copper electrode is connected to the SHE, its mass increases as Cu2+ is reduced to copper. Hence, copper is the cathode, and SHE the anode. Copper’s standard reduction potential of +0.34 V indicates a greater reductive potential than the SHE.
Standard electrode potentials provide a measure of oxidations or reductions to occur—the more positive, the greater the tendency for a reduction under standard conditions.
A redox reaction’s direction and spontaneity are determined by examining the individual standard electrode potentials.
A positive summation of the electrode potentials implies a spontaneous reaction. Thus, for a copper-zinc galvanic cell with zinc as the anode and copper as the cathode and a cell potential of +1.10 V, both half-cell reactions occur spontaneously in the forward direction.
Lastly, the standard electrode potential is an intrinsic property and unaffected by any change in the half-reaction stoichiometry.
18.4:
Standard Electrode Potentials
On comparing the reactivity of silver and lead, it is observed that the two ionic species, Ag+ (aq) and Pb2+ (aq), show a difference in their redox reactivity towards copper: the silver ion undergoes spontaneous reduction, while the lead ion does not. This relative redox activity can be easily quantified in electrochemical cells by a property called cell potential. This property is commonly known as cell voltage in electrochemistry, and it is a measure of the energy which accompanies the charge transfer. Potentials are measured using the SI unit Volts, defined as one joule of energy per one coulomb of charge. Thus,
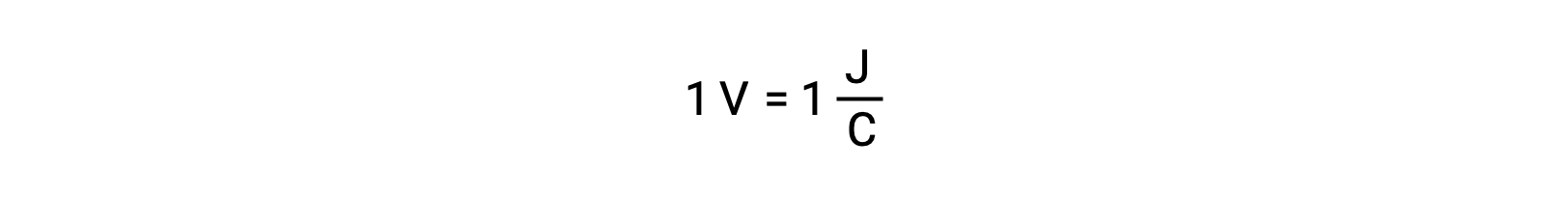
Standard Electrode Potential
When measured for electrochemical purposes, the cell potential is a measure of the driving force for a specific type of charge transfer processes, namely, the electron transfer between reactants. The potential of a single electrode or a single half-cell cannot be measured as electron transfer requires a donor and recipient or a reductant and an oxidant, respectively. Instead, a half-cell potential can only be measured relative to another half-cell. Thus, it is only possible to measure the difference in potential between two half-cells, Ecell, which is defined as

where Ecathode and Eanode represent the potentials of two different half-cells functioning as cathode and anode, respectively. The standard cell potential, E°cell, is the cell potential measured at standard-state conditions of both half-cells ( i.e., 1 M concentrations, 1 bar pressures, 298 K)

To easily calculate half-reaction potentials, the scientific community has designated one particular half-cell to serve as a universal reference for all cell potential measurements, with a potential of 0 V. This half-cell is known as the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE), and it is based on the half-reaction below:
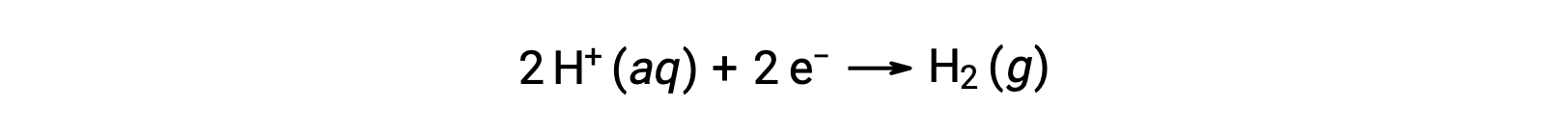
Typically, SHE consists of an inert platinum electrode which is immersed in 1 M aqueous H+, with a stream of bubbling H2 gas at 1 bar pressure, maintained at a uniform temperature of 298 K. The electrode potential (EX) for a half-cell X is thus defined as the potential measured for a cell X, which acts as a cathode, while the SHE acts as an anode.
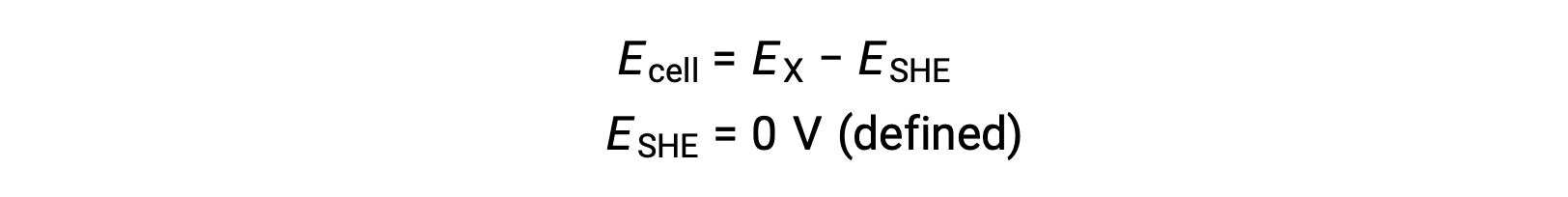
Therefore,
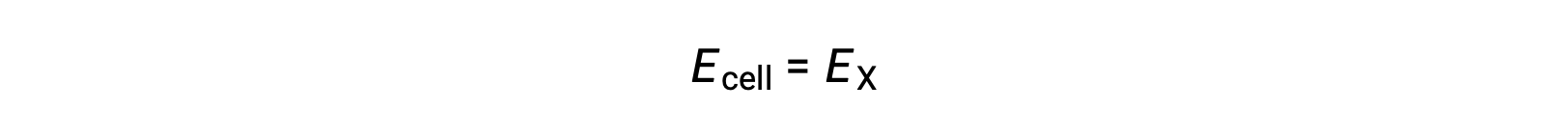
Under standard-state conditions, the potential of the half-cell X is equal to the standard electrode potential, E°X. As the definition of cell potential requires the half-cells to function as cathodes, these potentials are also called standard reduction potentials.
Prediction of Spontaneity and the Direction of a Redox Reaction
The cell and electrode potentials dictate the spontaneity of redox reactions. It is observed that the spontaneous reactions show a positive cell potential, while the nonspontaneous process shows a negative cell potential. If the summation of the electrode potentials is positive, the reaction is said to be spontaneous. Half-cell reactions having positive electrode potential occur in the forward direction, while those with values lesser than the hydrogen electrode usually occur in the reverse order.
A stronger oxidant exhibits greater standard electrode potential, E°. As electrode potentials measure reduction capacity, an increased E° corresponds to an increased driving force behind the reduction of the species and better oxidizing abilities. Thus, E°cell is positive when E°cathode > E°anode.
Considering this, it explains why copper is oxidized by silver, but not by lead:
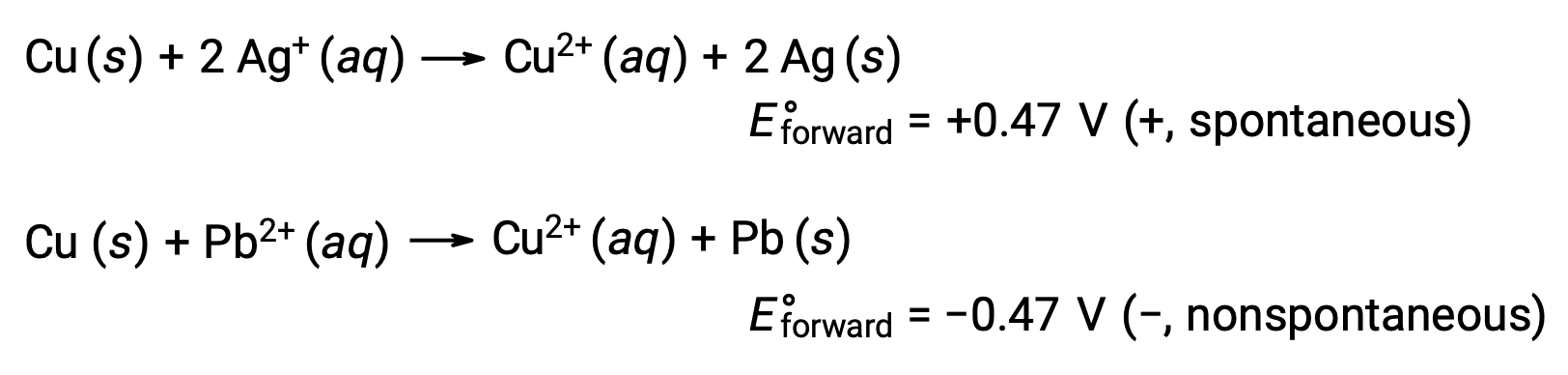
Prediction of Dissolution of Metal in Mineral Acids
One of the essential applications of the half-cell potentials is understanding whether a particular metal will dissolve in mineral acid. Most acids like hydrochloric acid dissolve metals by the reduction of protons to hydrogen gas and oxidation of metals to their respective ions. In the case of zinc reacting with hydrochloric acid, the reaction is spontaneous as the standard electrode potential of zinc is lower than that of hydrogen. However, copper does not react with hydrochloric acid on account of its higher electrode potential.
This text is adapted from OpenStax, Chemistry 2e, Section 17.3: Electrode and Cell Potentials.
