פלזמה מהירה ובידוד של מרכיבי דם שלמים בדגימות שהתקבלה מהגדרה מבוססת-קהילה
Summary
We outline a methodology for the processing of whole blood to obtain a variety of components for further analysis. We have optimized a streamlined protocol that enables rapid, high-throughput simultaneous processing of whole blood samples in a non-clinical setting.
Abstract
איסוף ועיבוד של דגימות דם כל בהגדרה הלא-קלינית מציע הזדמנות ייחודית כדי להעריך אנשים המתגוררים בקהילה עם או בלי תנאי preexisting. עיבוד מהיר של דגימות אלה הוא חיוני כדי למנוע השפלה של רכיבים סלולריים מפתח. כלולות כאן הם שיטות לתא בו זמנית היקפי mononuclear הדם (PBMC), DNA, RNA ובידוד בסרום מתיקו דם יחיד שבוצע בבתיהם של משתתפים בהסכמה ברחבי מטרופולין, עם עיבוד יזמו בתוך 2 שעות של אוסף. יש לנו בשימוש בטכניקות אלה לעבד מעל 1,600 דגימות דם חומר מניב עקבי, באיכות גבוהה, אשר לאחר מכן נעשה שימוש במתילציה DNA, genotyping, ביטוי גנים מוצלח וcytometry זרימת מנתח. חלק מהשיטות המועסקות הם סטנדרטיים; עם זאת, בשילוב באופן המתואר, הם מאפשרים עיבוד יעיל של דגימות ממשתתפי population- ו / ולקהילה,מחקרים מבוססים שבדרך כלל לא ניתן להעריך בסביבה קלינית. לכן, יש פרוטוקול זה הפוטנציאל להשיג דגימות (ובהמשך נתונים), כי הם יותר מייצג של האוכלוסייה הכללית.
Introduction
מחקרים רבים אפיינו הבדלים בביטוי גנים, מתילציה DNA ותת-קבוצה של תאים בדם בקרב אנשים עם ובלי נפש (או אחר) המחלות 1-4. מחקרים אלה, לעומת זאת, התקבלו מהגדרות קליניות שבו ההבדלים הקשורים מחלה עלולים להיות מוגדלים בשל האופי בדרך כלל חמור יותר של המחלות שחולים מחפשים טיפול. בשל התקדמות ב" ה"אומיקה "גישות, בעשור האחרון ראה התפוצצות של עניין בקבלת דגימות ביולוגיות מהקהילה ו / או הגדרות אפידמיולוגיים 5-7, על מנת לספק הערכות מבוססות-אוכלוסייה של שכיחות מחלה ותמונה רחבה יותר של גורמים סביבתיים של מחלות נפש ו / או פיזיות אלה.
אתגר מרכזי בהקשר זה הוא הדרישה לעיבוד מהיר של הדגימות שנאספו. השפלה של תאי mononuclear, רכיבי מערכת חיסון מפתח שfrequently משמש כדי להעריך את בריאותו של אדם, מתחילה מייד עם תיקו דם עם ירידה משמעותית בהתאוששות לאחר שעה 2 של אוסף 8-10. כדי להתמודד עם אתגר זה, אנו מציגים פרוטוקול מותאם שברכיבים מרובים של כל דם האנושי מבודדים זמנית מדגימות שהתקבלו בבתיהם של נושאים המתגוררים באזור מטרופולין גדול. הפרוטוקול מבוסס על האוסף והשינוי של טכניקות הנוכחיות, כוללים אחסון של כל השברים "תוספת" במקרה טכניקות עתיד לאפשר לבידוד נוסף שלנו / מנתח. בעוד שיטות או ערכות חלופיות עשויות להיות מועסקות במקום של השיטות בודדות שתוארו כאן, התוו אלה הוכיחו להיות אמצעי אמין ויעיל לעיבוד דגימות באופן תפוקה גבוהה. שברים באיכות גבוהה (PBMCs, DNA, סרום, ו- RNA) של דם טרי יכול להיות מיוצרים בשעה 2 של אוסף וכל דגימות assay-מוכן יכול להיות זמין בתוך 2 ימים (איור 1).
פרוטוקול זה פותח כדי לאפשר העיבוד יעיל של דגימות שנאספו מהקהילה-מגורים, התושבים בוגרים של העיר דטרויט לבדיקה במחקר בריאות שכונת דטרויט (DNHS; DA022720, RC1MH088283, DA022720-05-S1), המבוסס אוכלוסייה- מחקר של הגורמים החברתיים והביולוגיים של הפרעת דחק פוסט טראומטית (PTSD) ומחלות נפש אחרות. השכיחות של PTSD בדטרויט היא יותר מכפול מהממוצע הארצי 11,12. זיהוי גורמים ביולוגיים של PTSD באוכלוסייה זו עשויה לעזור לפתח תרופתי מתאימה ו / או התערבויות קוגניטיביות-התנהגותיות לסייע לאלו הסובלים מההפרעה, הן באוכלוסייה עירונית זה, ובאוכלוסיות בסיכון גבוה אחרים (למשל, חוזר יוצאי צבא). המעבדה שלנו, הממוקמת בעבר באוניברסיטה ויין סטייט בדטרויט, מישיגן, נבחרה לעיבוד המבוסס על המומחיות שלנו בטיפול בדגימות רקמה טריות המיוצרות ממגווןמקורות, את ההכרח להתחיל עיבוד הדגימות בתוך שעה 2 של אוסף, והקרבה שלנו לאתרי האיסוף. עם הזדמנות ייחודית זו ביד, המטרה שלנו הייתה כדי לייעל את העיבוד לתשואה הגדולה ביותר של ה- DNA, RNA, סרום ותאי הדם היקפיים mononuclear (PBMCs) מכל דגימה (כוללת של N = 1,639 דגימות מעל 5 גלים של אוסף דגימה). הנהלים שתוארו כאן ניתן לבצע בו זמנית בסביבה הלא-קלינית, ובכך לייצר חומר מוצא (ראה טבלה 1 לתשואות ממוצעת) עבור מספר רב של יישומים במורד הזרם כוללים microarray, אפיגנטיים, בזמן אמת RT-PCR, וcytometry זרימת מנתח.
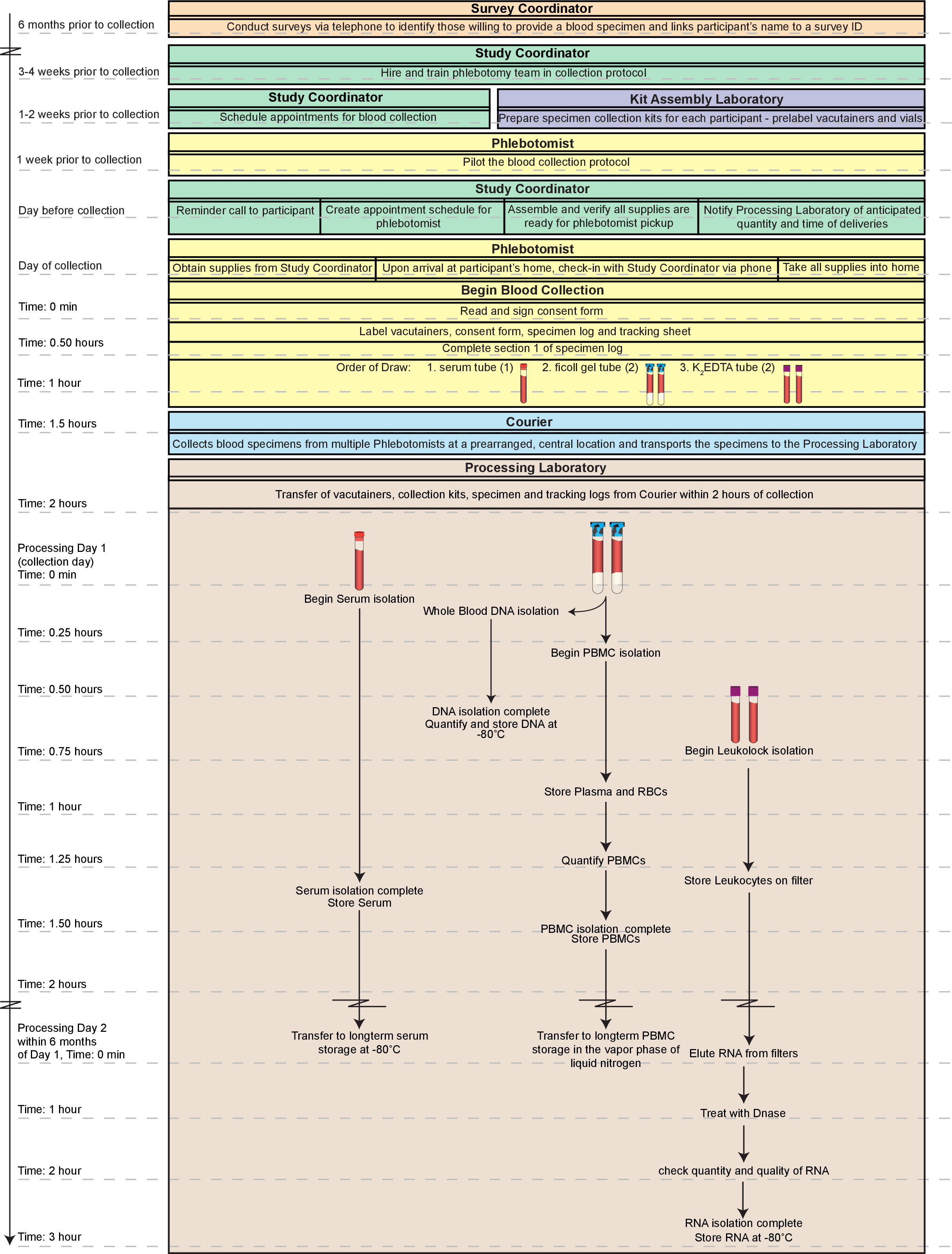
איור 1. זרימת עבודה בסך הכל. התהליך הכולל המתואר כאן כוללת את הלוגיסטיקה של קבלת דגימות דם מזיהוי לגבי השתתפות הסכמהipants לדם לצייר את עצמו. באיכות גבוהה, שברים (תאי דם היקפי mononuclear; PBMCs, DNA, סרום, ו- RNA) של כל דם טרי יכולה להיות מיוצרים בשעה 2 של אוסף וכל דגימות assay-מוכן יכולות להיות זמינות בתוך 2 ימים. יתר על כן, שברים שהוכנו באמצעות שיטה זו מתאימים לאחסון לטווח ארוך, אם דגימות אינן להיבדק מייד. ציר הזמן כולו המתוארים כאן יכול להסתיים ביום אחד (~ 5 סך הכל שעות). עם זאת, ביום כזה יהיה מאוד עבודה אינטנסיבית במיוחד עבור טכנאי יחיד עם ניסיון רב עם הטכניקות. לפיכך, אנו ממליצים לחלק את ההליכים ביום 1 בין לפחות שני טכנאים והשלמת עיבוד RNA ביום 2. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
יש לנו תיארנו פרוטוקול יעיל שיושם בהצלחה לעבד יותר מ -1,600 דגימות דם כל במחקר בריאות דטרויט השכונה. למרות שרבים מטכניקות אלה זמינים בספרות הקיימת, האוסף שלנו צעד-אחר-צעד, כוללים שינויים בעיתוי מדויק בין כל שלב, משקף פרוטוקול מותאם, יעיל שמייצר בהצלחה מגוון רחב של דגימות…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Henriette Mair-Meijers for invaluable attention to detail and hours devoted to processing the blood collections. We are grateful for the graphic design expertise of Natalie Jameson Kiesling. We also appreciate the approval of the manufacturers (Qiagen (Valencia, CA), BD Biosciences (San Jose, CA), Life Technologies (Grand Island, NY)) mentioned herein to publish the use of their products as described. Funding for this work was generously provided by the National Institutes of Health award numbers DA022720, RC1MH088283, and DA022720-05-S1.
Materials
| QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit | Qiagen | 51104 | Day 1: DNA isolation |
| Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) | Sigma | P5493-1L | Day 1: PBMC isolation |
| 5 ¾” Pasteur pipets | Fisher | 13-678-6A | Day 1: PBMC isolation |
| Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS), heat inactivated | Life Technologies | 10082147 | Day 1: PBMC isolation |
| Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) | Sigma | D8418-500ml | Day 1: PBMC isolation |
| RPMI Medium 1640, liquid | Invitrogen | 11875119 | Day 1: PBMC isolation |
| 0.4% trypan blue stain | Invitrogen | T10282 | Day 1: PBMC isolation |
| Countess Cell Counting Chamber | Invitrogen | C10283 | Day 1: PBMC isolation |
| Countess Automated Cell Counter or cell counting device such as a microscope and hemocytometer | Invitrogen | C10281 | Day 1: PBMC isolation |
| LeukoLOCK Fractionation & Stabilization Kit | Ambion | 1933 | Day 1: Leukocyte RNA isolation |
| 25G x 5/8 in. needles | Becton Dickinson | 305122 | Day 1: Leukocyte RNA isolation |
| Syringes (5ml) | Becton Dickinson | 309646 | Days 1 and 2: Leukocyte RNA isolation |
| Denaturing Lysis Solution | Ambion | 8540G | Day 2: Leukocyte RNA isolation |
| 5M NaCl | Life Technologies | 24740011 | Day 2: Leukocyte RNA isolation |
| TRI Reagent | Ambion | 9738 | Day 2: Leukocyte RNA isolation |
| Bromo-3-chloro-propane (BCP) | Sigma | B-9673 | Day 2: Leukocyte RNA isolation |
| spin cartridges | Ambion | 10051G | Day 2: Leukocyte RNA isolation |
| 0.1mM EDTA | Ambion | 9912 | Day 2: Leukocyte RNA isolation |
| DNA-free Kit | Ambion | AM1960 | Day 2: DNase treament |
| RNA 6000 Ladder | Agilent | 5067-1529 | Day 2: Bioanalyzer analysis |
| RNA 6000 Nano Series II Kit | Agilent | 5067-1511 | Day 2: Bioanalyzer analysis |
| RNaseZAP | Ambion | AM8782 | Day 2: Bioanalyzer analysis |
| Ethanol >99% | Sigma | E7023-500ml | |
| Isopropanol >99% | Sigma | I9516-500ml | |
| Nuclease-free ultra pure water | Invitrogen | 9938 | |
| Pipette tips (nuclease-free) | Eppendorf | 22491253 | |
| Pipetter (serological) | Eppendorf | 2223020-4 | |
| Pipetters (for volumes under 1ml) | Eppendorf | 3120000-054 | |
| Pipettes (serological) | Fisher | 13-678-27E | |
| Controlled rate freezing containers | Nalgene | 5100-0001 | |
| Cryoboxes (to hold 2ml and 5ml cryovials and 1.5ml microcentrifuge tubes) | Fisher | 03-395-464 | |
| Test tube rack | Thermo Scientific | 14-804-134 | |
| 15ml polypropylene tubes | Fisher | 14-959-49D | |
| 1.5ml and 0.65 microcentrifuge tubes | Fisher | 07-200-534 and 07-200-185 | |
| 2ml and 5ml cryovials | Fisher | 10-500-26 and 10-269-88F | |
| 8ml CPT vacutainer | BD Biosciences | 362761 | 2 tubes |
| 6ml K2 EDTA vacutainer | BD Biosciences | 367863 | 2 tubes |
| 8.5ml SST vacutainer | BD Biosciences | 367988 | 1 tube |
| Vortexer | Fisher | 2215365 | |
| Dry bath incubator with heating block for microcentrifuge tubes | Fisher | 11-715-1250 | |
| Filtration/vacuum system for use within the cell culture hood | Fisher | 01-257-87 | |
| Fixed-angle rotor for microcentrifuge tubes with aerosol-tight lid | Eppendorf | 22637002 | |
| Refrigerated centrifuge with a swing-bucket rotor and aerosol-tight caps for 16 x 125mm vacutainers and 15ml polypropylene tubes | Eppendorf | 22628157 | 2, one does not need to be refrigerated |
| Nanodrop 2000 (recommended for accuracy of small volumes) or other spectrophotometric device | Fisher | 13-400-411 | |
| Agilent Bioanalyzer | Agilent Technologies | G2940CA | |
| Liquid nitrogen tank | Thermo Scientific | 11-676-56 | |
| -80 ˚C freezer | Thermo Scientific | 992RAK | |
| Sharps container | Fisher | 22-037-970 | |
| Biological waste container | Thermo Scientific | 1223P52 | |
| Biosafety Level 2 certified cell culture hood | Thermo Scientific | 13-261-315 |
References
- Hernandez, M. E., Martinez-Fong, D., Perez-Tapia, M., Estrada-Garcia, I., Estrada-Parra, S., Pavon, L. Evaluation of the effect of selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors on lymphocyte subsets in patients with a major depressive disorder. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 20, 88-95 (2010).
- Weigelt, K., et al. TREM-1 and DAP12 expression in monocytes of patients with severe psychiatric disorders EGR3, ATF3 and PU.1 as important transcription factors. Brain Behav Immun. 25, 1162-1169 (2011).
- Robertson, M. J., et al. Lymphocyte subset differences in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome, multiple sclerosis and major depression. Clin Exp Immunol. 141, 326-332 (2005).
- Rotter, A., Asemann, R., Decker, A., Kornhuber, J., Biermann, T. Orexin expression and promoter-methylation in peripheral blood of patients suffering from major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord. 131, 186-192 (2011).
- Klengel, T., et al. Allele-specific FKBP5 DNA demethylation mediates gene-childhood trauma interactions. Nat Neurosci. 16, 33-41 (2013).
- Segman, R. H., Shefi, N., Goltser-Dubner, T., Friedman, N., Kaminski, N., Shalev, A. Y. Peripheral blood mononuclear cell gene expression profiles identify emergent post-traumatic stress disorder among trauma survivors. Mol Psychiatry. 10, 500-513 (2005).
- Smith, B. H., et al. Cohort Profile: Generation Scotland: Scottish Family Health Study (GS:SFHS). The study, its participants and their potential for genetic research on health and illness. Int J Epidemiol. 42, 689-700 (2013).
- Mallone, R., et al. Isolation and preservation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells for analysis of islet antigen-reactive T cell responses: position statement of the T-Cell Workshop Committee of the Immunology of Diabetes Society. Clin Exp Immunol. 163, 33-49 (2011).
- Duvigneau, J. C., Hartl, R. T., Teinfalt, M., Gemeiner, M. Delay in processing porcine whole blood affects cytokine expression. J Immunol Methods. 272, 11-21 (2003).
- Debey, S., et al. Comparison of different isolation techniques prior gene expression profiling of blood derived cells: impact on physiological responses, on overall expression and the role of different cell types. Pharmacogenomics J. 4, 193-207 (2004).
- Uddin, M., et al. Epigenetic and immune function profiles associated with posttraumatic stress disorder. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 107, 9470-9475 (2010).
- Kessler, R. C., Wang, P. S. The descriptive epidemiology of commonly occurring mental disorders in the United States. Annu Rev Public Health. 29, 115-129 (2008).
- . QIAamp® DNA Mini and Blood Mini Handbook Available from: https://www.qiagen.com/us/resources/resourcedetail?id=67893a91-946f-49b5-8033-394fa5d752ea (2010)
- Koenen, K. C., et al. SLC6A4 methylation modifies the effect of the number of traumatic events on risk for posttraumatic stress disorder. Depress Anxiety. 28, 639-647 (2011).
- Walsh, K., Uddin, M., Soliven, R., Wildman, D. E., Bradley, B. Associations between the SS variant of 5-HTTLPR and PTSD among adults with histories of childhood emotional abuse: Results from two African American independent samples. J Affect Disord. 161, 91-96 (2014).
- Bustamante, A. C., et al. Childhood maltreatment is associated with epigenetic differences in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis genes in the Detroit Neighborhood Health Study. , (2013).
- Sipahi, L., et al. Longitudinal epigenetic variation of DNA methyltransferase genes is associated with vulnerability to post-traumatic stress disorder. Psychol Med. 44, 3165-3179 (2014).
- Uddin, M., Koenen, K. C., Aiello, A. E., Wildman, D., de los Santos, R., Galea, S. Epigenetic and inflammatory marker profiles associated with depression in a community-based epidemiologic sample. Psychol Med. 41, 997-1007 (2011).
- Uddin, M., et al. Post-traumatic stress disorder is associated with immunosenescent T cell phenotypes in the Detroit Neighborhood Health Study. , (2011).
- Uddin, M., et al. Post-traumatic stress disorder is associated with immunosenescent T cell phenotypes in the Detroit Neighborhood Health Study. , (2011).
- Uddin, M. Biological signatures of post-traumatic stress disorder in the Detroit Neighborhood Health Study. , (2010).
- Aiello, A. E. Cytomegalovirus antibodies as a marker of immunosenescence in the Detroit Neighborhood Health Study. , (2010).
- Bustamante, A. C., et al. . Distinct gene expression profiles characterize lifetime PTSD and childhood maltreatment in the Detroit Neighborhood Health Study. , (2013).

