11.9: 克劳修斯-克拉伯龙方程(Clausius-Clapeyron Equation)
液体及其蒸汽之间的平衡取决于系统的温度;温度升高会导致其液体的蒸汽压相应升高。 克劳修斯-克拉伯龙方程(Clausius-Clapeyron Equation) 给出了一种物质的蒸汽压 (P) 与其温度 (T) 之间的定量的关系;它预测了每单位温度升高时蒸汽压的升高速度。
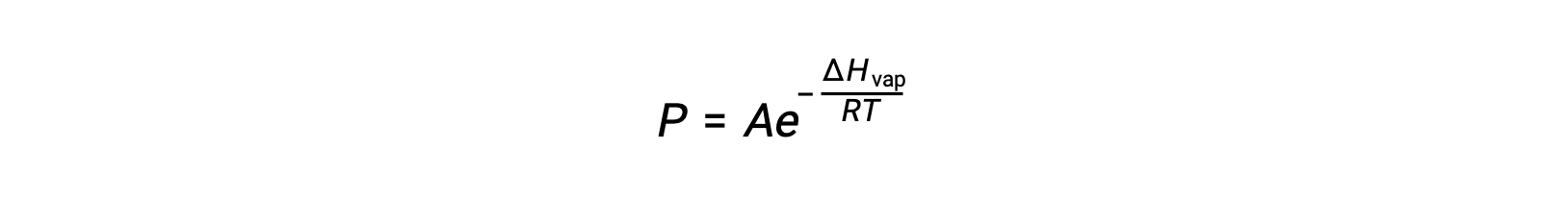
其中, ΔHvap 是液体汽化的焓, R 是气体常数, A 是一个常数,其值取决于物质的化学特性。 温度 (T) 必须在此方程式中以开氏为单位。 但是,由于蒸汽压和温度之间的关系不是线性的,因此公式通常重新排列为对数形式,以产率线性公式:
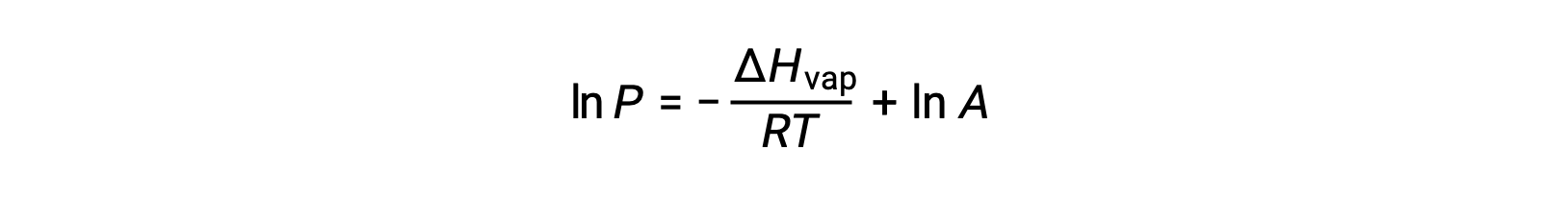
对于任何液体,如果已知特定温度下汽化和蒸汽压的焓, 克劳修斯-克拉伯龙方程(Clausius-Clapeyron Equation) 允许在不同温度下确定液体的蒸汽压。 为此,线性方程式可以两点格式表示。 如果在温度 T1 时蒸汽压为 P1 ,而在温度 T2 时蒸汽压为 P2 ,则相应的线性方程式为:
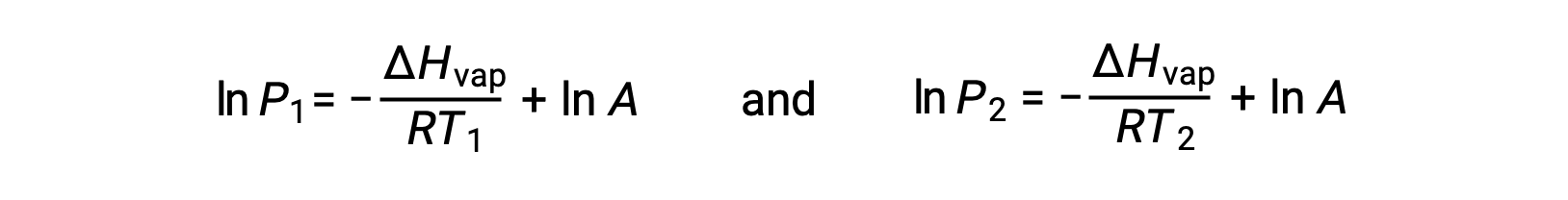
由于常量 A 相同,可以重新排列这两个方程式以隔离 ln a ,然后将它们设置为彼此相等:
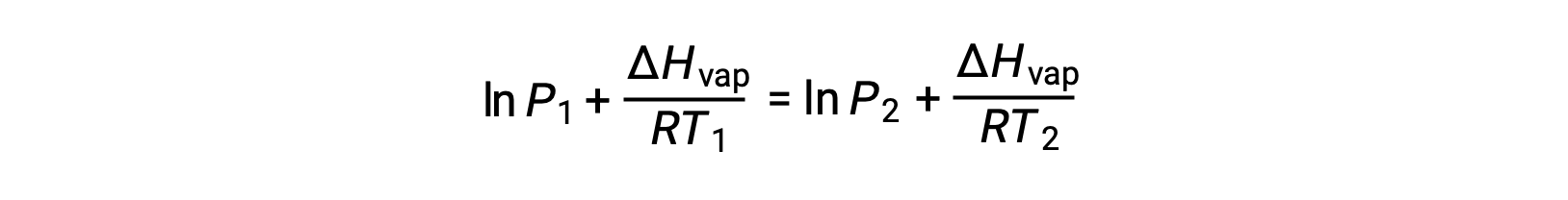
可组合到:
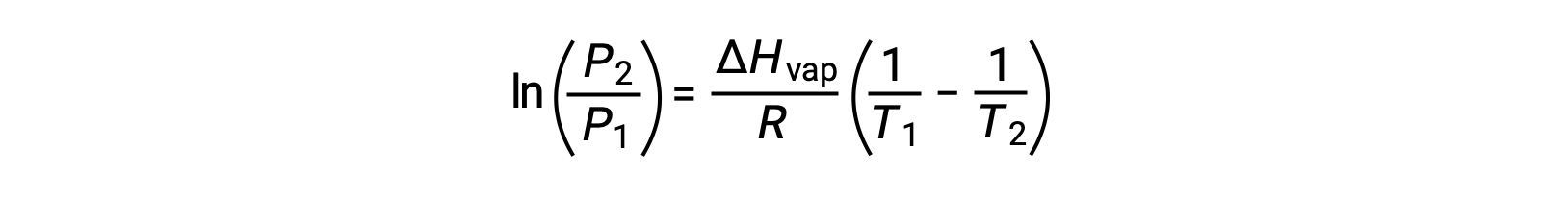
本文改编自 Openstax, 化学 2e, 第10.3节:相变。


